Ultimate Guide to Pipe Inspection Robots: Pipeline Maintenance Work

In an era where industrial innovation drives efficiency, pipe inspection robots have emerged as indispensable tools for maintaining critical infrastructure. Whether it’s for oil and gas pipelines, water supply networks, or industrial conduits, these robots ensure seamless inspection, reducing downtime, and enhancing safety.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about pipe inspection robots, from their capabilities and benefits to how they are revolutionizing pipeline maintenance. By the end, you’ll understand why these robotic solutions are becoming the go-to choice for engineers and inspectors around the world.
Table of Contents
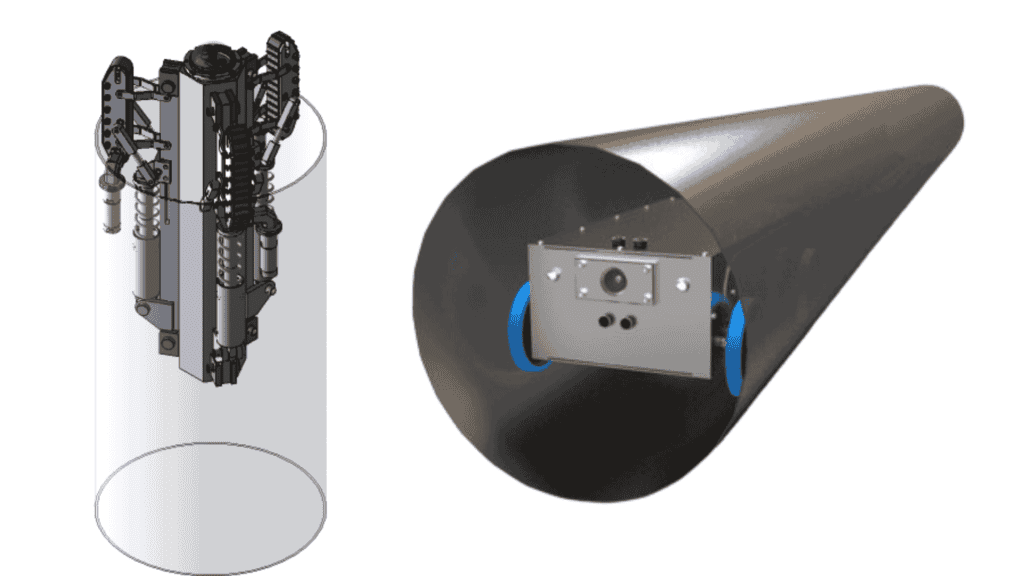
What is a Pipe Inspection Robot?
A pipe inspection robot is a specialized robotic system designed to navigate through pipelines, providing real-time video footage and data of the internal condition of pipes. These robots are used to inspect hard-to-reach areas in long, complex, or hazardous pipeline systems, helping industries avoid the time-consuming and risky task of manual inspection.
Equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, pipe inspection robots can identify problems like cracks, corrosion, blockages, and leaks, which might otherwise remain unnoticed until a catastrophic failure occurs.
How Does a Pipe Inspection Robot Work?
At its core, a pipe inspection robot is designed to travel through pipelines of various sizes. These robots come in several configurations—ranging from small, wheeled robots that traverse narrow pipes to larger, tracked models designed for more extensive pipeline systems. Depending on the model, a pipeline inspection robot might employ several features, such as:
- HD Cameras: Capture detailed visual inspections of the pipe’s interior.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Measure the thickness of pipe walls to detect corrosion.
- Laser Scanning: Create a 3D map of the pipeline’s interior for precise analysis.
- Tethered or Wireless Control: Some robots are tethered for power and data transmission, while others are wireless, offering more mobility.
These systems allow operators to view real-time data and make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs without the need for costly excavation or shutdowns.
Types of Pipe Inspection Robots
Different pipelines and industries require different types of pipe inspection robots. Below are the primary categories:
1. Wheeled Robots
Wheeled robots are ideal for smaller pipelines, particularly in industries like water treatment, sewage systems, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. These robots are highly maneuverable and are typically equipped with cameras to inspect the pipeline for clogs, corrosion, or structural damage.
2. Crawler Robots
Crawler robots, also known as pipeline inspection robots, are designed for larger, more industrial pipes, such as those used in the oil and gas industry. These robots are equipped with treads or legs, enabling them to move through debris-filled pipes or even climb slight inclines. They offer enhanced stability and can carry more equipment, such as ultrasonic sensors for detailed inspection.
3. In-Pipe Flying Robots
For pipelines that are vertical or have irregular geometry, in-pipe flying robots have proven highly effective. These drones can fly inside pipelines, utilizing sensors and cameras to provide a comprehensive view of the pipe’s interior, particularly in areas that are inaccessible to wheeled or crawler robots.
4. Modular Pipe Robots
Modular robots are a versatile solution capable of adjusting their configuration based on the size of the pipe. They can be expanded or contracted to fit various diameters, making them a popular choice for industries with pipelines of varying sizes.
Key Benefits of Using Pipe Inspection Robots
Implementing pipe inspection robots offers numerous advantages, making them an essential asset for pipeline maintenance. Here are the key benefits:
1. Enhanced Safety
By eliminating the need for manual inspection in hazardous environments, pipe robots greatly reduce the risk to human workers. This is particularly crucial for pipelines that carry volatile substances like oil, gas, or chemicals.
2. Increased Efficiency
Pipe inspection robots allow for quick and precise inspections without the need for excavations or system shutdowns. This minimizes downtime, ensuring that industrial operations continue smoothly while still maintaining pipeline integrity.
3. Cost Savings
Regular maintenance and early detection of issues such as leaks, cracks, or blockages can prevent costly repairs and avoid potential environmental disasters. Pipe robot inspection provides the data needed for preemptive action, reducing long-term maintenance costs.
4. Accurate Data Collection
With their advanced sensors, pipe inspection robots can gather high-quality data about the pipeline’s condition, including real-time video feeds and 3D models. This allows engineers to make data-driven decisions about repair schedules and methods.
5. Adaptability
Modern robots are designed to inspect a wide range of pipe diameters and materials, from small residential plumbing pipes to large industrial conduits, making them versatile tools in various industries.
Industries Benefiting from Pipe Inspection Robots
Several industries are leveraging the capabilities of pipe inspection robots to maintain their infrastructure:
1. Oil and Gas
Pipelines in the oil and gas industry are vast and often located in remote areas. Pipeline inspection robots can detect corrosion, cracks, and leaks in these crucial systems, ensuring the safe transport of these valuable resources.
2. Water and Sewage Systems
Municipal water and sewage systems require frequent inspections to prevent blockages, leaks, and contamination. Wheeled inspection robots are often used in these systems to ensure smooth operation and identify problem areas before they become severe.
3. Nuclear Industry
The nuclear industry uses pipe inspection robots in its cooling systems and other critical infrastructure. These robots can inspect pipes in radiation zones, protecting human workers from dangerous exposure.
4. Manufacturing and Industrial Plants
Industrial plants that use high-pressure steam, gas, or chemicals rely on pipe robot inspection to detect signs of wear and tear. This helps prevent hazardous leaks that could compromise worker safety or lead to production shutdowns.
Emerging Trends in Pipe Inspection Technology
The evolution of pipe inspection robots is being driven by several technological advancements:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI is enhancing robot capabilities by enabling machines to analyze video feeds and sensor data autonomously. AI-driven robots can identify and classify defects in real-time, reducing the burden on human operators.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity
IoT-enabled robots can transmit real-time data to centralized systems, allowing multiple robots to be monitored remotely. This makes large-scale inspections more efficient and cost-effective.
3. Improved Battery Life
Recent advancements in battery technology are extending the operational time of wireless robots, allowing for longer and more thorough inspections without needing frequent recharging.
4. Miniaturization
As robotics technology advances, pipe inspection robots are becoming smaller and more agile, making it possible to inspect even the narrowest and most convoluted pipeline systems.
How to Choose the Right Pipe Inspection Robot
Selecting the right pipe inspection robot depends on several factors:
- Pipeline Size: The diameter of the pipeline dictates whether you need a wheeled, crawler, or flying robot.
- Pipe Material: Certain sensors are better suited for specific materials (e.g., metal vs. PVC).
- Type of Inspection Needed: Some robots are optimized for visual inspections, while others offer ultrasonic or laser-based data collection.
- Operational Environment: Consider whether the robot will be used in hazardous, underwater, or high-temperature environments.
FAQs related to pipe inspection robots:
1. What is a pipe inspection robot, and how does it work?
A pipe inspection robot is a device designed to travel through pipelines and assess their condition. Equipped with cameras, sensors, and sometimes lasers, the robot collects data to identify issues like corrosion, leaks, or blockages. The robot’s movement can be controlled remotely, and it transmits real-time video and data to operators.
2. What types of pipes can inspection robots be used in?
Pipe inspection robots can be used in a wide range of pipelines, including water, sewage, oil, gas, chemical, and industrial systems. Their adaptability allows them to navigate pipes of varying diameters and materials, from small residential pipes to large industrial pipelines.
3. How do pipe inspection robots improve safety?
Pipe inspection robots enhance safety by reducing the need for human entry into hazardous environments, such as pipes that carry toxic chemicals, gases, or are in confined spaces. By performing inspections remotely, these robots minimize the risk to workers.
4. What are the key benefits of using pipe inspection robots?
Key benefits include improved safety, increased inspection efficiency, cost savings by preventing major repairs, accurate data collection, and the ability to inspect pipelines without disrupting operations.
5. What industries use pipe inspection robots?
Pipe inspection robots are used across multiple industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, sewage systems, power generation (nuclear and thermal plants), manufacturing, and even aerospace for inspecting fuel and hydraulic lines.
6. What types of pipe inspection robots are available?
The main types include:
- Wheeled robots for small pipelines.
- Crawler robots for large, industrial pipelines.
- Flying drones for vertical or irregular pipelines.
- Modular robots that can adjust to different pipe sizes.
7. How much does a pipe inspection robot cost?
The cost of a pipe inspection robot varies depending on its features, size, and capabilities. Basic wheeled robots can cost a few thousand dollars, while advanced crawler robots with high-tech sensors and cameras may cost upwards of $100,000.
8. Can pipe inspection robots detect all types of pipeline damage?
Yes, modern pipe inspection robots are equipped with advanced technologies such as HD cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and laser scanners to detect various issues, including corrosion, cracks, leaks, blockages, and structural weaknesses.
9. What is the difference between a tethered and a wireless pipe inspection robot?
Tethered robots are connected to a control system via a cable that provides power and data transmission. Wireless robots, on the other hand, are battery-powered and communicate with operators wirelessly, offering greater mobility but sometimes with limited operational time.
10. How often should pipelines be inspected using robots?
The frequency of inspections depends on the type of pipeline, its usage, and the risk of damage. Critical infrastructure, such as oil and gas pipelines, may require regular inspections every 6-12 months, while less critical systems may only need annual or biennial inspections.
These FAQs are designed to help both industry professionals and those unfamiliar with pipe inspection robots understand their significance, functionality, and applications.
Conclusion
Pipe inspection robots are transforming the way industries maintain and monitor critical pipeline infrastructure. These robotic systems are not only improving safety and efficiency but also reducing long-term costs associated with pipeline maintenance. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of these robots will only expand, making them an essential tool in the industrial sector.
For more insights and the latest innovations in industrial technologies, explore our comprehensive resources at EngiTech. Stay updated and ensure your operations run smoothly with cutting-edge robotic solutions.
Ready to revolutionize your pipeline maintenance? Visit EngiTech to explore our in-depth guides, expert tips, and the latest advancements in pipe inspection robots and other industrial technologies.