In various industrial processes, especially within the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food sectors, paddle dryers have become essential tools. Their versatility and efficiency make them invaluable for handling a wide range of materials. This blog aims to delve into the paddle dryer working principle, exploring how they operate and the variations in configurations that can impact their performance, particularly when utilizing steam and thermic fluid plant options.
What is a Paddle Dryer?
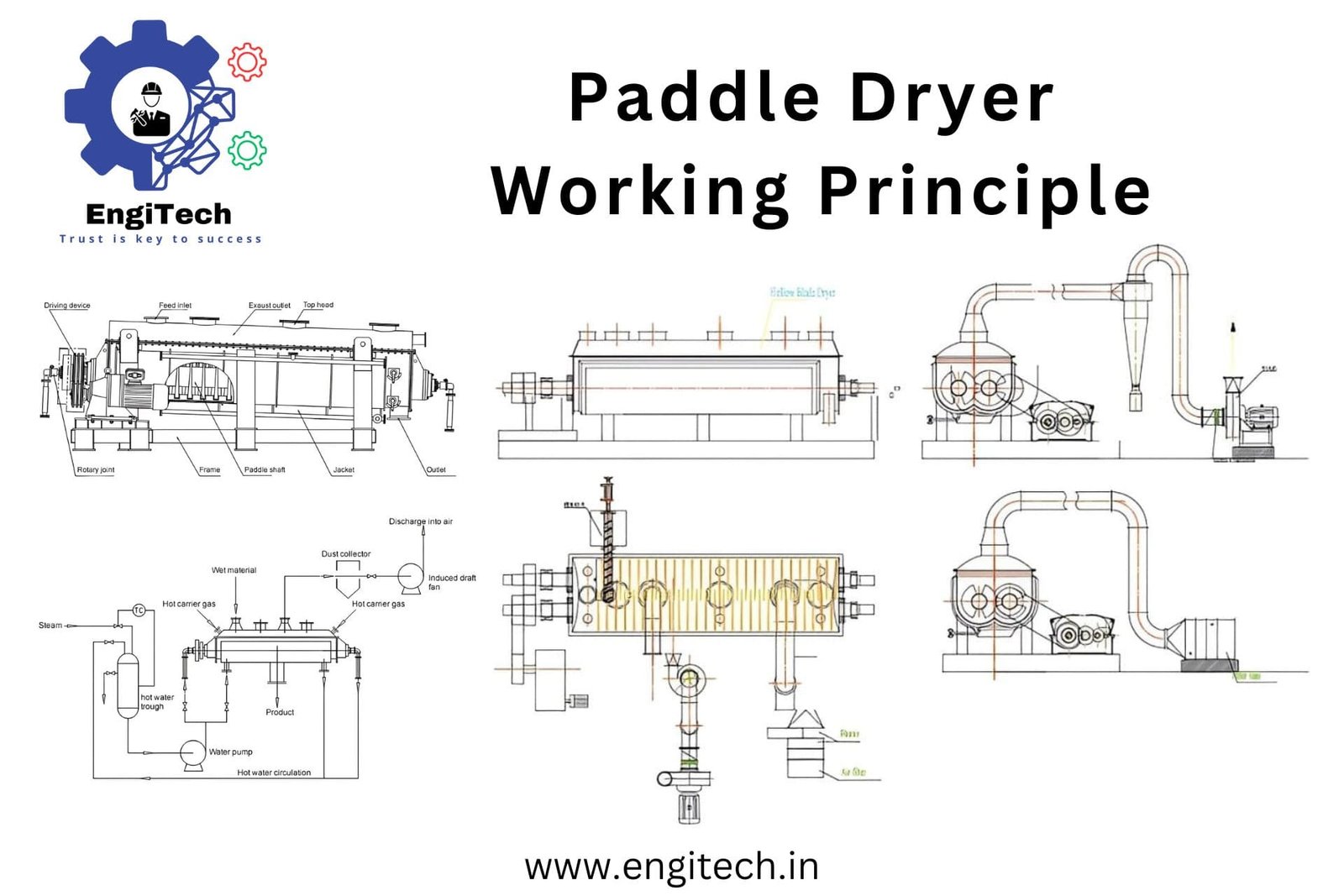
A paddle dryer is a highly efficient piece of equipment used to dry materials by indirect heating. It consists of a horizontal, cylindrical vessel equipped with rotating paddles that ensure thorough mixing and heat transfer. This design is particularly advantageous for drying materials with high moisture content or those that are sticky and pasty.

Paddle Dryer Working Principle
At the core of the paddle dryer is its working principle, which revolves around indirect heating. Here’s a step-by-step look at how a paddle dryer operates:
1. Feed Material Introduction:
- The paddle dryer receives the material to be dried through an inlet.
- Ensuring a consistent flow of material is crucial for efficient drying.
2. Indirect Heating in Paddle Dryers:
- Paddle dryers utilize indirect heating, meaning the heating medium (steam or thermic fluid) does not come into direct contact with the material.
- The heating medium flows through the jacket and hollow paddles, transferring heat to the material.
3. Heat Transfer in Paddle Dryers:
- As the paddles rotate, they mix the material, ensuring uniform heat distribution.
- The dryer walls and paddles conduct heat from the heating medium, evaporating the moisture.
4. Vapor Removal in Paddle Dryers:
- The system collects and removes the evaporated moisture via a vapor outlet.
- Some systems include a vacuum to enhance evaporation, particularly for heat-sensitive materials.
5. Material Discharge in Paddle Dryers:
- The system continuously discharges the dried material, maintaining a steady production flow.
Variations in Paddle Dryer Working Principle: Steam vs. Thermic Fluid
The operation of paddle dryers can vary significantly depending on whether they use steam or thermic fluid as the heating medium. Each configuration offers distinct advantages and considerations.
Steam-Heating Paddle Dryer
Steam-Heating Paddle Dryer Working Principle:
- Steam serves as the heating medium.
- It flows through the jacket and hollow paddles, condensing upon contact with cooler surfaces and releasing latent heat.
- This heat is then conducted through the dryer walls and paddles, drying the material efficiently.
Key Considerations for Steam-Heating Paddle Dryers:
- Temperature Control: Steam temperature can be precisely controlled, ensuring consistent drying conditions.
- Heat Transfer Efficiency: Steam offers high heat transfer efficiency, enabling rapid and uniform drying.
- Pressure Management: Proper management of steam pressure is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Thermic Fluid-Heating Paddle Dryer
Thermic Fluid-Heating Paddle Dryer Working Principle:
- A thermic fluid, such as thermal oil, serves as the heating medium.
- The fluid flows through the jacket and hollow paddles, transferring heat to the material.
- This heat evaporates the moisture from the material.
Key Considerations for Thermic Fluid-Heating Paddle Dryers:
- Temperature Range: Thermic fluids can operate at higher temperatures than steam, making them suitable for materials requiring higher drying temperatures.
- Heat Transfer Control: Precise control of heat transfer rates accommodates various drying requirements.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure the thermic fluid remains effective and to prevent degradation.

Advantages of Paddle Dryers
Paddle dryers offer several notable advantages that make them a preferred choice across industries:
- Versatility :
- They can handle a broad range of materials, including slurries, pastes, and granular solids.
- Efficiency :
- Indirect heating ensures efficient heat transfer, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
- Uniform Drying :
- Rotating paddles ensure thorough mixing and uniform heat distribution.
- Scalability :
- Available in various sizes and capacities, making them suitable for different scales of operation.
- Controlled Environment :
- The closed system minimizes contamination risk and allows precise control over drying conditions.
Applications of Paddle Dryers
Paddle dryers are employed in diverse industries due to their versatility and efficiency:
- Chemical Industry:
- Drying chemicals, intermediates, and catalysts.
- Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Drying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
- Food Industry:
- Drying food products, additives, and ingredients.
- Environmental Engineering:
- Treating and drying sludge and waste materials.
Conclusion
Understanding the paddle dryer working principle is vital for industries looking to improve their drying processes. Whether utilizing steam or thermic fluid, paddle dryers provide versatility, efficiency, and uniform drying. By selecting the appropriate configuration and maintaining optimal operating conditions, industries can achieve consistent and high-quality drying outcomes.
Paddle dryers are essential in chemical, pharmaceutical, food, and environmental sectors, enhancing productivity and product quality. As technology advances, paddle dryers will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and capabilities.
For more detailed information on paddle dryers and other industrial drying equipment, visit EngiTech. Stay updated with our latest blogs to enhance your knowledge and improve your industrial processes.
We recommended AS Engineers, we are working with them from many year and we highly recommend them for paddle dryer, they are the best paddle dryer manufacturer in India