Agitated Thin Film Dryers (ATFDs) Plant Process: A Complete Guide

In industries where liquid separation is essential, Agitated Thin Film Dryers (ATFDs) have emerged as a reliable and efficient solution. These advanced drying systems are widely used to concentrate or recover materials from liquids, especially in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and wastewater treatment. If you are wondering how the ATFDs plant process works or why it plays a crucial role in modern industries, this guide will provide all the answers.
This article will walk you through the step-by-step Agitated Thin Film Dryer plant process, offering practical insights into its operation, design, and advantages. By the end, you’ll understand why ATFDs are considered a superior drying technology and how industries leverage them for improved productivity and performance.
Table of Contents
What is an Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD)?
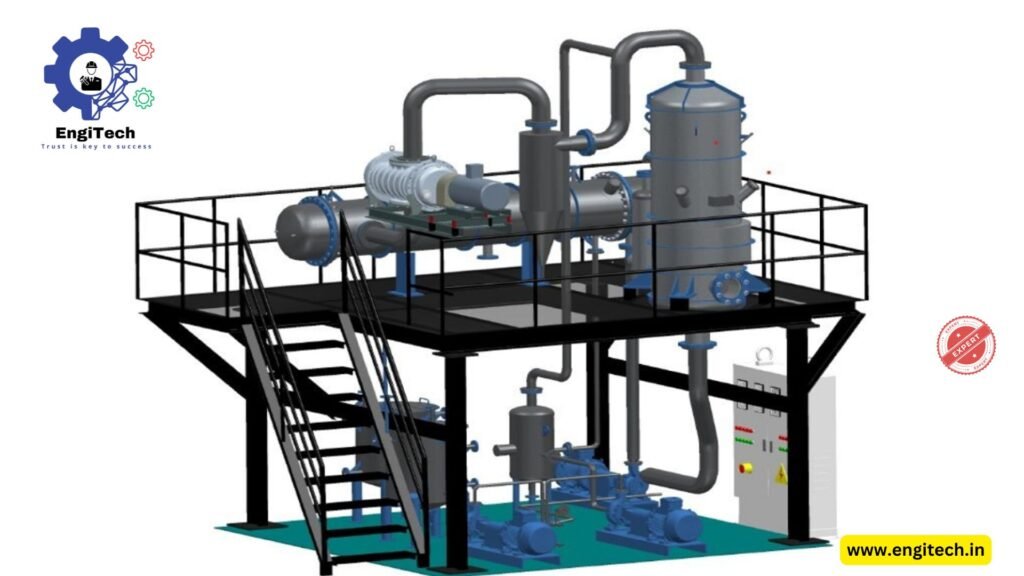
An Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD) is a mechanical system designed to efficiently remove solvents and water from solutions by creating a thin film of liquid over a heated surface. In this process, the liquid is spread into a thin layer by rotating blades, enhancing heat transfer and allowing rapid evaporation of moisture or solvents.
The technology behind ATFDs is ideal for applications where high heat sensitivity or viscosity issues limit the use of conventional drying techniques.
Key Applications of ATFDs
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Drying heat-sensitive drugs and APIs.
- Chemical Processing: Removing solvents from specialty chemicals.
- Food Industry: Drying extracts, concentrates, and food additives.
- Wastewater Treatment: Concentrating brine and recovering usable by-products.
Step-by-Step ATFD Plant Process
The ATFD plant process is a streamlined approach that maximizes drying efficiency. Below is a detailed breakdown of how the process works:
1. Feed Introduction
The liquid feed containing solvents, water, or other volatile components is pumped into the ATFD unit. The feed rate is controlled to ensure steady film formation inside the dryer.
- Primary Keyword Placement: ATFDs plant process begins with a carefully controlled feed.
2. Thin Film Formation
Inside the dryer, agitated blades spread the liquid into a thin film over a heated cylindrical surface. This thin film ensures uniform exposure to heat, speeding up the evaporation process.
- Expert Insight: The thickness of the film is critical. A thin, uniform film prevents heat degradation, making ATFDs ideal for temperature-sensitive products.
3. Heat Transfer and Evaporation
Heat is applied either through steam or hot oil, and the moisture or solvent within the thin film evaporates almost instantly. This rapid phase separation ensures minimal product retention and maximizes recovery.
- Pro Tip: The efficiency of ATFDs is enhanced by operating under vacuum conditions, which lowers the boiling point of the liquids being dried.
4. Vapor Condensation and Recovery
The vapor generated during evaporation is collected and routed to a condenser, where it is cooled and condensed back into liquid form. This step ensures that any valuable solvents are recovered and reused.
- Secondary Keyword Use: The ATFDs plant process ensures efficient solvent recovery through advanced condensation systems.
5. Product Collection
The concentrated or dried product is discharged from the bottom outlet of the dryer. Depending on the application, the product may be in powder or paste form, ready for further processing or packaging.
Benefits of Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD) Technology
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The thin film maximizes contact between the product and heated surface.
- Suitable for Heat-Sensitive Materials: Operates efficiently under vacuum to reduce thermal degradation.
- Handles Viscous Products: The agitating blades ensure uniform drying, even for highly viscous fluids.
- Energy-Efficient Operation: Reduced drying time results in lower energy consumption.
- Closed-Loop Recovery: ATFDs facilitate the recovery of valuable solvents, minimizing waste.
ATFD Plant Process vs. Traditional Drying Methods
| Feature | ATFDs Plant Process | Traditional Dryers |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Rapid (seconds to minutes) | Longer (hours) |
| Heat Sensitivity | Suitable for sensitive products | Risk of degradation |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate to low |
| Product Handling | Handles viscous products with ease | Struggles with viscous fluids |
| Solvent Recovery | Efficient closed-loop recovery | Minimal solvent recovery |
The ATFDs plant process offers a clear advantage over traditional drying systems by reducing time, energy consumption, and product wastage.
How to Optimize the ATFD Plant Process
To ensure optimal performance, it’s essential to fine-tune specific parameters during the ATFD operation.
- Feed Rate Control: Adjusting the feed flow ensures uniform film formation.
- Temperature Settings: Proper control prevents thermal degradation.
- Vacuum Level Optimization: Operating under the right vacuum level enhances solvent recovery.
- Blade Speed Regulation: Adjusting the rotation speed improves film spread and evaporation.
- Maintenance Schedule: Regular cleaning of the heated surface ensures uninterrupted operation.
Common Challenges in the ATFD Plant Process and Solutions
Even with advanced technology, challenges can arise in ATFD operations. Below are common issues and their solutions:
- Issue: Clogging of agitating blades.
Solution: Regular cleaning and inspection of the blades. - Issue: Uneven film formation.
Solution: Adjust the feed rate and blade rotation speed. - Issue: Product degradation due to overheating.
Solution: Use vacuum conditions to lower the operating temperature.
ATFDs and Sustainability: A Step Towards Green Processing
The ATFDs plant process aligns with sustainability goals by reducing energy consumption and facilitating the recovery of solvents. The technology minimizes waste generation, making it a greener alternative to conventional drying methods. In industries aiming for net-zero emissions, ATFDs play a crucial role in improving environmental performance.
Conclusion
The Agitated Thin Film Dryers (ATFDs) plant process is a game-changer in industrial drying, offering unparalleled efficiency, sustainability, and performance. Its ability to handle heat-sensitive and viscous materials with ease makes it a preferred choice across multiple industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing.
By adopting ATFDs, companies can enhance productivity, reduce energy consumption, and recover valuable by-products, contributing to both business success and environmental sustainability.
Looking to learn more about cutting-edge industrial drying technologies? Explore EngiTech for comprehensive insights and stay updated on the latest innovations in ATFDs plant processes and other industrial solutions.


