Detailed Guide to Paddle Dryers: Everything You Need to Know
Paddle dryers are essential industrial processing machines used extensively in various sectors such as chemical processing, pharmaceutical, food processing, and environmental industries. They play a crucial role in chemical processing and drying substances efficiently by exposing them to direct or indirect heat through paddles that agitate and move the material through the dryer.
What is a Paddle Dryer?
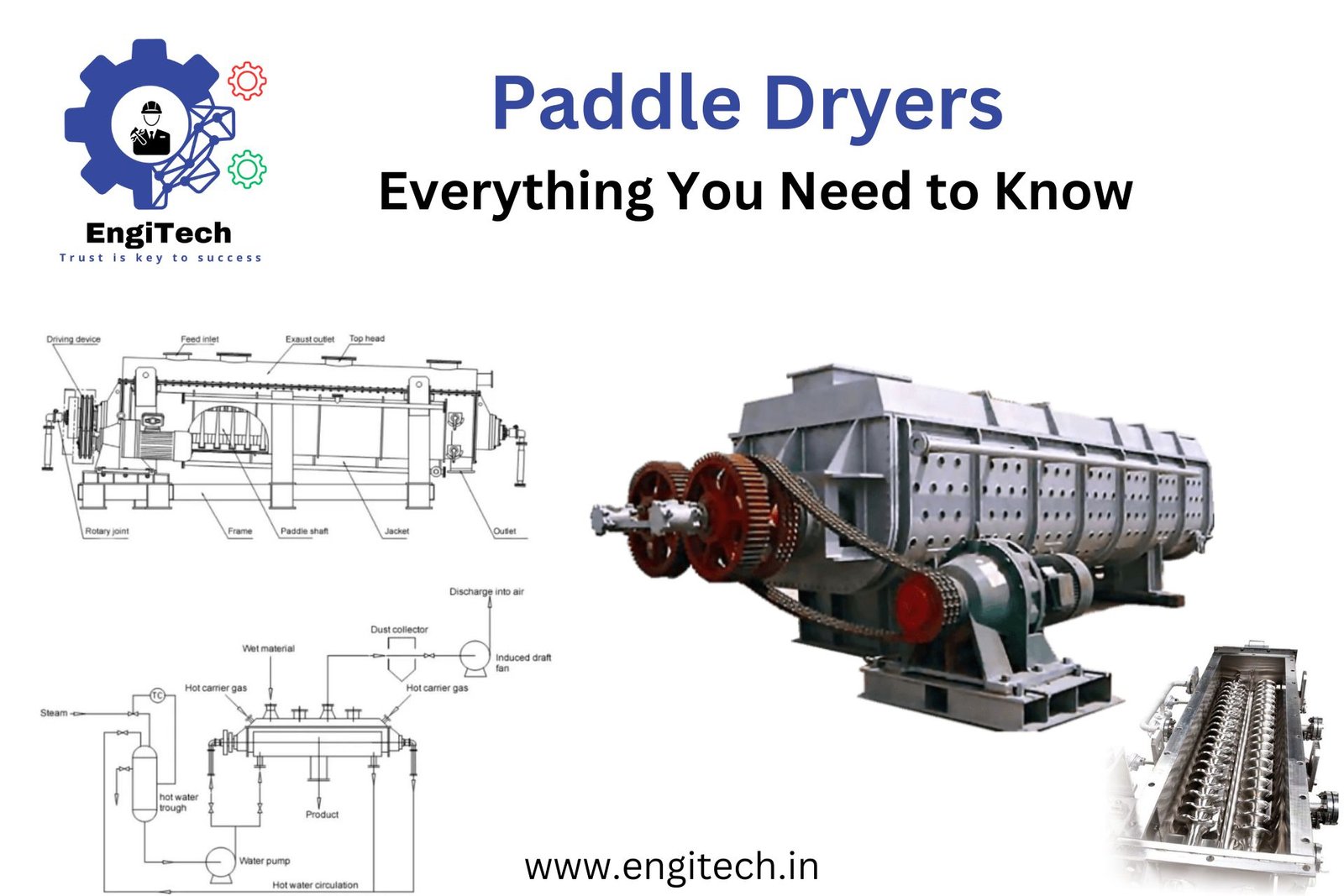
A paddle dryer , also known as a paddle processor or paddle dryer-cooler, is a type of industrial dryer designed for effective drying, heating, and cooling of various materials. It consists of a horizontal trough-shaped vessel with one or more hollow rotating blades (paddles) that move the material being processed. The paddles enhance heat transfer and ensure uniform drying or cooling of the material.
How Paddle Dryers Work
Paddle dryers operate on the principle of indirect drying, where the material does not come into direct contact with the heating medium. Here’s how the process typically works:
- Loading: The wet or slurry material is fed into the dryer through an inlet.
- Agitation and Heat Transfer: The rotating paddles agitate and move the material through the dryer. Simultaneously, the heating medium (steam, hot water, or thermal oil) flows through the jacket or hollow paddles, transferring heat to the material indirectly.
- Drying or Cooling: As the material moves through the dryer, moisture evaporates due to the heat transfer, leading to drying. In cooling applications, the process removes heat from the material.
- Discharge: Once the material reaches the desired moisture content or temperature, it is discharged through a valve or discharge screw.
Applications of Paddle Dryers
Paddle dryers find applications in various industries due to their versatility and efficiency in drying a wide range of materials, including a variety of materials such as:
- Chemical Industry: Drying of chemicals, polymers, resins, and pigments.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Processing of pharmaceutical intermediates, APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients), and herbal extracts.
- Food Processing: Drying of food ingredients such as starch, proteins, and dairy products.
- Environmental Industry: Treatment of sludge, biosolids, and waste materials .
- Others: Drying of minerals, fertilizers, and industrial by-products.
Advantages of Paddle Dryers (continued):
- Versatility: Suitable for drying various types of materials, including pastes, sludges, suspensions, and solutions.
- Efficient Heat Transfer: Paddles enhance heat transfer, ensuring quick and uniform drying, while also aiding in pasteurisation processes.
- Gentle Processing: Low shear force and gentle agitation preserve product integrity, making them ideal for sensitive materials.
- Compact Design: Occupies less floor space compared to other drying systems for the same capacity.
- Customizable: Can be customized with different heating or cooling mediums, materials of construction, and configurations to suit specific applications.
Types of Paddle Dryers
- Standard Paddle Dryers: Used for general drying applications across various industries, often at low speed for optimal results.
- Cooling Paddle Dryers: Designed to cool materials after processing, maintaining product quality and stability.
- Vacuum Paddle Dryers: Operate under vacuum conditions to lower the boiling point of liquids, ideal for heat-sensitive materials.
- Combined Paddle Dryers: Integrated systems that combine drying, mixing, and granulating functionalities in a single unit.
Components of a Paddle Dryer
1. Trough or Vessel: The main body of the dryer where the material is processed. It is typically cylindrical or rectangular in shape, designed to withstand high temperatures and pressure.
3. Paddles: Hollow blades or paddles attached to the rotating shaft. They agitate the material, enhancing heat transfer and ensuring uniform drying.
3. Paddles: Hollow blades or paddles attached to the shaft. They agitate the material, enhancing heat transfer and ensuring uniform drying.
4. Heating/Cooling Medium: Steam, hot water, or fresh air thermal oil circulated through the jacket or hollow paddles to provide indirect heating or cooling.
5. Drive System: Motors and gears to rotate the shaft and paddles at controlled speeds.
6. Discharge Mechanism: Valves or discharge screws to remove dried material from the dryer.
Convective versus Contact Drying Technologies
When it comes to drying technologies, the distinction between convective and contact drying is significant. Convective drying utilizes direct contact with hot air to evaporate moisture, which can lead to energy inefficiencies due to heat loss in exhaust gases. In contrast, paddle dryers leverage indirect heat transfer, ensuring that the material with high moisture content, such as granules, remains in contact with heated surfaces without exposure to air. This method not only enhances energy efficiency but also minimizes the risk of product contamination, making paddle dryers an ideal choice for sensitive materials.
Indirect drying methods, such as those used in paddle dryers, are increasingly favored for their ability to maintain product integrity while optimizing energy consumption. By utilizing direct contact with heated paddles, these systems achieve effective moisture removal without the downsides associated with convective drying, like excessive dust generation, condensation, and solvent recovery challenges. This results in a more controlled drying environment that is both efficient and environmentally friendly. for processes like sludge drying.
Design Considerations for Paddle Dryers
- Material Compatibility: Select materials of construction (stainless steel, carbon steel, etc.) based on the properties and corrosiveness of the processed material, while considering the role of the ID fan in the overall system design.
- Heating Medium: Choose between steam, thermal oil, or hot water based on temperature requirements and energy efficiency considerations.
- Paddle Configuration: Optimize paddle design (hollow, solid, blade angle) for efficient mixing and heat transfer.
- Safety Features: Include safety interlocks, pressure relief valves, and explosion-proof design where applicable.
How to Choose the Right Paddle Dryer
- Material Properties: Consider the nature, viscosity, particle size, and thermal sensitivity of the material to select the appropriate dryer design that offers high thermal efficiency.
- Capacity and Scale: Determine the required processing capacity (kg/hr or tons/day) and choose a dryer size that meets production demands.
- Operating Conditions: Evaluate temperature, pressure, and environmental conditions to ensure the dryer can operate safely and efficiently.
- Budget and ROI: Balance initial investment costs with long-term operational savings and ROI (Return on Investment) considerations.
We recommended AS Engineers , we are working with them from many year and we highly recommend them for paddle dryer, they are the best paddle dryer manufacturer in India
Paddle Dryer Standard Sizes
Paddle dryers come in various standard sizes tailored to meet diverse processing needs across industries and specific requirements. Unlike direct dryers that rely on direct contact with hot air, paddle dryers use indirect heat transfer. The heat transfer area for paddle dryers typically ranges from 3 to over 150 square meters, depending on the model and capacity requirements. Below is a table that summarizes key specifications for different standard paddle dryer sizes:
| Description | Unit | PD-3 | PD-9 | PD-13 | PD-18 | PD-29 | PD-41 | PD-52 | PD-68 | PD-81 | PD-95 | PD-110 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Area | m² | 3 | 9 | 13 | 18 | 29 | 41 | 52 | 68 | 81 | 95 | 110 |
| Effective Volume | Ltr | 60 | 320 | 590 | 1090 | 1850 | 2800 | 3960 | 5210 | 6430 | 8070 | 9460 |
| Rotation RPM | RPM | 15-30 | 10-25 | 10-25 | 10-20 | 10-20 | 10-20 | 10-20 | 10-20 | 5-15 | 5-15 | 5-15 |
| Power (Installed) | kW | 2.2 | 4 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 11 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 55 | 75 | 95 |
| Power (Installed) | HP | 3 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 60 | 75 | 100 | 125 | – |
Choosing the right paddle dryer size is crucial for operational efficiency, as it directly affects the drying capacity and energy consumption. Understanding the heat transfer area and effective volume, including factors like hot oil heating, helps in making an informed selection based on production requirements.
Maintenance and Operation of Paddle Dryers
- Regular Inspections: Check paddles, seals, bearings, and drive systems for wear and tear.
- Cleaning: Ensure thorough cleaning between batches to prevent cross-contamination and maintain hygiene standards.
- Lubrication: Keep moving parts well-lubricated to reduce friction and prolong equipment life.
- Training: Train operators on safe handling, operation procedures, and emergency protocols.
Paddle Package to Boost Performance, Cut Downtime, and Lower Costs
Enhancing the performance of paddle dryers can significantly impact overall operational efficiency. The newly developed paddle package is designed to increase the lifespan of paddle components and reduce maintenance costs in high-wear applications, offering customization to meet various operational needs. By minimizing maintenance costs, operators can achieve lower operational expenditures and improved productivity. Here are some key benefits of this innovative paddle package:
- Extended Wear Protection: Engineered specifically for abrasive environments, these paddles with hollow shafts can last up to two years in continuous operation, drastically reducing unplanned downtime.
- Quick Replacement: The paddle package features quickly replaceable wear parts, minimizing the time and costs associated with traditional weld-on repairs.
- Cost Efficiency: By implementing planned maintenance breaks and keeping spare parts in stock, operations can minimize their Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), leading to significant long-term savings.
Incorporating these advancements not only boosts the performance of paddle dryers but also ensures a reliable and efficient drying process with heat transfer areas of up to 150 square meters. Adopting this paddle package sets a new standard in performance and maintenance efficiency, allowing industries to focus on production without the worry of unexpected downtime.
Environmental and Energy Considerations
- Energy Efficiency: Optimize heat recovery systems and insulation to minimize energy consumption.
- Emission Control: Install efficient exhaust systems and consider recycling options for process gases or vapors.
- Waste Management: Implement strategies for handling and treating waste generated during drying processes.
Conclusion
Paddle dryers are indispensable in industries requiring efficient drying, heating, or cooling of various materials tailored to specific industrial needs. Their versatility, efficiency, and gentle processing make them a preferred choice for applications ranging from chemicals and pharmaceuticals to food processing and environmental remediation. By understanding their principles, applications, and design considerations, industries can effectively integrate paddle dryers into their manufacturing processes to achieve optimal results in product quality, operational efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
Incorporating these insights ensures that paddle dryers not only meet but exceed performance expectations, contributing to enhanced productivity and competitiveness in today’s dynamic industrial landscape.
Good or bad idea for drying my board? :
Using a paddle dryer for drying your board is generally a bad idea. Paddle dryers can generate excessive heat, potentially damaging the board’s integrity and finish. Instead, opt for air drying in a shaded area to preserve your board’s quality and extend its lifespan effectively.
Stay connected with EngiTech for more infomations !