Flash Dryer Design, Diagram, Applications, and Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Industrial drying is an essential process in various industries, where reducing moisture content is crucial for product quality and usability. Among the many drying technologies available, the flash dryer stands out for its efficiency and versatility. In this blog, you will learn everything about flash dryers, including their design, working mechanism, applications, and types. Whether you’re a professional in the engineering sector or someone exploring industrial drying technologies, this guide will provide valuable insights to address your questions and needs.
Table of Contents
What Is a Flash Dryer?
A flash dryer is a drying system that uses high-speed hot air to dry materials rapidly. The drying process occurs in a matter of seconds, making it ideal for handling heat-sensitive materials. Flash dryers are commonly used in industries like food processing, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
Flash Dryer Design
The design of a flash dryer plays a pivotal role in its efficiency and effectiveness. Let’s break it down into key components and their functions.
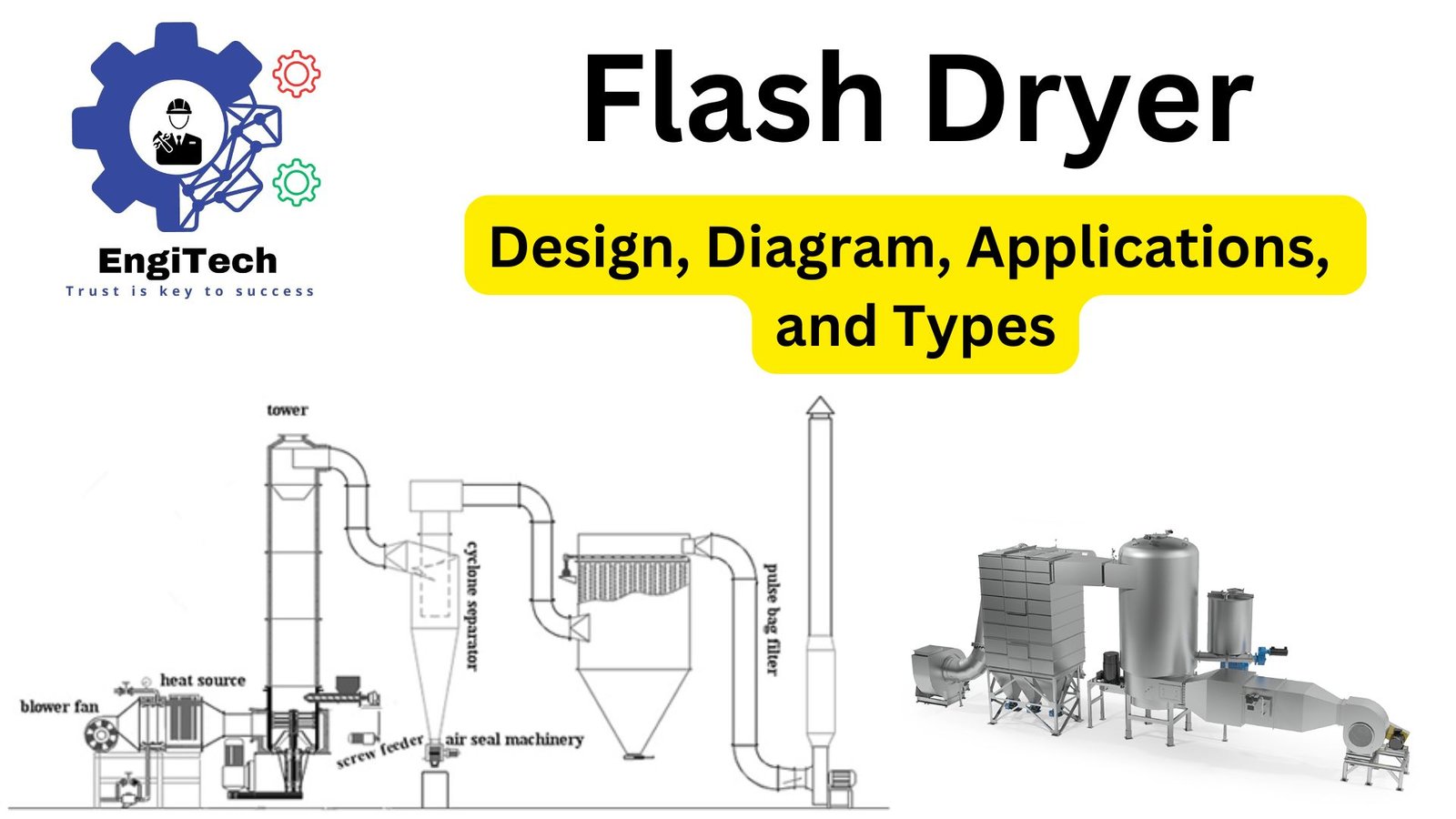
Key Components
- Feed System
- Materials are fed into the dryer through a controlled feeding mechanism.
- Common feeding methods include screw feeders and rotary valves.
- Drying Chamber
- The main area where drying occurs.
- Typically a vertical or horizontal chamber with sufficient space for material-air interaction.
- Hot Air Generator
- Provides the necessary heat for drying.
- Uses gas, oil, or electricity as a heating source.
- Air Disperser
- Ensures even distribution of hot air for consistent drying.
- Cyclone Separator
- Separates the dried material from the exhaust air.
- Collects the final product in a dust-free form.
- Exhaust Fan
- Expels moist air out of the system, maintaining airflow.
Flash Dryer Diagram
Here is a schematic representation of a typical flash dryer:
How Does a Flash Dryer Work?
The flash drying process is straightforward yet highly efficient:
- Material Feeding: The material enters the dryer through the feed system.
- Hot Air Introduction: Preheated air enters the drying chamber at high velocity.
- Drying: The material comes into direct contact with hot air, causing rapid moisture evaporation.
- Separation: Dried particles are separated from the air using a cyclone separator or bag filter.
- Discharge: The final product exits the system, ready for packaging or further processing.
Applications of Flash Dryers
Flash dryers are versatile and find applications across multiple industries.
1. Food and Beverage
- Drying starch, powdered milk, and spices.
- Ensures uniform moisture reduction without compromising quality.
2. Chemical Industry
- Drying polymers, resins, and chemical powders.
- Ideal for heat-sensitive chemicals that require rapid drying.
3. Pharmaceuticals
- Used for drying bulk powders and granules.
- Maintains the integrity of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
4. Agriculture
- Drying agricultural by-products like husks and bran.
- Facilitates easier storage and transportation.
5. Minerals and Metals
- Drying of ores and mineral powders.
- Enhances usability in further processing stages.
Types of Flash Dryers
Flash dryers are categorized based on their design and application.
1. Spin Flash Dryers
- Incorporate a spinning mechanism for thorough mixing.
- Suitable for materials with high moisture content.
2. Pneumatic Flash Dryers
- Rely on high-velocity air for drying.
- Best for fine powders and lightweight materials.
3. Vertical Flash Dryers
- Feature a vertically aligned drying chamber.
- Save space and improve drying efficiency.
4. Horizontal Flash Dryers
- Offer a larger drying area.
- Used for high-capacity drying processes.
Advantages of Flash Dryers
Flash dryers offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice:
- Energy Efficiency: Rapid drying minimizes energy consumption.
- Space-Saving: Compact design compared to other drying technologies.
- High Throughput: Handles large volumes of material efficiently.
- Preserves Quality: Ideal for sensitive materials requiring gentle drying.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenges
- Clogging: Occurs when material feeds are inconsistent.
- Overheating: Can degrade sensitive materials.
Solutions
- Use precise feed control systems to prevent clogging.
- Incorporate advanced temperature control mechanisms to avoid overheating.
Expert Tips for Selecting the Right Flash Dryer
- Assess Material Properties: Understand the moisture content and thermal sensitivity.
- Consider Throughput Requirements: Choose a dryer that matches your production needs.
- Evaluate Energy Efficiency: Opt for designs that minimize operational costs.
- Partner with Experts: Consult with flash dryer manufacturers for tailored solutions.
Conclusion
Flash dryers are indispensable in industries requiring efficient and rapid drying solutions. By understanding their design, working principles, applications, and types, you can select the right system for your needs. Whether you’re optimizing processes in food production, pharmaceuticals, or other industries, flash dryers provide a reliable solution to meet your drying requirements.
Explore More
For more in-depth insights into industrial drying technologies and expert recommendations, visit EngiTech. Stay ahead of the curve with our resources, updates, and innovative solutions!