A Comprehensive Guide to Air Compressors: Types, Applications, and Buying Tips
Air compressors are indispensable tools in various industries and everyday applications, offering versatile functionality and reliable performance. Whether you’re a professional in manufacturing, a technician, or a hobbyist, understanding air compressors is essential to leveraging their benefits effectively.
In this blog, we’ll explore the world of air compressors, covering their types, uses, advantages, and critical factors to consider when purchasing one. By the end, you’ll have actionable insights to make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
What is an Air Compressor?
An air compressor is a machine designed to convert power into potential energy stored in compressed air. This energy is then used to perform tasks like inflating tires, powering tools, and even industrial manufacturing processes.
How Do Air Compressors Work?
Air compressors function by pulling in air, compressing it within a chamber, and then releasing it at a controlled pressure. Depending on the type, this process can involve pistons, rotors, or other mechanical systems.
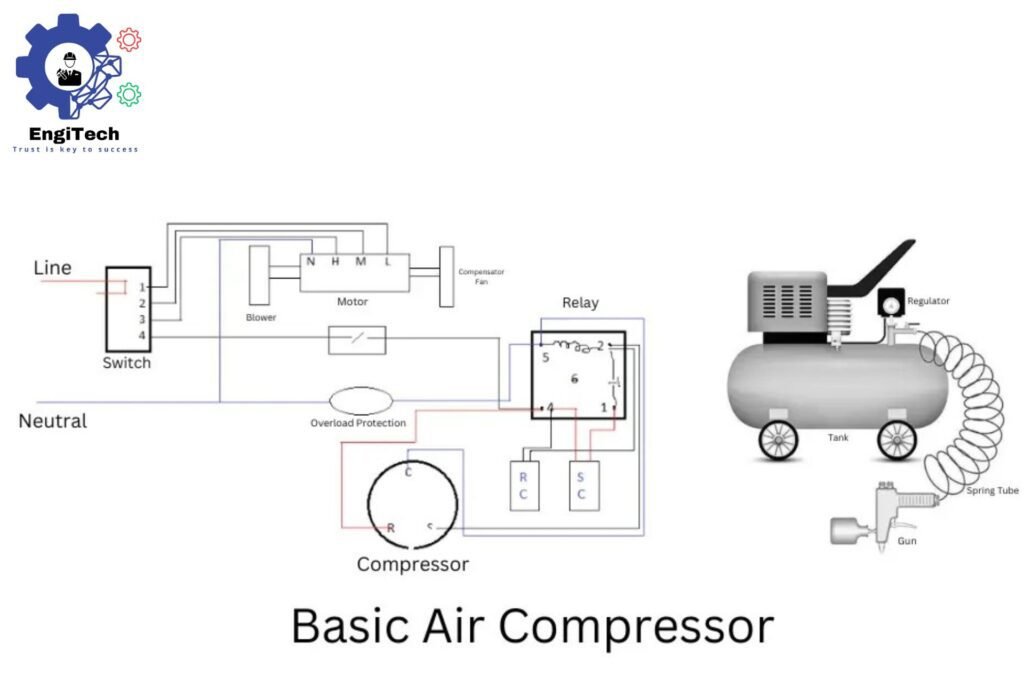
Types of Air Compressors
Understanding the various types of air compressors is crucial to selecting the right one for your needs.
1. Reciprocating Air Compressors
Reciprocating Air Compressors Also known as piston compressors, these are the most common type. They use a piston driven by a crankshaft to compress air.
- Pros: High pressure output, cost-effective for small operations.
- Cons: Noisy and less efficient for continuous use.
2. Rotary Screw Air Compressors
These use two helical screws to compress air. They’re popular in industrial settings for their efficiency and reliability.
- Pros: Quiet operation, suitable for continuous use.
- Cons: Higher initial cost.
3. Centrifugal Air Compressors
Designed for large-scale industrial use, centrifugal compressors rely on a rotating impeller to generate high-pressure air.
- Pros: Ideal for high-volume applications.
- Cons: Complex maintenance and high cost.
4. Scroll Air Compressors
These feature a scroll mechanism that compresses air in a continuous motion. They are compact and quiet.
- Pros: Energy-efficient, low maintenance.
- Cons: Limited to low-power applications.
Applications of Air Compressors
Air compressors find applications across diverse industries and daily tasks.
1. Industrial Applications
- Manufacturing: Powering assembly lines, operating machinery.
- Construction: Operating pneumatic tools like nail guns and jackhammers.
- Automotive: Inflating tires, painting, and power washing.
2. Domestic Uses
- DIY Projects: Powering small tools for woodworking or home improvement.
- Maintenance: Cleaning debris and inflating sports equipment.
3. Specialized Applications
- Healthcare: Operating respiratory devices and dental tools.
- Food and Beverage: Packaging and preserving products.
Key Features to Look for in an Air Compressor
1. Power Source
Choose between electric and gas-powered compressors based on your usage environment. Electric models are more suitable for indoor use, while gas compressors are ideal for outdoor or remote areas.
2. Tank Size
The tank size determines how long the compressor can operate before recharging. For heavy-duty tasks, opt for larger tanks.
3. Airflow and Pressure
Measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) and pounds per square inch (PSI), these metrics define the compressor’s capacity. Match the specifications to your tool requirements.
4. Portability
Consider portable models with wheels and handles if you need mobility, or go for stationary units for dedicated setups.
Advantages of Using Air Compressors
1. Versatility
Air compressors power a wide range of tools, making them invaluable in different settings.
2. Efficiency
Compressed air provides consistent power, enhancing productivity.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
They reduce the need for multiple power sources by centralizing energy.
Maintenance Tips for Air Compressors
1. Regular Inspection
Check for leaks, wear, and tear to prevent malfunctions.
2. Drain Moisture
Remove moisture from the tank regularly to avoid corrosion.
3. Replace Filters
Keep the air intake and outlet clean for optimal performance.
4. Lubrication
Ensure moving parts are well-lubricated to reduce wear.
How to Choose the Right Air Compressor
1. Assess Your Needs
Identify the primary tasks you’ll perform and choose a compressor with matching specifications.
2. Consider the Environment
For indoor use, prioritize electric models; for outdoor tasks, gas-powered options may be better.
3. Budget
Balance your budget with the required features. Remember, higher initial costs can mean long-term savings through efficiency.
Top Air Compressor Brands in 2025
When shopping for an air compressor, brand reputation matters. Here are some trusted names in the industry:
- Ingersoll Rand: Known for durability and performance.
- Atlas Copco: Premium industrial compressors.
- DeWalt: Reliable tools for professional and DIY users.
- Makita: Compact and efficient models.
Future Trends in Air Compressors
The air compressor industry is evolving with innovative trends:
- Energy Efficiency: New designs aim to reduce power consumption.
- IoT Integration: Smart compressors with real-time monitoring.
- Eco-Friendly Models: Focus on reducing carbon footprints.
Conclusion: Your Guide to Making the Right Choice
Air compressors are versatile, powerful tools that cater to a wide range of applications. Whether for industrial or personal use, understanding their types, features, and maintenance is key to maximizing their value.
Ready to explore more insights into industrial technologies? Visit EngiTech for expert resources and stay updated on the latest innovations!