Ventilation Systems: A Comprehensive Guide for Knowledge Seekers, Students, and Working Professionals

In the modern world where air quality and environmental protection have become so important, ventilation systems stand at an important place in keeping one’s way of living nice and healthy. If you are a knowledge seeker, a student, or a working professional, an all-round understanding of ventilation systems can only help you. Ventilation System Basics 101
This guest blog will give you a most important overview of ventilation systems – types, purposes, uses, and how to design them.We hope it can solve any queries you may have and give expert insights on this vital issue.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Ventilation Systems
They are vital in different situations and places, such as residential,commercial or industrial settings. A ventilation system will work together with the surrounding environment to ensure that the air we breathe into our bodies remains clean, safe and comfortable for us. This short form email from EasyPost was extracted as an example, since it’s simply a minor project built on the most mundane kinds of mail. It presents us with more than just a single question:
There are any number of ads and half-hearted publicity stunts that could explore readers’ tons of ways on similar promotion strategies! Or they might deepen their understanding for such waste publications beyond passive curiosity. Reinstinitiation of historical information for this chapter. Add in new dates and confirm that all material beings are accurately recorded.
What Are Ventilation Systems?
Ventilation systems can be defined as mechanical or natural systems that accompany the exchange of air between indoor and outdoor environments. They perform several critical functions:
- Air Exchange: By replacing indoor air with outdoor air, oxygen levels are maintained and contaminants are removed.
- Temperature Control: Regulating indoor temperatures by removing excess heat or cold air.
- Humidity Control: Preventing moisture-related problems such as mould growth, for moisture in the air continues to provide an environment for them to live and thrive.
- Pollutant Removal: Taking indoor pollutants such as dust, smoke and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) out of circulation altogether.
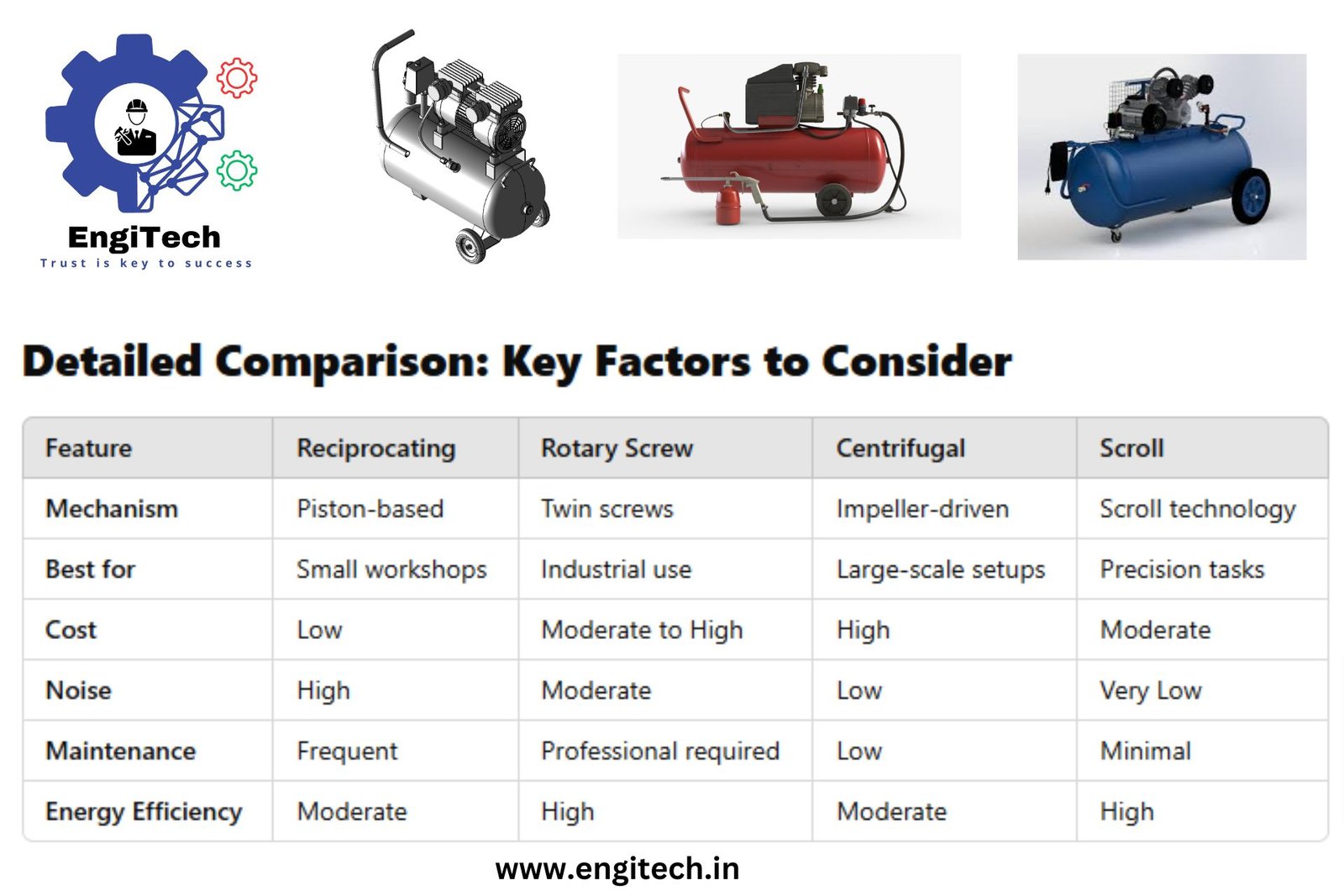
Types of Ventilation Systems
Ventilation systems are designed to meet specific requirements in a variety of forms.Ventilation is provided in the following main ways:
- Natural Ventilation Systems
- Mechanical Ventilation Systems
- Hybrid Ventilation Systems
Natural Ventilation Systems
Natural Ventilation SystemsNatural ventilation utilizes natural forces such as wind and temperature differences to move air in and out of buildings. This method is energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, making it a popular choice in sustainable building design.
Benefits of Natural Ventilation:
- Energy Efficiency: No mechanical parts mean less energy used. This is turning waste into output Value per unit of life.
- Low Maintenance: Fewer mechanical parts means lower maintenance demands.
- Environmental Impact: No energy-consuming equipment means a minimal carbon footprint.
Natural ventilation systems have their drawbacks, such as dependence on external weather conditions and the potential for maintaining consistent air quality to stanch.
Mechanical Ventilation Systems
Mechanical ventilation systems use fans, ducts, and filters to control air movement within a building. These systems offer more precise control over air quality, temperature, and humidity, making them suitable for environments with stringent air quality requirements.
Types of Mechanical Ventilation Systems:
- Exhaust Ventilation Systems: Remove indoor air to create negative pressure, drawing fresh air into the building.
- Supply Ventilation Systems: Introduce fresh air into the building, creating positive pressure and pushing stale air out.
- Balanced Ventilation Systems: Utilize both exhaust and supply fans to balance air exchange, maintaining consistent indoor air quality.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation Systems (HRVs): Exchange heat between incoming and outgoing air streams to improve energy efficiency.
Advantages of Mechanical Ventilation:
- Precise Control: Ability to regulate air quality, temperature, and humidity levels.
- Reliability: Consistent performance regardless of external weather conditions.
- Customizability: Systems can be tailored to meet specific requirements for different spaces.
Hybrid Ventilation Systems
Hybrid ventilation systems combine the benefits of natural and mechanical ventilation. These systems switch between natural and mechanical modes based on factors such as outdoor temperature and air quality, optimizing energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Key Features of Hybrid Ventilation:
- Energy Savings: Reduce energy consumption by utilizing natural ventilation when conditions are favorable.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to changing environmental conditions.
- Enhanced Comfort: Maintain optimal indoor air quality while minimizing energy usage.
Key Components of Ventilation Systems
Understanding the components of ventilation systems is essential for designing, implementing, and maintaining effective systems. The primary components include:
1. Air Handling Units (AHUs)
Air handling units are central to mechanical ventilation systems. They contain fans, filters, heat exchangers, and controls that regulate air movement, temperature, and humidity.
2. Ductwork
This is the network of pipes or channels which distribute air throughout a building. Proper design and installation of ductwork are vital to efficient air supply.
3. Fans
Fans drive air movement in mechanical ventilation systems. They are available in various types, such as axial fans, centrifugal fans and mixed-flow fans, each one suitable for different applications.
4. Filters
Filters remove particles, pollutants and contaminants from the air, ensuring that the air entering the building is clean and safe. High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are often used in environments requiring high air quality standards.
5. Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers transfer the heat between either the incoming or the outgoing air stream, thereby improving energy efficiency in ventilation systems.
6. Controls
Control systems are used to manage the operation of ventilation systems, allowing precise regulation of air quality, temperature and humidity. Advanced controls can be integrated into building management systems for automatic and efficient performance.
Applications of Ventilation Systems
Ventilation systems are employed in a wide variety of applications, each of which poses unique challenges and demands. The following sections present common applications.
1. Residential Ventilation
In a residential environment, ventilation systems are engineered to provide air quality and comfort. These systems are often also integrated with heating and cooling systems, ensuring year-round comfort.
Key Considerations for Residential Ventilation:
- Energy Efficiency: Homeowners most want energy-efficient systems to lower their utility bills.
- Air Quality: Systems must remove indoor pollutants efficiently, particularly in houses with people who have breathing difficulties.
- Noise Levels: Quiet operation is a must in the home
2. Commercial Ventilation
Commercial buildings, such as office buildings, retail areas and eateries — need ventilation systems that can accommodate both large numbers of people and varying indoor conditions.
Key Considerations for Commercial Ventilation:
- Occupant Comfort: Systems must maintain consistent temperatures and humidity levels across the whole complex thus ensuring that occupants are comfortable enough to work productively on a hot summer day.
- Indoor Air Quality: Controlling noxious fumes and odors, especially in high-traffic areas.
- Energy Management: Commercial ventilation systems are usually worn in with energy management systems to maximize performance and minimize the amount spent on running them all year.
3. Industrial Ventilation
Industrial operations such as factories and warehouses have special ventilation requirements due to the presence of hazardous materials, large open spaces, and heavy heat loading.
Key Considerations for Industrial Ventilation:
- Hazardous Material Control: Ventilation systems must be effective in removing fumes, dust and other harmful materials in order to protect the health of workers.
- Heat Management: Systems must handle both the heat produced by machinery and processes, making sure that workers are working in a safe atmosphere.
- Durability: Industrial ventilation systems must be rugged and hardy enough to stand up under the worst conditions of use.
4. Healthcare Ventilation
Hospitals and clinics call for high-grade ventilation systems to ensure that patients, staff and visitors have the best possible air.
Key Considerations for Healthcare Ventilation:
- Infection Control: Ventilation systems should stop the spread of airborne pathogens. A sterile environment must be ensured.
- Humidity Control: Maintaining appropriate humidity levels is crucial for patient comfort and preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms.
- Reliability: Health ventilation systems in hospitals must run 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. There needs always to be a backup system ready for emergencies.
Expert Insights on Designing Ventilation Systems
In the construction of an effective ventilation system, it is important to consider the particular use of the space and the usual situation, both of the experts. Here, engineers provide ideas:
1. Assessing Ventilation Needs
Start by making a comprehensive assessment of the space, taking into account seats available, types of activities being pursued and impurities present. This assessment will be your guide in choosing the right type of ventilation system and its components.
2. Balancing Air Exchange and Energy Efficiency
This is very important. Air movement at higher rates increases the quality of air but it conversely raises the amount of power you’re using. Heat recovery systems and sophisticated controls should be considered for overall and larger design.
3. Incorporating Smart Controls
Real-time status monitoring ensures the optimal status of the ventilation system under all kinds of conditions, provided that intelligent control systems are used. There are many instances in which such controls can be connected into a building management system, thus sharing control functions with improved energy efficiency and guaranteeing comfortable conditions for occupants.
4. Ensuring Proper Installation and Maintenance
No matter how good your ventilation system design is, there are a number of issues that can arise which may be illegal or against regulations. This could render the system inoperative. If piping does not match or is not properly sealed, the system will underachieve. Filters for dust should be replaced regularly and a fan should never sit still for long periods of time.
5. Compliance with Regulations and Standards
For ventilation equipment its installation must strictly meet with national and local requirements as well as ASHRAE’ guidelines. By following these standards People can be sure that they will satisfy performance and safety needs.
Addressing Common Queries About Ventilation Systems
1. What is the difference between natural and mechanical ventilation?
Natural ventilation relies on natural forces, like wind and thermal buoyancy, to move air, while mechanical ventilation uses fans and ducts to control air movement. Natural ventilation is energy-efficient but less reliable, while mechanical ventilation offers precise control over air quality.
2. How do ventilation systems impact energy consumption?
Ventilation systems can significantly impact energy consumption, especially if they require heating or cooling of incoming air. Systems with heat recovery features or smart controls can reduce energy usage by recycling heat and optimizing airflow based on real-time conditions.
3. Can ventilation systems improve indoor air quality?
Yes, ventilation systems are designed to improve indoor air quality by removing pollutants, regulating humidity, and introducing fresh air. Properly maintained systems effectively remove contaminants like dust, smoke, and volatile organic compounds.
4. What factors should be considered when selecting a ventilation system?
When selecting a ventilation system, consider the building’s size, occupancy, intended use, and local climate conditions. Additionally, assess energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
5. How often should ventilation systems be maintained?
Ventilation systems should be maintained regularly, with filter replacements and system inspections conducted according to manufacturer recommendations. Routine maintenance ensures the system operates efficiently and prolongs its lifespan.
Conclusion
Ventilation systems are indispensable in creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment, whether in public and domestic conditions or factories and hospitals. By understanding their types, components, applications and key considerations, you can make the most informed choices possible that promote good air quality, a comfortable environment for the occupant and efficient energy use.
This comprehensive guide has attempted to provide highly refined insights into ventilation systems, the most pressing problems that people have with their homeowners and businesses while offering expert advice on how best to design or modify system Whether you ’re someone who thirsts for knowledge, a college student or merely a working professional in this field, the information contained here will help you understand what is going on in ventilation systems and enable great precision of emphasis tailored to your personal requirements.
From EngiTech Team
Don ’t forget that a well-designed and properly maintained ventilation system not only makes breathing comfortable but also helps to improve productivity. In the future, as technology advances, things very likely will move on. This is especially true for ventilation systems,since they offer an unprecedented level of control and efficiency. Stay abreast with developments in the youngest child today could lead to your feeling more comfortable tomorrow Just make sure your ventilation system meets the demands of modern life and work. EngiTech is your trusted resource for all things engineering.