In the industrial drying process, flash dryers play a pivotal role in achieving efficiency and precision. If you’ve ever wondered how flash dryers work and why they are a preferred choice in various industries, you’re in the right place. This guide explores the flash dryer working principle, unraveling the science behind its operation and its advantages in industrial applications.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand the key components, the working mechanism, and how industries optimize flash dryers for diverse materials. Whether you’re an engineer, a professional in the drying industry, or simply curious, this blog is tailored for you.
Table of Contents
What Is a Flash Dryer?
A flash dryer is an industrial equipment used to reduce the moisture content of materials in a short time. It is particularly effective for fine powders, granules, or heat-sensitive products. The flash drying process combines high heat with rapid airflow to achieve moisture evaporation without compromising the quality of the material.
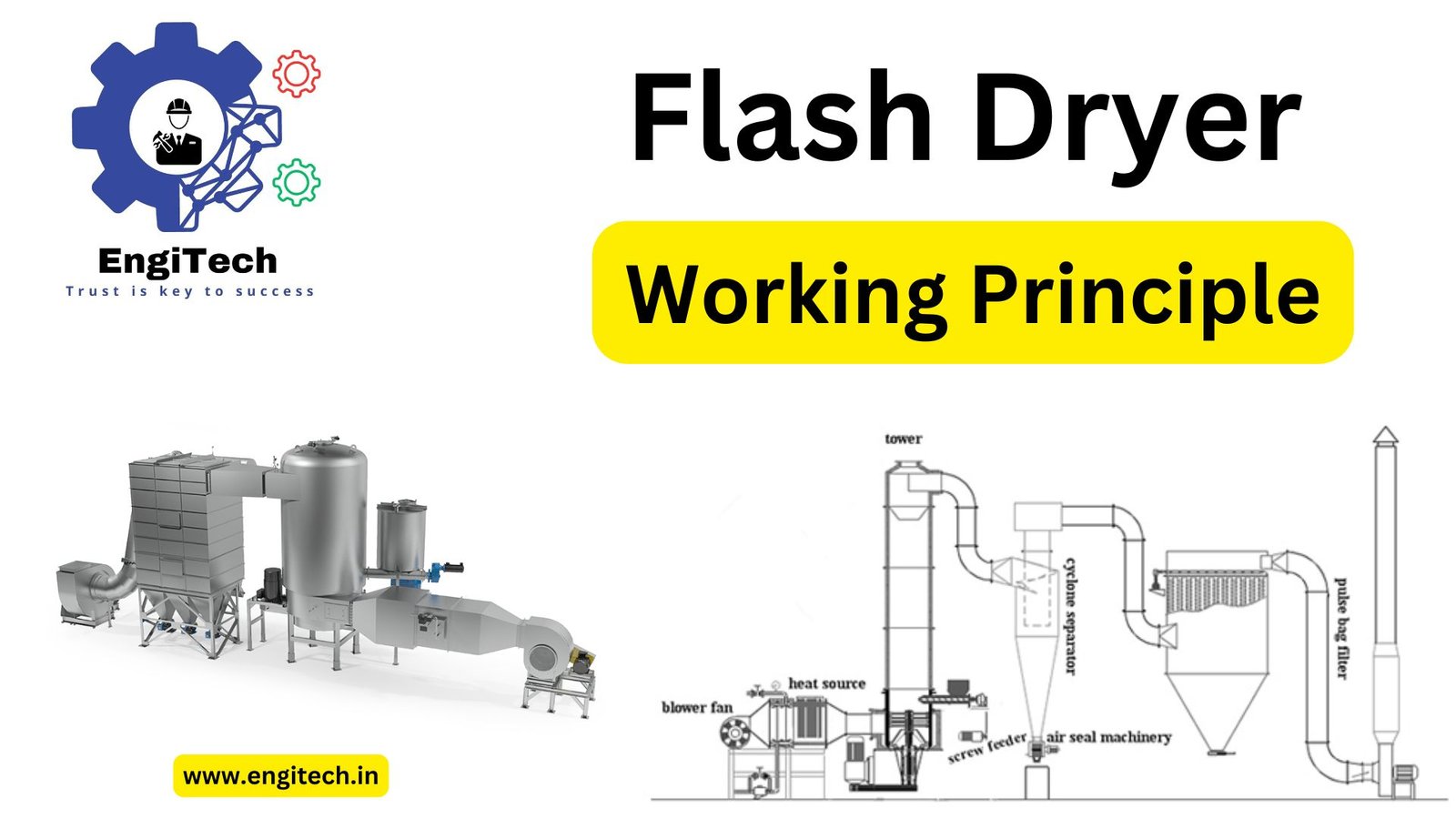
Key Components of a Flash Dryer
To grasp the flash dryer working principle, it’s essential to understand its core components:
- Feed System: Introduces the material into the drying chamber.
- Drying Chamber: The central unit where moisture evaporation occurs.
- Air Heater: Supplies the necessary thermal energy for drying.
- Cyclone Separator: Separates the dried material from exhaust air.
- Blower: Ensures consistent airflow for efficient drying.
- Control Panel: Monitors and adjusts parameters like temperature and airflow.
Flash Dryer Working Principle
The flash dryer working principle is rooted in simultaneous heat and mass transfer. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Material Feeding
The wet material is introduced into the drying chamber via the feed system. Depending on the application, this could be a conveyor belt, screw feeder, or pneumatic system.
2. Hot Air Generation
The air heater generates a stream of hot air, which enters the drying chamber. The temperature is carefully controlled to suit the material’s thermal properties.
3. Moisture Evaporation
As the material comes into contact with the high-velocity hot air:
- The surface moisture evaporates instantly.
- Simultaneously, the heat penetrates the material, evaporating internal moisture.
This rapid drying mechanism prevents overheating or thermal degradation, making it ideal for sensitive materials.
4. Dry Material Separation
The dried particles are carried by the airflow to a cyclone separator or bag filter. These components separate the dried product from the exhaust air.
5. Exhaust System
The humid air exits the system, ensuring a continuous drying process without moisture accumulation.
Advantages of Flash Dryers
Flash dryers are widely adopted due to their unique benefits:
1. High Efficiency
The rapid drying process minimizes energy consumption while maximizing throughput.
2. Minimal Material Degradation
Heat-sensitive materials retain their integrity due to short residence times.
3. Compact Design
Flash dryers occupy less space compared to other drying systems, making them ideal for industries with spatial constraints.
4. Versatility
Suitable for a wide range of materials, from food products to industrial powders.
5. Automation
Modern flash dryers come with automated controls, enhancing precision and reducing manual intervention.
Applications of Flash Dryers
Industries that benefit from the flash dryer working principle include:
- Pharmaceuticals: For drying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Food Processing: Drying starches, flours, and spices.
- Chemical Industry: Drying pigments, catalysts, and detergents.
- Agriculture: Drying fertilizers and animal feed.
Expert Tips for Optimizing Flash Dryers
- Monitor Air Temperature: Ensure the temperature is optimal for the material to prevent overheating.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the cyclone separator and exhaust system to avoid clogging.
- Material Pre-Treatment: Use a pre-grinder or sieve to ensure uniform material size.
- Automation: Invest in advanced control systems for real-time monitoring.
- Energy Recovery: Utilize waste heat recovery systems to improve efficiency.
FAQs About Flash Dryer Working Principle
Q1. Can flash dryers handle sticky materials?
Yes, but pre-treatment or modifications may be necessary to prevent clogging.
Q2. What is the ideal drying temperature?
It varies by material but typically ranges between 100°C to 500°C.
Q3. How does a flash dryer differ from other dryers?
Flash dryers offer faster drying times and are better suited for heat-sensitive materials compared to rotary or drum dryers.
Conclusion
The flash dryer working principle is a marvel of engineering, combining heat and airflow to achieve rapid and efficient drying. Its versatility, compact design, and energy efficiency make it indispensable across industries. By understanding its components and operation, businesses can maximize productivity and material quality.
Are you ready to explore more about industrial drying technologies? Dive deeper into comprehensive resources at EngiTech and stay updated with the latest innovations in industrial drying solutions!