Drum Dryers: Understanding the Working Principle
Introduction
Drum dryers, also known as rotary dryers, are essential in various industries, offering an efficient solution for drying a wide range of materials. Whether you’re in food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, or mining, understanding how drum dryers work can help optimize your operations. In this blog post, we will explore the working principle of drum dryers, addressing key questions and providing detailed explanations.
Questions This Blog Will Answer:
- What is the working principle of a drum dryer?
- How do drum dryers handle different types of materials?
- What are the key advantages of using drum dryers in industrial applications?
- How can businesses optimize the use of drum dryers?
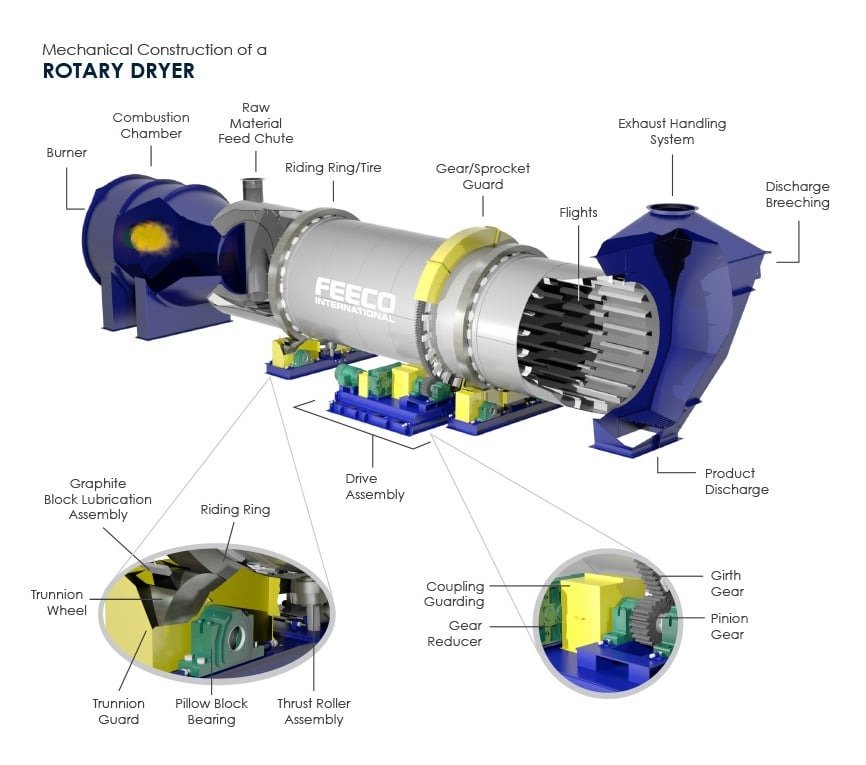
Working Principle of Drum Dryers
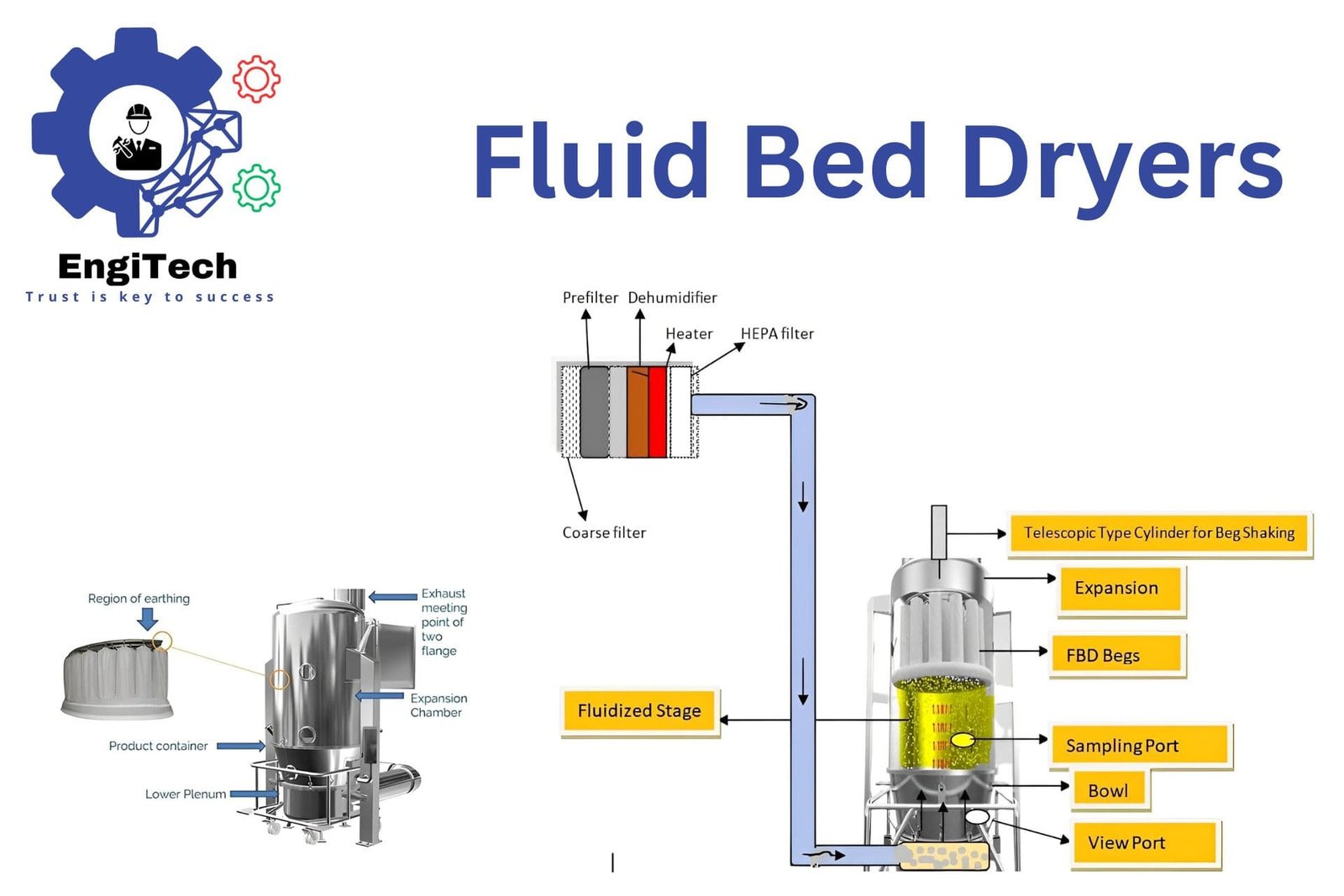
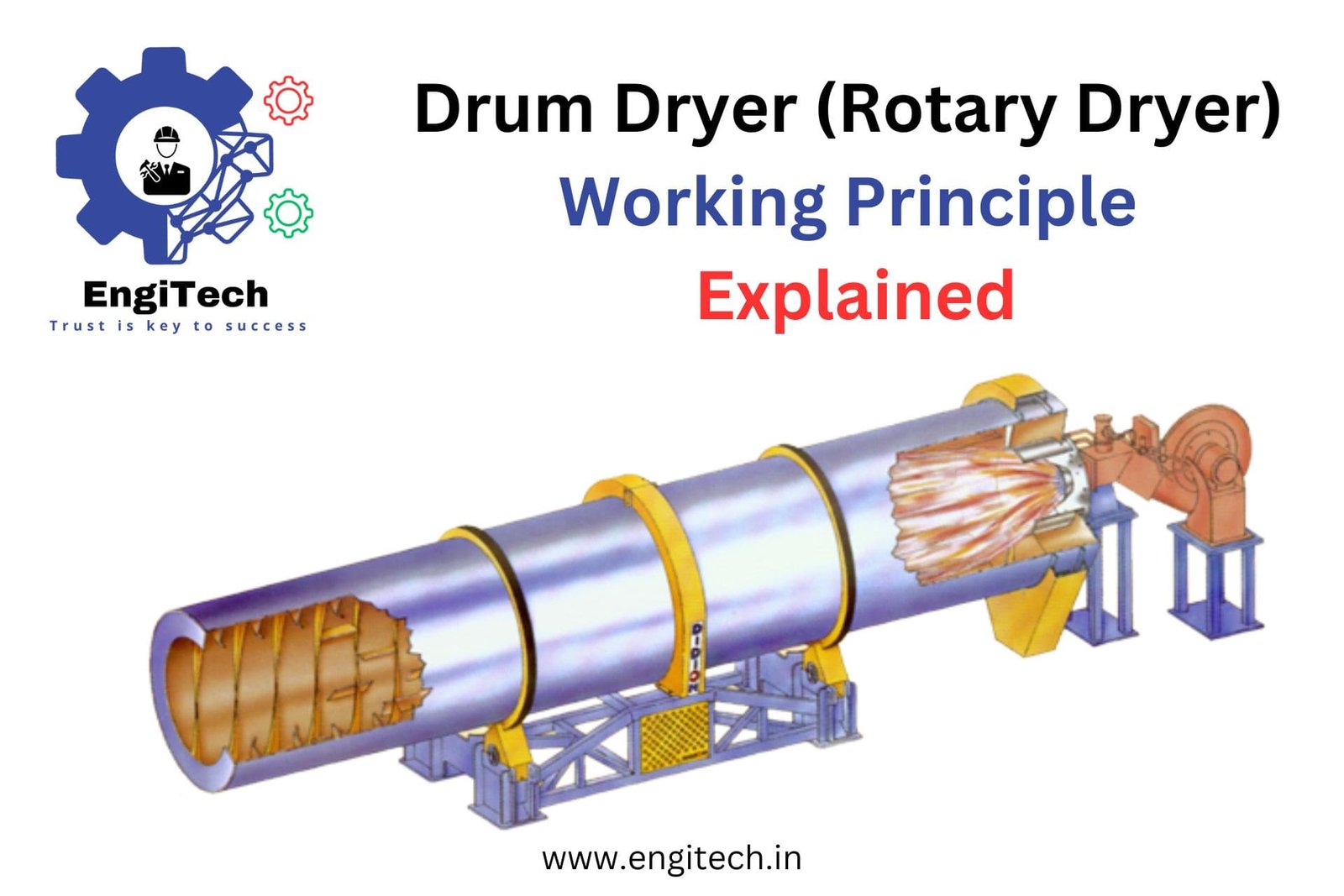
Drum dryers, or rotary dryers, consist of a large, rotating cylindrical drum that uses hot air or gas to dry materials. The drum is slightly inclined to facilitate the movement of materials through the drying chamber.
- Feed Material Introduction: Introduce wet material into the drum dryer through a feed hopper or conveyor system. This step ensures a steady flow of material into the drying chamber.
- Heat Transfer: Hot air or gas is introduced into the drum through a burner or heat exchanger. The heat source can vary, including natural gas, propane, oil, or steam. The hot air or gas flows through the drum, transferring heat to the material.
- Drum Rotation: The drum rotates at a controlled speed, causing the material to tumble and cascade through the hot air stream. This tumbling action ensures even exposure to the heat, promoting uniform drying.
- Moisture Evaporation: As the material moves through the drum, the heat evaporates the moisture. The combined effect of airflow and rotation facilitates efficient drying.
- Exhaust System: The moisture-laden air is expelled through an exhaust system equipped with filters to capture any fine particles, ensuring a clean and safe operation.
- Discharge: The dried material exits the drum and is collected for further processing or packaging. This step completes the drying process, delivering a product with the desired moisture content.
Handling Different Types of Materials
Drum dryers are versatile and can handle a variety of materials, including solids, pastes, and slurries. Here’s how they adapt to different materials:
- Solids: For granular materials like grains, minerals, and chemicals, drum dryers ensure consistent drying by providing uniform heat exposure.
- Pastes and Slurries: When dealing with pastes and slurries, the drum’s rotation and heat help break down the material, facilitating effective moisture evaporation.
Key Advantages of Using Drum Dryers
- Efficiency: Drum dryers offer high drying efficiency due to the direct contact between the material and the hot air or gas. This direct contact speeds up the drying process.
- Versatility: These dryers can handle a wide range of materials, making them suitable for various industrial applications. From food processing to mining, drum dryers are adaptable.
- Scalability: Drum dryers are available in various sizes, accommodating both small-scale and large-scale operations. This scalability ensures that businesses of all sizes can benefit from their use.
- Energy Savings: Modern drum dryers are designed to optimize energy usage, reducing operational costs. Innovations in heat transfer and airflow control contribute to these energy savings.
- Uniform Drying: The rotating drum ensures even exposure to heat, resulting in uniform drying. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining the quality of the dried product.
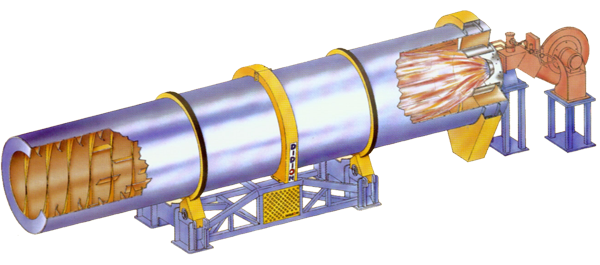
Optimizing the Use of Drum Dryers
To optimize the use of drum dryers, businesses should consider the following tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly maintain the drum dryer to ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime. This includes cleaning filters, inspecting the drum, and checking the heat source.
- Temperature Control: Precisely control the temperature to avoid over-drying or under-drying the material. Using advanced control systems can help achieve the desired drying conditions.
- Material Feed Rate: Adjust the material feed rate to ensure a consistent flow through the drum. This helps maintain uniform drying and prevents bottlenecks.
- Monitor Exhaust Systems: Regularly monitor and maintain the exhaust system to ensure it effectively removes moisture-laden air and captures fine particles.
Conclusion
Understanding the working principle of drum dryers can help industries optimize their drying processes and improve product quality. By leveraging the efficiency, versatility, and scalability of drum dryers, businesses can enhance their operations and achieve better results. As technology advances, drum dryers will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and sustainability.
For more in-depth articles and resources on industrial drying technologies and innovations, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and applications in the industry!