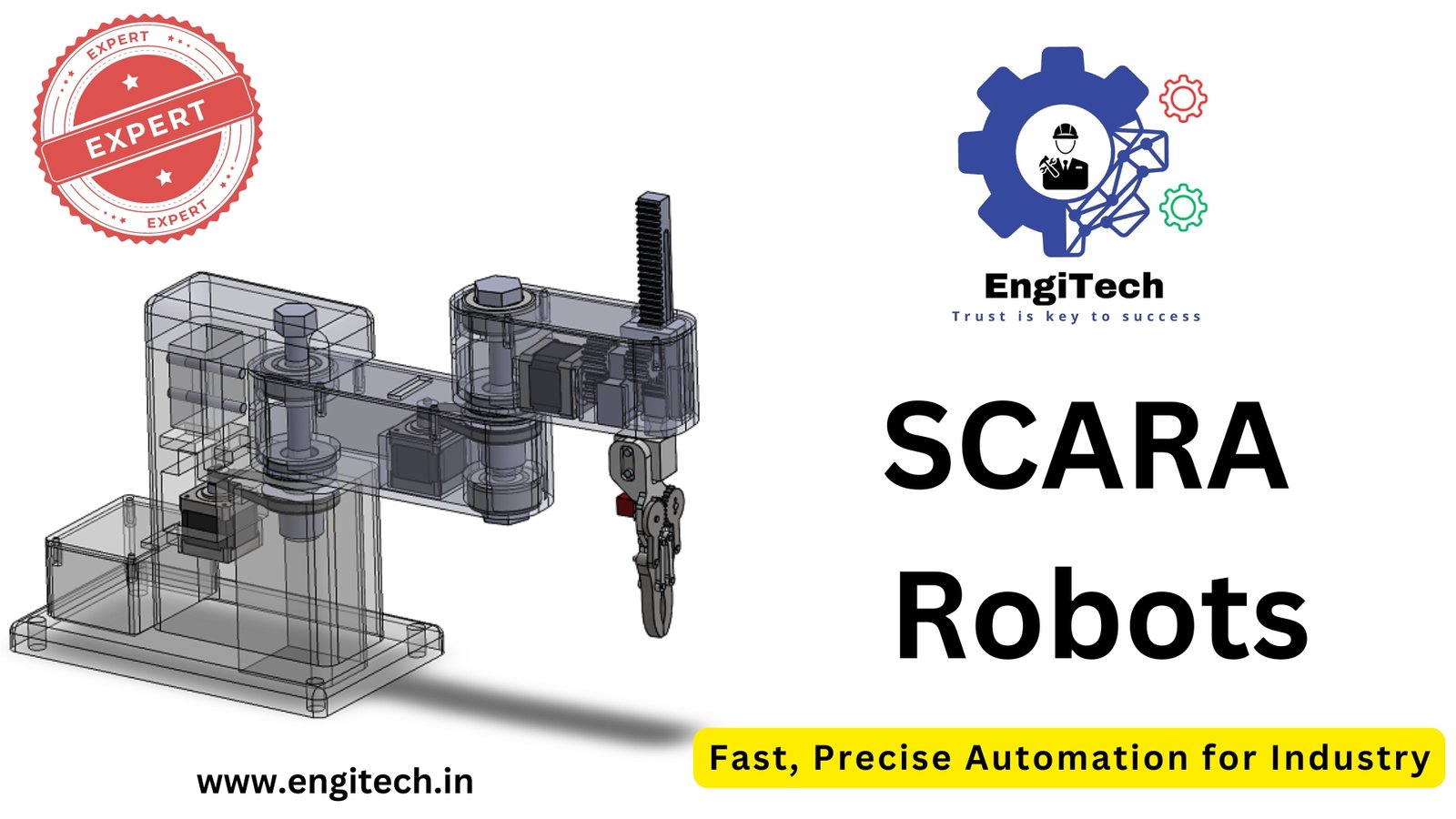
Smart Manufacturing, Explained: Why It Matters & What You Need to Know Now
Picture a factory in which machines are all connected, production lines self-correct as problems arise and human error is highly unlikely. Now it’s not just science fiction; it’s the reality of the power in smart manufacturing, a critical force in the age of Industry 4.0 that’s driving innovation and efficiency in the future.
The fourth industrial revolution brings together breakthrough technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics, and marrying this with manufacturing to creating work and production, that is not only smarter but also adapt giving real-time insights and predictions. With 16% of the world’s GDP generated in manufacturing, advancements in this sector can impact economies around the world.
If you’ve wondered just what smart manufacturing is, how it fits into Industry 4.0 and how it’s changing the world of manufacturing automation, you’re in the right place. This guide will answer all your questions, bust myths and give you practical perspective on this game-changing revolution in production.
Table of Contents
What Is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing: The utilization of advanced digital technologies including IoT, AI, big data analytics and robotics to enhance manufacturing. Unlike the conventional series of commands often used in traditional manufacturing processes, which can restrict adaptability and flexibility, smart manufacturing models are focused on connectivity, flexibility, and data-driven decisions.
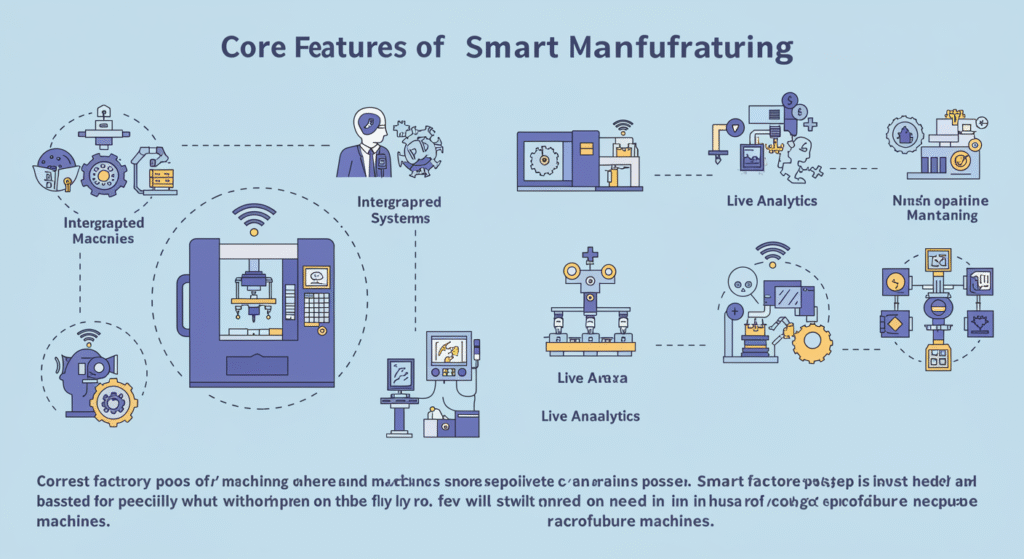
Core Features of Smart Manufacturing
- Integrated Systems: Vending machines, sensors and machines share live data across integrated networks.
- Live Analytics: AI and machine learning are applied to data in order to perfect operations on the fly, without the need for human input.
- Predictive Maintenance: Rather than waiting for machines to malfunction, systems predict when equipment will fail and save time and money.
personalized manufacturing Smart factories can produce stuff based on the need instead of needing people to go in and retool and laboriously reconfigure machines.
On a practical level, smart manufacturing holds tremendous promise for increased efficiency, reduced cost, and improved product quality.
What Is the Relationship Between Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also referred to as the 4th Industrial Revolution, is the collective term for the digitalisation of industries. Smart manufacturing is a central role in this, providing the technology foundation that supports Industry 4.0 efforts such as automation, data exchange, and smart factories.
The Evolution of Industry 4.0
Industry 1.0: Mechanization via water and steam power.
Industry 2.0: Mass production possible with electricity.
Industry 3.0: It was the era of computerisation and of automation with programmable logic.
Industry 4.0: The time of smart technologies such as the Internet of Things, machine learning, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence.
Fundamentally, Industry 4.0 is fueled by the tenets of connectivity, innovation, and intelligent decision-making —– all of which are underpinned by smart manufacturing techniques.
Why Smart Manufacturing Matters Now
Nowhere has it been more urgent to move ahead with smart manufacturing than in industry. Here’s why this transformation is a good thing but also, quite simply, a necessity.
Rising Market Demand
Consumers are demanding nothing short of the very best—high quality, tailored products that are delivered fast. The ‘smart’ factories of today cut production times without compromising quality, even for the most discerning of markets.
Workforce Shortages
A worldwide shortage of labor — especially for skilled workers — is the latest headache for the manufacturing sector. Smart manufacturing lets humans offload the dirty, dull, and dangerous work and focus on where they can add value.
Sustainability Goals
I increased the legal society importance because of the need now for sustainable building and pressure from society and more scarce rules. Smart factories can also use sensors to track energy much more closely, waste less and minimize carbon footprints via software-driven efficiency.
For instance, large corporations, such as Siemens, are using digital twins that enable manufacturers to test and optimize production configurations online, slashing waste dramatically.
Manufacturing Automation in Smart Manufacturing
What Is Manufacturing Automation?
Manufacturing automation is the use of control systems and information technologies to reduce the need for human work in the production of goods. Automation, when combined with intelligent systems, creates a new level of innovation.
Traditional Automation vs. Smart Automation
| Traditional Automation | Smart Automation |
|---|---|
| Operates based on pre-programmed rules | Adapts and learns from real-time data and feedback |
| Functions in isolation from other systems | Seamlessly integrates and communicates with other platforms |
| Offers limited flexibility and fixed capabilities | Highly configurable, scalable, and adaptable to change |
| Requires manual updates and reprogramming | Continuously evolves with minimal human intervention |
| Designed for repetitive, rule-based tasks | Handles complex, dynamic, and context-aware operations |
Smart automation allows manufacturers to easily and quickly reconfigure production lines for new products or expand operations without extensive retooling.
Common Myths About Smart Manufacturing
Myth #1: It’s Only for Large Corporations The truth:.
On the contrary, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) have been increasingly embracing smart manufacturing technologies. Cloud system options are now both cost effective and obtainable for companies across-the-board.
Myth #2: Jobs Will Be Automated Away
So yes, automation is changing the workforce, but the market for workers who are good at making and managing that system — in robotics, in data analytics, in system management — is booming. Instead of taking away jobs, they say, smart manufacturing comes with an opportunity for workers to reskill.
Myth #3: It’s Too Expensive
While there is often an upfront cost associated with the use of these technologies, such technologies invariably end up paying for themselves in a relatively short amont of time, due to savings in cost, efficiencies and minimizing downtime. For most businesses, the ROI can be achieved in a few years.
FAQs About Smart Manufacturing
What Are the Key Advantages of Smart Manufacturing?
- Faster production cycles.
- Real-time quality monitoring.
- Lower operational costs.
- Fewer workers harming themselves with automation.
How Are IoT Devices Used in Smart Factories?
- IoT equipment mesh machines, sensors, and systems, so that data can flow uninterrupted and predictive analysis can take place. It keeps everything running smoothly and prevents downtime.
Can Smart Manufacturing Reduce Downtime?
- Yes! Predictive maintenance detects potential tool failure before it happens, reducing downtime and the risk of a production shutdown.
Smart Manufacturing: How to Get Started
- Evaluate Current Systems: Begin by auditing current workflows, machines and data systems. Spot bottlenecks, areas for improvement.
- Invest in Scalable Technologies: Invest in modular systems that can scale with your production requirements. The majority of businesses should start with a cloud-based platform.
- Train Your Workforce: Empower your team with skills to maintain and sustain the next generation system. Workforce adaption relies heavily on upskilling programs.
- Partner with Industry Experts: Work together with technology vendors who focus on smart manufacturing offerings. Organizations like Bosch or Siemens offer tested tools and approaches specialized for various industries.
Use Case: Smart Manufacturing Success Story
Case Study:
One of the world’s largest automotive companies saw production lead times decrease by 30% thanks to smart manufacturing. They incorporated IoT sensors and AI-based quality checks, allowing them to make accurate, real-time modifications to their assembly lines.
And this change of process generated a higher quality product, lower costs, quicker customer deliveries, and fit all the necessary environmental restraints.
The Future of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is not just a technological progression, but a rethinking of the way production operates. By capitalizing on automation, data and connection, manufacturers are strategically positioning to move forward in a rapidly changing world economy.
There is no boundary of what innovation, efficiency and sustainability could be realized today for those investing on these technologies. Whether it’s using resource conserving methods of production, individualized product creation, or just purely improved conditions for workers, smart manufacturing is the spearhead of the industry of the future.
Final Thoughts
Today, smart manufacturing is what will keep you competitive in an Industry 4.0 world. Its seamless integration of connectivity, automation, and data intelligence is shaping the future of manufacturing for next generation businesses.
Curious how your business could keep up with this metamorphosis? Get started on a small scale – Try out scalable technologies, enhance system performance and invest in workforce training. You will start to see the full potential of the 4th Industrial Revolution ready to transform your business for the better.
Ready to move on to the next step? Find out how smart manufacturing applications can protect and future-proof your business. Get in touch today and put us to work in making your factory succeed.