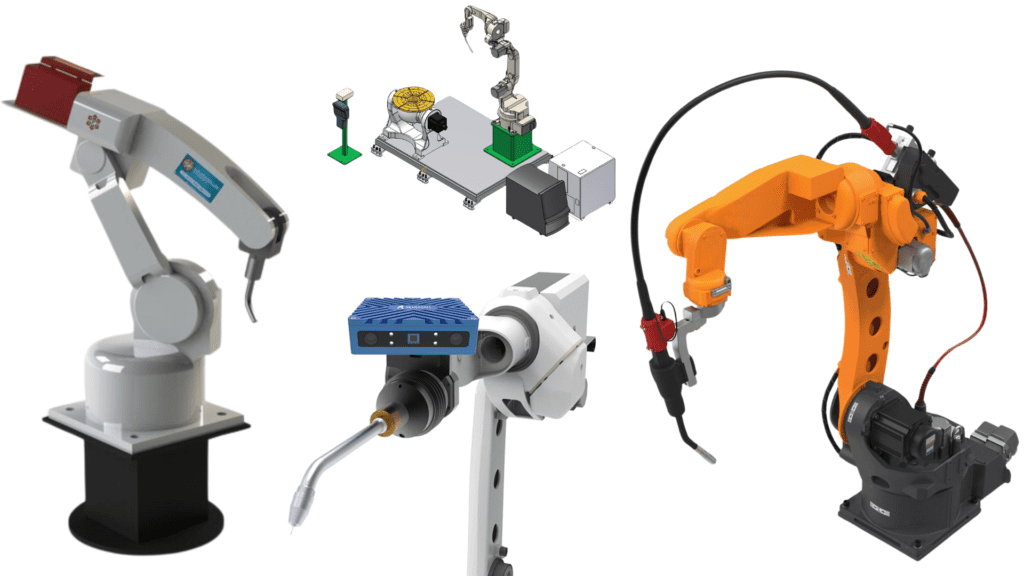
Welding Robots: Revolutionizing Modern Manufacturing

Welding robots are transforming the industrial landscape by providing efficient, precise, and cost-effective solutions for welding tasks. These automated machines have become essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction, allowing businesses to improve productivity and reduce errors.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits of welding robots, how they work, and their role in revolutionizing manufacturing. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking to optimize your factory’s production line, this post will give you actionable insights to harness the power of welding robots.
Table of Contents
What Are Welding Robots?
Welding robots are automated machines designed to perform welding tasks with minimal human intervention. These robots are equipped with programmable arms and welding tools that execute precise welds at high speeds, making them ideal for repetitive, complex, or dangerous welding tasks. Welding robots come in various configurations, including articulated, Cartesian, and collaborative types, each suited for specific industrial needs.
Key Components of a Welding Robot
- Robot Controller – The brain of the robot, responsible for programming and controlling movement.
- Robot Arm – The movable part that positions the welding tool at the right angles and distances.
- Welding Torch – The tool used to perform the welding task.
- Power Supply – Provides the necessary electrical current for the welding process.
- Safety Systems – Sensors and systems designed to ensure safe operation in a factory environment.
Benefits of Welding Robots
The rise of automation in the welding industry has brought numerous benefits. Here’s how welding robots are making a difference:
1. Increased Productivity
Welding robots can work continuously, significantly boosting production rates. Unlike human welders, robots do not need breaks, meaning they can work 24/7, enhancing throughput in manufacturing lines.
2. Consistency and Precision
Welding robots offer unparalleled accuracy. They can perform complex welds repeatedly with the same precision, reducing the margin for error. This ensures consistent product quality, which is critical in industries like automotive and aerospace.
3. Cost Savings
While the initial investment in welding robots can be substantial, the long-term cost benefits are significant. Reduced labor costs, fewer material wastages, and higher production efficiency all contribute to a swift return on investment (ROI).
4. Improved Safety
Welding involves high temperatures, hazardous fumes, and bright light, all of which can pose risks to human welders. Robots, on the other hand, can handle these dangerous tasks without risk of injury, ensuring a safer work environment.
5. Versatility
Modern welding robots can be reprogrammed and equipped with different tools to perform a variety of welding techniques, such as MIG, TIG, and spot welding. This flexibility makes them suitable for various industries and applications.
Types of Welding Robots
Different welding robots cater to different needs. Here are the most common types:
1. Articulated Welding Robots
These robots have multiple rotating joints, which allow for a wide range of motion and flexibility. Articulated robots are ideal for complex welding tasks that require precision.
2. Cartesian Welding Robots
Cartesian robots operate on a three-axis system, moving in straight lines along the X, Y, and Z axes. They are often used in tasks that require high-speed welding with simpler movements, such as in flat surfaces or specific angles.
3. Collaborative Welding Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers. These robots are equipped with sensors and safety systems to ensure safe collaboration, making them perfect for applications where human oversight or intervention is required.
How Welding Robots Work: Step-by-Step Process
Understanding the welding robot’s process can help you optimize its use in your factory.
- Program the Robot – The first step is to program the robot with specific welding tasks, including the type of weld, the path it will follow, and the speed at which it will work.
- Position the Parts – Parts to be welded are positioned in a fixture or assembly line.
- Execute the Weld – The robot’s arm moves to the designated position and performs the weld, ensuring precise alignment and temperature control.
- Quality Check – Post-weld, the robot or another system performs a quality check to ensure there are no defects in the weld.
Applications of Welding Robots
Welding robots are used across various industries, from automotive manufacturing to shipbuilding. Let’s explore some of the key sectors that benefit from robotic welding technology:
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry was one of the early adopters of welding robots. They are used for spot welding car bodies, making the production process faster and more efficient.
2. Aerospace Industry
Precision and safety are paramount in the aerospace industry, and welding robots play a crucial role in manufacturing aircraft components. Their ability to create precise welds ensures high-quality, defect-free parts.
3. Construction Industry
In the construction industry, welding robots are used for creating steel frameworks, pipelines, and other metal structures. These robots help speed up the construction process while maintaining high weld quality.
Key Considerations When Implementing Welding Robots
Before integrating welding robots into your production line, there are several factors you need to consider:
1. Initial Costs
Welding robots require a significant upfront investment. However, the long-term savings in labor and increased productivity often justify the expense. Consider financing options and calculate your expected ROI before making a purchase.
2. Programming and Maintenance
Welding robots require skilled operators for programming and maintenance. While they reduce the need for manual labor, you’ll need to train staff or hire experts to manage these tasks.
3. Space and Layout
Robots take up floor space and may require rearranging your current factory layout. Make sure you plan the integration carefully to avoid disruptions in your existing processes.
The Future of Welding Robots: Trends and Innovations
As technology advances, the future of welding robots looks bright. Here are some of the exciting trends and innovations to watch:
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Incorporating AI into welding robots allows for real-time adjustments and improvements. These robots can learn from previous welds, improving their accuracy and efficiency over time.
2. Cloud-Based Monitoring
Cloud technology enables real-time monitoring and data collection from welding robots. This allows manufacturers to track performance, troubleshoot issues remotely, and optimize the welding process.
3. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots are becoming more advanced, allowing for seamless integration into human workflows. They are safer, more intuitive to program, and ideal for SMEs (small and medium-sized enterprises) looking to automate welding processes.
FAQs about welding robots:
1. What are welding robots, and how do they work?
Welding robots are automated machines that perform welding tasks by following pre-programmed instructions. They use a robotic arm to position a welding tool and apply controlled heat to join materials, typically metals, in a precise and repeatable manner.
2. What are the main types of welding robots?
The three most common types of welding robots are articulated robots, Cartesian robots, and collaborative robots (cobots). Each type serves different welding needs, from complex, multi-axis movements to simpler, linear applications.
3. What industries use welding robots?
Welding robots are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing. They are ideal for tasks requiring high precision and consistency, such as welding car bodies, aircraft components, and metal frameworks.
4. How do welding robots improve manufacturing productivity?
Welding robots can work continuously, performing repetitive tasks without breaks, which significantly boosts production rates. They also enhance precision and reduce errors, leading to fewer reworks and higher output quality.
5. What are the cost savings associated with welding robots?
While welding robots require an initial investment, they reduce long-term costs by decreasing labor needs, minimizing material wastage, improving accuracy, and speeding up production. These factors lead to a quick return on investment (ROI).
6. What safety benefits do welding robots provide?
Welding robots remove human workers from hazardous environments. They handle dangerous tasks such as exposure to extreme heat, harmful fumes, and bright welding arcs, reducing the risk of workplace injuries and illnesses.
7. What types of welding can robots perform?
Welding robots can perform various types of welding, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), and spot welding. They are versatile and can be adapted for different materials and joint types.
8. Can welding robots be programmed to handle different tasks?
Yes, modern welding robots are highly flexible. They can be reprogrammed to handle a wide range of welding tasks, making them adaptable for different production needs and types of welds, such as seams, spots, or custom joints.
9. What are the key factors to consider before investing in welding robots?
Key factors include the initial cost, the space available for installation, the complexity of the tasks, training and maintenance requirements, and your expected return on investment. Additionally, you’ll need to ensure proper integration into your production line.
10. How long does it take to set up and implement a welding robot?
The time required for setup depends on the complexity of the tasks, the type of welding robot, and the integration into the production line. Typically, installation and programming can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks.
11. What is the lifespan of a welding robot?
With proper maintenance, welding robots can have a lifespan of 10-15 years or more. Regular maintenance and software updates can extend their operational life and ensure optimal performance.
12. What are the latest trends in welding robot technology?
The latest trends include the integration of AI and machine learning for real-time adjustments, cloud-based monitoring systems for performance tracking, and the rise of collaborative robots (cobots) designed to work safely alongside human workers.
These FAQs cover the essential questions prospective buyers or industry professionals might have about welding robots.
Conclusion: Are Welding Robots Right for Your Business?
Welding robots offer unmatched productivity, precision, and safety benefits, making them an essential tool in modern manufacturing. Whether you’re in the automotive, aerospace, or construction industry, these robots can streamline your production processes and help you stay competitive in today’s market.
Interested in learning more about how welding robots can transform your business? Explore EngiTech for comprehensive resources and stay updated on the latest innovations in industrial automation.