Tunnel Dryers Working Principle, Diagram, Applications and Features
Tunnel dryers are essential for various industries due to their efficient and versatile drying capabilities. This blog post will provide a detailed explanation of the working principle of tunnel dryers, illustrated with a diagram, and discuss their various applications. We’ll answer key questions related to tunnel dryer working principles and diagrams, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of this drying technology.
Table of Contents
Questions This Blog Will Answer:
- What is the working principle of a tunnel dryer?
- What does the diagram of a tunnel dryer look like?
- What are the primary applications of tunnel dryers?
Tunnel Dryer Working Principle
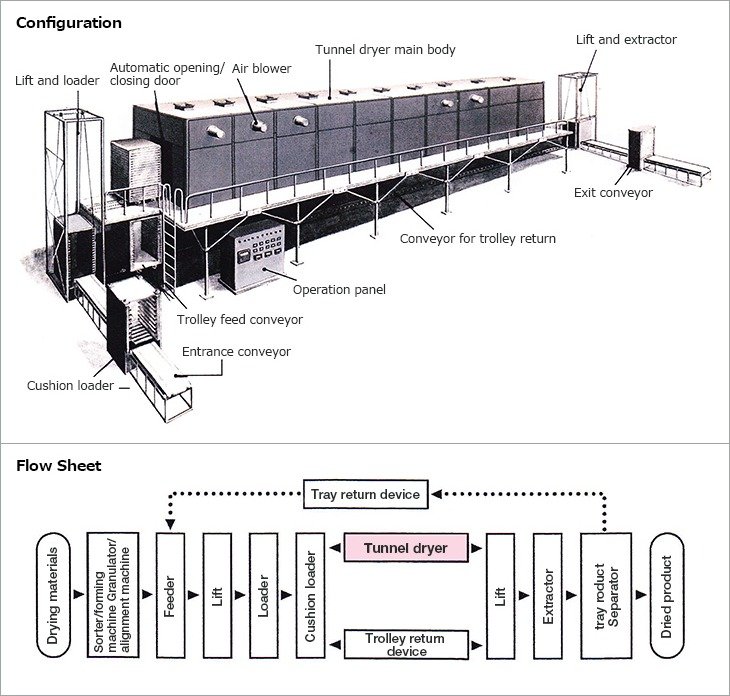
Tunnel dryers use hot air or advanced heating techniques like microwave, RF, or infrared to dry materials. The process involves a tunnel with a door at one end that opens to allow material entry and closes to maintain a controlled environment. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Material Feeding:
- The material to be dried is placed on a trolley or conveyor belt and fed into the tunnel. The entry door opens, allowing the material to enter, and then closes to maintain the drying environment.
- Air Circulation:
- Fans circulate hot air within the tunnel. The air can move in different patterns: counterflow, parallel flow, or combined flow, depending on the design and drying requirements.
- Heating:
- The tunnel uses a heat source, which could be traditional hot air or advanced techniques like microwave, RF, or infrared heating. The choice of heating technology depends on the material and desired drying speed.
- Drying Process:
- As the material moves through the tunnel on a conveyor or trolley, it is exposed to the hot air or heating source. The airflow and temperature settings ensure uniform drying.
- Material Discharge:
- Once the drying process is complete, the exit door opens, and the dried material is collected from the tunnel for further processing or packaging.
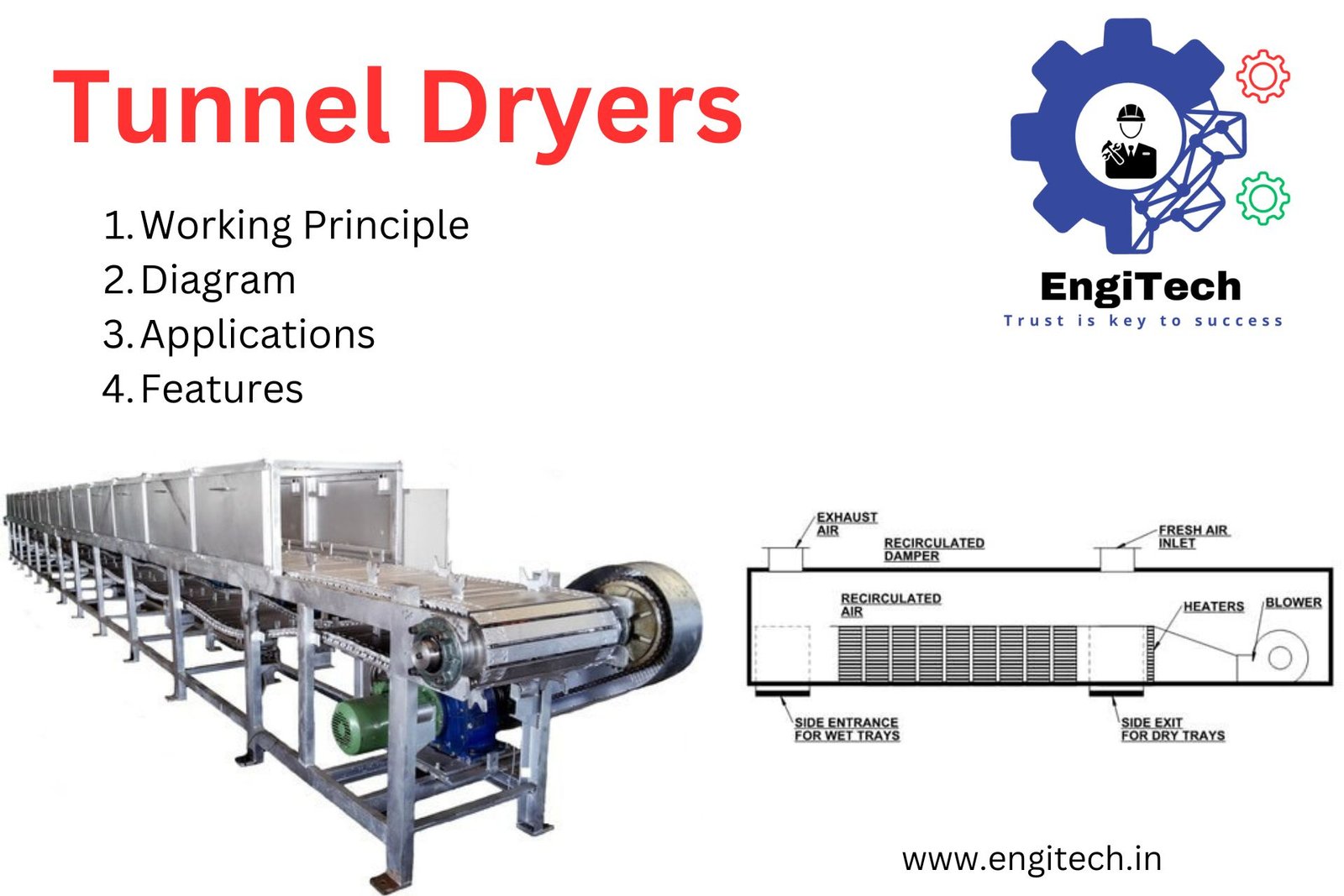
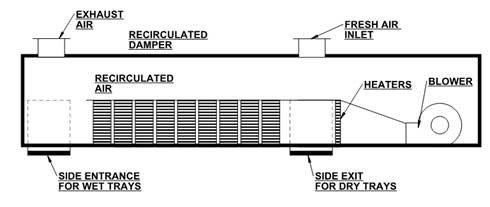
Tunnel Dryer Diagram
Below is a simplified diagram of a typical tunnel dryer:
- Entry Door: Allows material to enter the tunnel.
- Conveyor/Trolley: Moves the material through the tunnel.
- Heat Source: Provides the necessary heat for drying (can be hot air, microwave, RF, or infrared).
- Fans: Circulate the hot air within the tunnel.
- Air Inlet: Introduces hot air or other heating methods.
- Drying Zones: Sections within the tunnel where the drying process occurs.
- Exit Door: Allows the dried material to exit the tunnel.
- Control Panel: Sets temperature, conveyor speed, and other parameters.

Applications of Tunnel Dryers
Tunnel dryers are versatile and find applications across various industries due to their ability to handle different types of materials. Here are some primary uses:
- Food Processing:
- Drying fruits, vegetables, roots, eggs, and confectioneries.
- Preserving nutrients and extending shelf life.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Drying tablets, powders, and sterilizing containers.
- Ensuring stable moisture content and sterility.
- Textiles:
- Drying textile fabrics.
- Enhancing the quality and durability of fabrics.
- Packaging:
- Drying packaging materials like plastics, caps, spoons, vials, and containers.
- Ensuring packaging is free from moisture.
- Paper and Printing:
- Drying ink and paper.
- Ensuring the quality and longevity of printed materials.
- Ceramics:
- Drying molded ceramics.
- Preparing ceramics for further processing or use.
- Coating Lines:
- Drying coated materials.
- Ensuring even coating and drying.
- Food Industry:
- Drying fresh fruits, vegetables, and other food products.
- Maintaining flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
Features of Tunnel Dryers
- Insulated Inner Surface:
- Minimizes energy loss and maximizes energy efficiency.
- High-Quality Heat Exchanger:
- Ensures low air moisture and consistent heating.
- Enhanced Handling:
- Robust construction to endure moisture and varying conditions.
- Air Circulation System:
- Improves airflow and decreases drying time.
- Multiple Length and Width Ratios:
- Available in various sizes to suit different applications.
- Advanced Control Mechanisms:
- Touchscreen control panels for precise temperature and conveyor speed settings.
- Automated and Semi-Automated Options:
- Available in both automated and semi-automated configurations.
- Environmental Efficiency:
- Minimal environmental losses with optimized drying techniques.
- Uniform Drying:
- Ensures even drying of all materials fed into the tunnel.
- Modular Assembly:
- Facilitates easy transport and installation.
- Multiple Drying Zones:
- Allows for the drying of a wide range of materials under different conditions.
Conclusion
Tunnel dryers are indispensable tools in many industries due to their efficiency, versatility, and advanced drying capabilities. By understanding their working principles and applications, businesses can optimize their drying processes and improve product quality. As technology advances, tunnel dryers will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and sustainability.
For more in-depth articles and resources on industrial drying technologies and innovations, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and applications in the industry!