Ultrasonic welding machines are essential tools in modern manufacturing, offering a fast, reliable, and efficient method for joining materials without the need for adhesives, soldering, or other traditional bonding techniques.
This blog will explore everything you need to know about ultrasonic welding machines, from how they work to their applications, benefits, and maintenance. Whether you’re a knowledge seeker, a student, or a working professional, this guide aims to provide detailed insights and clear answers to your queries.
Table of Contents
What is Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding is a process that uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create a solid-state weld between two materials. Unlike conventional welding methods that rely on heat or adhesives, ultrasonic welding generates localized friction, which melts and fuses the materials together. The process is widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and packaging, where precision, speed, and cleanliness are paramount.
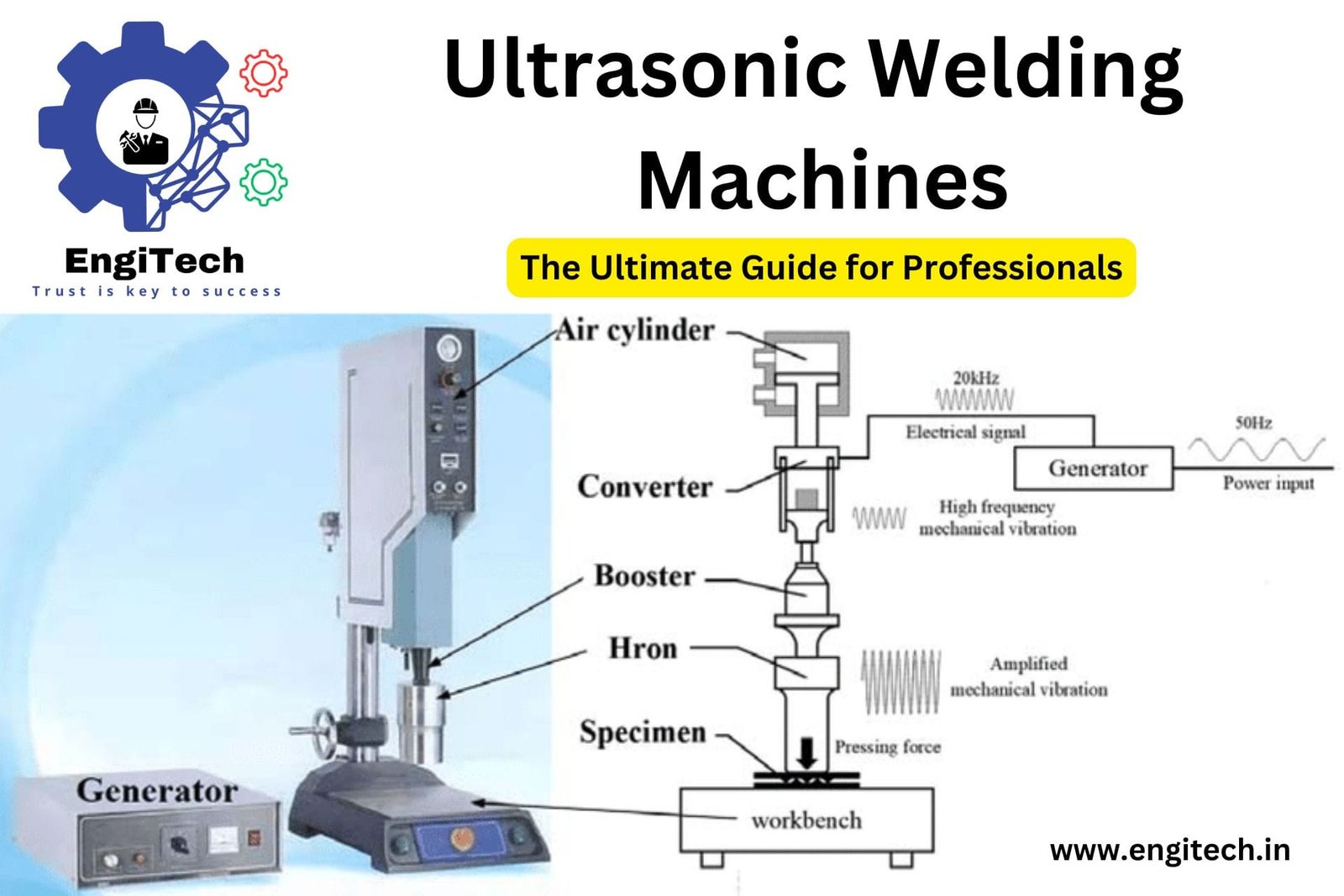
How Ultrasonic Welding Machines Work
Ultrasonic welding machines operate by converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations. These vibrations are then transmitted through a sonotrode, a component designed to focus the ultrasonic energy onto the workpiece. When the sonotrode makes contact with the materials to be joined, the ultrasonic vibrations generate friction, causing the materials to melt and bond at a molecular level.
- The Power Supply: The ultrasonic welding machine’s power supply converts standard electrical energy into high-frequency electrical signals, typically ranging from 20 kHz to 40 kHz.
- The Transducer: The transducer, also known as the converter, receives the high-frequency electrical signals and converts them into mechanical vibrations.
- The Booster: The booster amplifies the mechanical vibrations, increasing their amplitude to the required level for effective welding.
- The Sonotrode: The sonotrode, or horn, delivers the amplified mechanical vibrations to the materials. It is custom-designed for each specific application to ensure optimal energy transfer.
- The Anvil: The anvil supports the materials being welded, ensuring that they remain in place during the welding process.
Applications of Ultrasonic Welding Machines
Ultrasonic welding machines are versatile and can be used to join a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites. Here are some of the key applications:
1. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, ultrasonic welding machines are used to bond components such as instrument panels, door panels, and engine parts. The process ensures strong, durable bonds without the need for additional materials, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency.
2. Electronics Industry
Ultrasonic welding is widely used in the electronics industry to assemble components such as circuit boards, connectors, and battery packs. The process provides a clean, precise weld that minimizes the risk of damaging sensitive electronic components.
3. Medical Devices
Ultrasonic welding machines are essential in the production of medical devices, where cleanliness and precision are critical. The process is used to assemble products such as catheters, blood filters, and surgical instruments, ensuring that they meet stringent regulatory standards.
4. Packaging Industry
In the packaging industry, ultrasonic welding is used to seal containers, blisters, and pouches. The process provides a hermetic seal that protects the contents from contamination, ensuring product safety and shelf life.
5. Textiles and Apparel
Ultrasonic welding machines are also used in the textiles and apparel industry to bond synthetic fabrics, eliminating the need for stitching. The process creates strong, seamless bonds that enhance the durability and appearance of the finished product.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding Machines
Ultrasonic welding machines offer numerous advantages over traditional bonding methods, making them the preferred choice in many industries. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Fast and Efficient
Ultrasonic welding is a rapid process that can be completed in a matter of seconds. This speed increases production efficiency and reduces labor costs, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
2. Strong and Reliable Bonds
The ultrasonic welding process creates bonds that are as strong as the original materials. This strength ensures the durability and longevity of the welded components, reducing the risk of failure in critical applications.
3. No Need for Consumables
Unlike other bonding methods that require adhesives, solder, or other consumables, ultrasonic welding relies solely on the materials being joined. This reduces material costs and simplifies the production process.
4. Clean and Environmentally Friendly
Ultrasonic welding generates minimal waste and does not produce harmful fumes or residues. This makes it an environmentally friendly option that aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
5. Precision and Accuracy
The ultrasonic welding process is highly precise, allowing for tight control over the welding parameters. This precision ensures consistent, high-quality welds that meet exacting standards.
6. Versatility
Ultrasonic welding machines can be used with a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, and composites. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications across multiple industries.
Understanding the Ultrasonic Welding Process in Detail
The ultrasonic welding process involves several critical steps, each of which must be carefully controlled to achieve a successful weld. Let’s take a closer look at each step:
1. Material Preparation
Before welding, the materials must be properly prepared. This involves cleaning the surfaces to remove any contaminants that could interfere with the welding process. In some cases, the materials may also need to be pre-heated or pre-treated to enhance their weldability.
2. Fixture Setup
The materials are then placed in a fixture, which holds them in place during the welding process. The fixture must be designed to provide even pressure across the entire welding area, ensuring a uniform bond.
3. Ultrasonic Energy Application
Once the materials are in place, the ultrasonic welding machine is activated. The sonotrode delivers ultrasonic energy to the materials, causing them to vibrate and generate heat. This heat melts the materials at the interface, allowing them to fuse together.
4. Cooling and Solidification
After the ultrasonic energy is applied, the materials are allowed to cool and solidify. This cooling process is critical to the strength of the bond, as it ensures that the materials fuse together at a molecular level.
5. Inspection and Testing
The final step in the ultrasonic welding process is inspection and testing. This involves checking the weld for defects such as voids, cracks, or incomplete fusion. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection, may be used to verify the integrity of the weld.
Common Challenges in Ultrasonic Welding
While ultrasonic welding offers many advantages, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these challenges and how to overcome them is essential for achieving successful welds:
1. Material Compatibility
Not all materials are compatible with ultrasonic welding. For example, some plastics may have different melting points or thermal properties that make them difficult to weld. It’s important to select materials that are compatible with the ultrasonic welding process.
2. Proper Fixture Design
The fixture design is critical to the success of the welding process. A poorly designed fixture can result in uneven pressure, leading to weak or incomplete welds. It’s essential to work with experienced engineers to design fixtures that provide uniform pressure across the welding area.
3. Controlling Welding Parameters
The success of the ultrasonic welding process depends on precise control of the welding parameters, including the frequency, amplitude, and duration of the ultrasonic energy. Variations in these parameters can affect the quality of the weld, so it’s important to monitor and adjust them as needed.
4. Avoiding Overheating
Overheating is a common challenge in ultrasonic welding, particularly with materials that have low melting points. To avoid overheating, it’s important to carefully control the amount of ultrasonic energy applied and to use cooling mechanisms as needed.
Expert Insights on Ultrasonic Welding Machines
To provide you with deeper insights into ultrasonic welding machines, we reached out to our expert engineers, who have extensive experience in the field. Here are their key takeaways:
1. Importance of Material Selection
According to our experts, material selection is one of the most critical factors in ultrasonic welding. “Choosing the right materials can make or break the welding process,” says one engineer. “It’s important to select materials that are not only compatible with ultrasonic welding but also meet the specific requirements of the application.”
2. The Role of Process Optimization
Process optimization is another area where our experts emphasize the importance of expertise. “Ultrasonic welding is not a one-size-fits-all process,” explains another engineer. “Each application requires careful optimization of the welding parameters to achieve the best results.”
3. The Future of Ultrasonic Welding
Our experts also shared their thoughts on the future of ultrasonic welding. “As industries continue to demand faster, more efficient manufacturing processes, ultrasonic welding will play an increasingly important role,” predicts one engineer. “We’re already seeing advances in ultrasonic welding technology that are making it even more versatile and capable.”
Maintenance and Care of Ultrasonic Welding Machines
Proper maintenance and care are essential to ensure the longevity and performance of ultrasonic welding machines. Here are some best practices for maintaining your equipment:
1. Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning of the sonotrode, booster, and anvil is essential to prevent contamination and ensure consistent weld quality. Use non-abrasive cleaning agents and avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage the components.
2. Routine Inspection
Inspect the machine regularly for signs of wear or damage, particularly in the transducer, booster, and sonotrode. Any worn or damaged components should be replaced immediately to prevent further issues.
3. Calibration and Tuning
Calibrate and tune the ultrasonic welding machine regularly to ensure that it operates at the correct frequency and amplitude. This will help maintain consistent welding performance and prevent issues such as overheating or incomplete welds.
4. Proper Storage
When not in use, store the ultrasonic welding machine in a clean, dry environment to prevent corrosion and damage. Cover the machine with a protective cover to keep dust and debris from accumulating on the components.
5. Training and Safety
Ensure that all operators are properly trained in the use of ultrasonic welding machines. Proper training not only enhances safety but also improves the quality of the welds. Operators should be familiar with the machine’s controls, maintenance procedures, and safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure optimal performance.
6. Use of Quality Spare Parts
Always use high-quality spare parts when maintaining or repairing ultrasonic welding machines. Using substandard parts can lead to machine failures, reduced performance, and potential safety hazards. It’s advisable to source spare parts from reputable manufacturers or directly from the machine’s original manufacturer.
7. Monitoring Machine Performance
Regularly monitor the machine’s performance, including welding speed, energy consumption, and weld quality. By keeping track of these metrics, you can identify potential issues before they become serious problems, allowing for proactive maintenance and adjustments.
Future Trends in Ultrasonic Welding Technology
Ultrasonic welding technology continues to evolve, driven by advancements in materials science, automation, and precision engineering. Here are some of the trends that are shaping the future of ultrasonic welding machines:
1. Integration with Industry 4.0
The integration of ultrasonic welding machines with Industry 4.0 technologies is a growing trend. Machines are increasingly being equipped with sensors and connectivity features that allow for real-time monitoring, data collection, and predictive maintenance. This integration enhances the efficiency and reliability of the welding process, reducing downtime and improving overall production quality.
2. Advanced Materials
As new materials are developed, ultrasonic welding machines are being adapted to handle more complex and demanding applications. For example, the growing use of composite materials in industries such as aerospace and automotive requires ultrasonic welding machines that can deliver precise, high-quality welds without damaging the materials.
3. Automation and Robotics
Automation is becoming more prevalent in ultrasonic welding, with machines being integrated into automated production lines. Robotics are also being used to handle the welding process, allowing for greater precision, repeatability, and speed. This trend is particularly important in high-volume manufacturing environments where consistency and efficiency are critical.
4. Miniaturization and Micro Welding
The demand for smaller, more intricate components, particularly in the electronics and medical device industries, is driving the development of ultrasonic micro-welding technology. These machines are capable of welding extremely small parts with high precision, making them ideal for applications where traditional welding methods are not feasible.
5. Environmental Considerations
As sustainability becomes a priority across industries, ultrasonic welding machines are being designed to minimize energy consumption and reduce waste. The development of more energy-efficient machines and environmentally friendly welding processes is expected to continue, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and promote green manufacturing practices.
Ultrasonic Welding vs. Other Welding Methods
Understanding how ultrasonic welding compares to other welding methods can help you make informed decisions when selecting the right process for your application. Here’s a comparison of ultrasonic welding with some of the most common welding methods:
1. Ultrasonic Welding vs. Heat Welding
Heat welding relies on the application of heat to melt and join materials, while ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency vibrations to achieve the same result. Ultrasonic welding is generally faster and cleaner than heat welding, as it does not require additional heat sources or consumables. Additionally, ultrasonic welding can be used with materials that are sensitive to heat, making it a more versatile option.
2. Ultrasonic Welding vs. Laser Welding
Laser welding uses concentrated laser beams to melt and fuse materials. While laser welding offers high precision and is effective for a wide range of materials, it can be more expensive and requires specialized equipment. Ultrasonic welding, on the other hand, is often more cost-effective and easier to integrate into existing production lines. However, laser welding may be preferred for applications that require extremely fine detail or where ultrasonic welding is not suitable.
3. Ultrasonic Welding vs. Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding involves using glues or other adhesives to join materials. While adhesive bonding can be effective for certain applications, it often requires long curing times and may not provide the same level of strength as ultrasonic welding. Additionally, adhesives can introduce contaminants and may not be suitable for environments where cleanliness is critical. Ultrasonic welding offers a cleaner, faster, and more reliable alternative, particularly in high-volume production settings.
4. Ultrasonic Welding vs. Resistance Welding
Resistance welding uses electrical currents to generate heat and bond materials. It is commonly used for joining metals but can be less effective for plastics and composites. Ultrasonic welding, by contrast, is highly effective for non-metallic materials and does not require the high electrical currents used in resistance welding. This makes ultrasonic welding a safer and more energy-efficient option for certain applications.
Choosing the Right Ultrasonic Welding Machine
Selecting the right ultrasonic welding machine for your needs involves considering several factors, including the materials to be welded, the required production speed, and the specific application. Here are some key considerations:
1. Material Compatibility
Ensure that the ultrasonic welding machine you choose is compatible with the materials you intend to weld. Different machines may be optimized for specific materials, such as plastics, metals, or composites. Consulting with the manufacturer or an experienced engineer can help you determine the best machine for your application.
2. Machine Frequency and Power
The frequency and power output of the ultrasonic welding machine are critical to achieving successful welds. Machines with higher frequencies are generally used for delicate materials and fine detail work, while lower frequencies are better suited for larger, thicker materials. The power output should be matched to the material and the size of the weld area to ensure consistent results.
3. Customization and Tooling
Many ultrasonic welding machines offer customizable options and tooling to meet the specific needs of your application. Consider whether the machine can be adapted with different sonotrodes, boosters, and fixtures to accommodate various materials and part geometries. Custom tooling can enhance the machine’s versatility and improve weld quality.
4. Automation and Integration
If you plan to integrate the ultrasonic welding machine into an automated production line, consider its compatibility with existing systems. Look for machines that offer easy integration with robotics, conveyors, and other automation equipment. This can streamline production and reduce manual intervention.
5. Maintenance and Support
Consider the availability of maintenance services and technical support when selecting an ultrasonic welding machine. Machines that require frequent maintenance or have limited support options can lead to costly downtime. Choose a machine from a reputable manufacturer that offers reliable support and readily available spare parts.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding machines are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, offering a fast, reliable, and efficient method for joining materials. From automotive components to medical devices, ultrasonic welding provides strong, clean, and precise bonds that meet the demands of various industries. By understanding the ultrasonic welding process, its advantages, challenges, and future trends, you can make informed decisions that optimize your production and ensure the success of your projects.
Whether you’re a knowledge seeker, a student, or a working professional, this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into the world of ultrasonic welding machines. As this technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements will help you leverage ultrasonic welding to its fullest potential.
By following the guidelines outlined in this blog, and ensuring that your ultrasonic welding machines are properly maintained and operated, you can achieve high-quality welds that meet the exacting standards of today’s industries. As always, consult with expert engineers and trusted manufacturers to ensure that you are using the best possible equipment for your specific needs.
From EngiTech Team
EngiTech is your trusted source for in-depth knowledge and cutting-edge insights into industrial mechanical engineering. Our expertly crafted content empowers professionals, students, and enthusiasts with the information they need to excel in their fields. From advanced drying technologies to the latest in automation, we provide valuable resources that drive innovation and efficiency. Join our growing community and stay ahead of the curve with our comprehensive guides, expert analyses, and the latest industry trends. Explore EngiTech—where engineering expertise meets practical application.