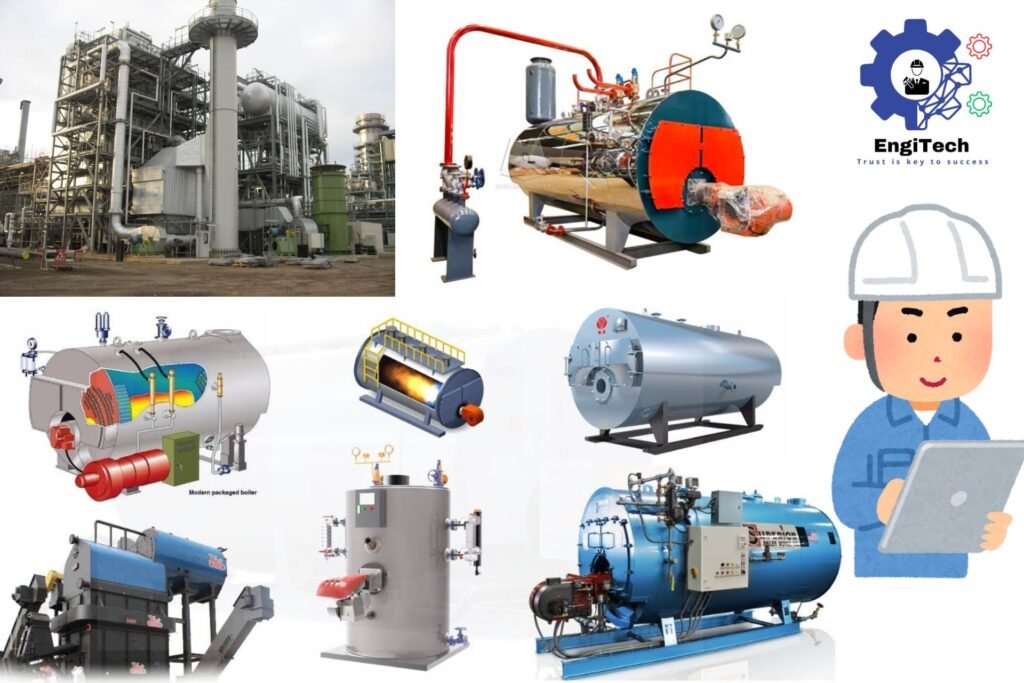
Experts Guide to Boilers: Types, Applications, and Maintenance

Boilers are essential components in various industries and domestic applications. They play a crucial role in heating and power generation. This guide provides a detailed overview of boilers, including their types, working principles, applications, and maintenance practices. Understanding these aspects will help you select the right boiler for your needs and ensure efficient operation.
What is a Boiler?
A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other suitable liquids are heated to generate steam or vapor. The generated steam or vapor is used for various purposes, such as heating applications (water heating, central heating), power generation, and other industrial processes. Essentially, boilers work on the same principle as pressure cookers but on a much larger scale.
How Does a Boiler Work?
Boilers operate by heating water or other fluids to create steam or vapor. This process involves several key components:
- Burner: The burner initiates the combustion process, heating the fluid.
- Combustion Chamber: The combustion chamber, made of cast iron, withstands high temperatures and burns the fuel to generate heat.
- Heat Exchanger: The heat exchanger transfers the generated heat to the water or fluid, increasing the boiler’s efficiency.
- Steam Drum and Mud Drum: The steam drum collects the steam, while the mud drum collects and removes solid particles periodically.

Types of Boilers
Boilers come in various types, each suited for specific applications and fuel types. Here are some common types:
Fire Tube Boiler
Fire tube boilers are commonly used in small and medium-sized industries. They consist of a series of tubes through which hot gases pass, heating the surrounding water. These boilers are ideal for low to medium-pressure steam requirements and are often factory-made, ready for installation.
- Advantages: Easy to install, compact, and cost-effective for small to medium operations.
- Disadvantages: Limited to lower pressures and capacities, higher risk of explosion.
Water Tube Boiler
Water tube boilers are designed for high-pressure applications, commonly used in large manufacturing plants. They have water-filled tubes that are heated by hot gases. These boilers offer better control over steam pressure and capacity.
- Advantages: High efficiency, suitable for high-pressure applications, rapid steam generation.
- Disadvantages: More complex design, higher initial cost, and maintenance requirements.
Electric Boiler
Electric boilers use electricity to generate heat and produce steam. They are highly efficient and environmentally friendly, as they do not rely on fossil fuels.
- Advantages: No emissions, quiet operation, easy installation, and low maintenance.
- Disadvantages: High operational cost due to electricity prices, limited by power supply capacity.
Condensing Boiler
Condensing boilers use natural gas and feature two heat exchangers to maximize efficiency. They recover heat from exhaust gases, achieving up to 98% thermal efficiency.
- Advantages: Extremely efficient, lower energy costs, environmentally friendly.
- Disadvantages: Higher initial cost, complex design, and requires proper maintenance.
Oil Boiler
Oil boilers use oil as a fuel source and are typically used in residential applications for heating water. They can achieve efficiencies of up to 90% or more.
- Advantages: High efficiency, reliable, and suitable for areas without natural gas supply.
- Disadvantages: Higher fuel costs, requires oil storage, and regular maintenance.
Natural Gas Boiler
Natural gas boilers use natural gas to heat water or generate steam. They are regulated by temperature gauges and thermoelectric devices to minimize fuel wastage.
- Advantages: Efficient, cost-effective, widely available fuel source.
- Disadvantages: Requires gas supply infrastructure, potential safety hazards if not properly maintained.
Key Components of Industrial Boilers
Industrial boilers have several critical components that ensure efficient operation:
- Burner: Initiates the combustion process by igniting the fuel.
- Combustion Chamber: Burns the fuel to generate heat.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the combustion gases to the water or fluid.
- Steam Drum and Mud Drum: Collects steam and removes solid impurities.
- Fuel Source: Can be coal, oil, natural gas, or other fuels.
- Control Systems: Regulate temperature, pressure, and fuel supply to maintain optimal performance.

Applications of Boilers
Industrial Applications
Boilers are widely used in various industrial sectors for multiple applications:
- Power Generation: Boilers generate steam to drive turbines for electricity production.
- Chemical Processing: Used in chemical plants for heating and steam generation.
- Food and Beverage: Essential for sterilization, cooking, and pasteurization processes.
- Textile Industry: Used for dyeing, drying, and printing fabrics.
- Paper and Pulp: Provides steam for the production process and drying paper products.
Domestic Applications
Boilers also play a significant role in domestic settings:
- Central Heating: Boilers provide heating for residential buildings.
- Water Heating: Used in homes for hot water supply in bathrooms and kitchens.
- Cooking: In some regions, boilers are used for cooking applications.
Boiler Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Efficient boiler technology is more critical than ever, given the emphasis on energy conservation and environmental protection. Modern boilers use advanced technologies to maximize efficiency and minimize emissions:
- Natural Gas Boilers: These boilers are more environmentally friendly, as they produce fewer emissions compared to coal or oil boilers.
- Condensing Boilers: They recover heat from exhaust gases, reducing energy wastage and emissions.
- Electric Boilers: They have zero emissions during operation, making them ideal for areas with strict environmental regulations.
Boiler Maintenance and Safety
Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of boilers. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the burner, heat exchanger, and other components.
- Cleaning: Clean the combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and fuel lines to prevent soot buildup.
- Calibration: Calibrate control systems to ensure accurate temperature and pressure settings.
- Safety Checks: Install safety valves, smoke detectors, and alarms to prevent accidents.
- Fuel Management: Monitor fuel levels and ensure proper circulation to avoid inefficiencies.
Types of Boiler Fuels
Boilers can use various types of fuels, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Coal: Traditional fuel with high energy content but produces significant emissions.
- Oil: Offers high efficiency but requires proper storage and handling.
- Natural Gas: Clean-burning fuel with lower emissions and widespread availability.
- Electricity: Zero emissions during operation but high operational costs.
- Biomass: Renewable fuel source with lower emissions but requires specific handling and storage.
Conclusion
Boilers are indispensable in both industrial and domestic settings, providing essential heat and power. Understanding the different types of boilers, their working principles, and applications can help you choose the right boiler for your needs. Regular maintenance and proper fuel management are crucial to ensure efficient and safe operation. As technology advances, modern boilers continue to improve in efficiency and environmental friendliness, contributing to a sustainable future.
For more detailed articles and resources on boilers and related technologies, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and applications in the field!