Label Cutting Machine – The Ultimate Guide to Efficient Label Production

Have you ever wondered how product labels maintain such precise shapes and crisp edges, even when mass-produced by the thousands? The answer often lies in a specialized piece of equipment known as the label cutting machine. If you operate in the printing, packaging, textile, or manufacturing sector, chances are you’ve already heard about these machines—or you’re on the hunt for one that can refine your workflow. Whether you’re looking to boost productivity, enhance label quality, or reduce manual labor, the label cutting machine is a game-changer.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of label cutting machines, exploring their evolution, how they work, key features to consider, and much more. By the time you finish reading, you’ll understand exactly why these machines are so indispensable and how to make the most of them in your operation. Above all, this resource aims to help you identify the best possible label cutting machine for your unique needs—because when it comes to your business, efficiency and precision should always be top priorities.
Table of Contents
1. The Evolution of Label Cutting Machines
Before label cutting machines became a staple in modern production lines, labels were typically cut by hand or with manual die cutters—a time-consuming and often imprecise process. As mass production soared during the Industrial Revolution, the need for faster, more accurate methods increased dramatically. Eventually, rudimentary mechanical cutters entered the market, offering a welcome leap forward.
- Early Mechanical Cutters: Simple mechanical cutters used crank mechanisms and rudimentary dies to slice labels from sheets of paper or rolls of textile material. While they were faster than manual labor, these machines were still relatively slow by today’s standards.
- Rise of Automation: The arrival of automated machinery in the late 20th century signaled a turning point. With programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and more advanced motors, label cutting machines became both faster and more versatile.
- Modern Digital Advancements: Today, the label cutting machine has embraced digital technology. Advanced machines feature computerized controls that enable precise calibration, real-time data tracking, and integration with design software. This allows for intricate custom cuts and seamless production workflows.
As consumer demand grows for customized, short-run products, the importance of efficient label cutting has only intensified. In the packaging and branding landscape—where distinctive labeling can make all the difference—staying abreast of technological innovations in label cutting is essential.
2. Understanding the Different Types of Label Cutting Machines
Not all label cutting machines are created equal. While the unifying goal is always precision cutting, the methods and technologies vary widely depending on industry needs.
2.1 Rotary Die-Cutting Machines
Rotary die-cutting machines use cylindrical dies—sharp metal edges arranged in a pattern—to slice through the label material. Often employed in high-speed production lines, these machines are perfect for large runs of uniform labels.
- Advantages:
- High speed production
- Consistent cut quality
- Ideal for large volumes
- Considerations:
- Custom dies can be expensive
- Less flexibility for frequent design changes
2.2 Flatbed Die-Cutting Machines
Flatbed die-cutting machines rely on a flat cutting die that presses down onto a sheet of material. Although not quite as rapid as rotary machines, flatbeds are often favored for more intricate shapes and diverse material types.
- Advantages:
- Highly accurate cuts
- Better for short runs and varied designs
- Suitable for thicker materials
- Considerations:
- Slower speed than rotary systems
- Dies must be changed manually
2.3 Laser Cutting Machines
Leveraging a high-intensity laser beam, laser cutting machines excel at extremely detailed and complex cuts. There’s no need for physical dies, meaning less downtime and more flexibility for custom shapes.
- Advantages:
- Extremely precise, intricate designs
- Rapid switching between different label designs
- Minimal material waste
- Considerations:
- Higher initial cost
- May require specialized ventilation or safety measures
2.4 Digital Plotter Cutting Machines
Plotter-style cutting machines use a small blade or cutting tool guided by a computer-controlled system. These are especially popular among businesses that require frequent design changes or one-off samples.
- Advantages:
- Ideal for prototyping and short runs
- Quick design changeover
- No dies required
- Considerations:
- Slower than rotary or laser systems for large-scale operations
- Blades can wear out and need regular replacement
2.5 Hot Knife / Thermal Cutting Machines
For fabric or synthetic labels, hot knife machines melt through the material to form a clean, sealed edge that resists fraying.
- Advantages:
- Perfect for woven labels and textiles
- Sealed edges prevent unraveling
- Lower cost compared to laser cutting
- Considerations:
- May not be suitable for thick or non-synthetic materials
- Possible discoloration for certain fabrics
Understanding these diverse machine types is the first step toward finding the perfect label cutting machine solution. Each offers specific advantages, so the ideal choice depends on the nature of your business, material requirements, and production goals.
3. Key Benefits of Using a Label Cutting Machine
Investing in a label cutting machine can revolutionize your production line, boosting everything from output speeds to label consistency. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
- Enhanced Precision
Manual cutting methods often result in slight variances—even the most skilled worker can’t consistently match machine-level accuracy. Automated label cutting ensures every piece meets exact specifications, vital for brand recognition and regulatory compliance. - Higher Throughput
A well-configured label cutting machine can process tens of thousands of labels per hour, drastically reducing production time compared to manual methods. - Lower Labor Costs
While any machine requires some level of supervision and maintenance, the labor required is far less intensive than cutting labels manually. This frees up employees for higher-value tasks like quality control and product development. - Versatility
From paper and plastic to fabric and foil, modern machines can handle a broad range of materials. This flexibility is a major advantage for businesses that offer multiple label types or frequently update designs. - Reduced Waste
Precise cuts mean less material waste, which translates into cost savings. Over time, even minor waste reduction can significantly impact a business’s bottom line. - Consistency in Branding
Cohesion in label design is critical. A label cutting machine guarantees uniform appearance across all labels, reinforcing brand credibility and consumer trust.
By adopting a specialized label cutting machine, you position your company to produce labels more quickly, precisely, and consistently, ensuring that you remain competitive in an ever-evolving market.
4. Materials & Industry Applications
Label cutting machines are integral to various industries, from apparel to pharmaceuticals. Understanding the range of materials these machines can handle provides insight into their broad applicability.
4.1 Common Materials
- Paper and Cardstock: Used extensively in food, beverage, and consumer goods packaging.
- Plastic Films (PET, PP, PVC): Common in durable product labels and shrink sleeves.
- Fabric and Woven Labels: Often seen in clothing, home textiles, and footwear.
- Foil and Metalized Materials: Adds a premium look, commonly seen in luxury packaging.
- Adhesive Sheets: Includes vinyl and special pressure-sensitive adhesives for custom stickers.
4.2 Industry Applications
- Food and Beverage: High-volume production with strict labeling regulations.
- Pharmaceutical and Healthcare: Labels often require tamper-evident features and must adhere to stringent safety guidelines.
- Textile and Apparel: Woven labels, care instruction labels, and brand tags that must be cut to perfection without fraying.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Durable, heat-resistant labels for components and parts.
- Electronics: ESD-safe (Electrostatic Discharge) labels or highly detailed caution labels.
One of the greatest strengths of a label cutting machine lies in its adaptability. Whether you’re processing delicate fabric labels for designer apparel or robust plastic labels for chemical drums, the right cutting machine can meet virtually any industrial labeling requirement.
5. How Label Cutting Machines Work
The specific mechanics vary by machine type—rotary die, flatbed, laser, etc.—but the underlying process usually involves feeding label material into a cutting assembly that uses either physical or digital tooling. Below is a general overview:
- Material Feeding
The label material, often in roll or sheet form, is loaded onto the machine’s feeding mechanism. High-capacity machines typically include tension control systems to prevent wrinkling or misalignment. - Cutting Mechanism
- Physical Dies: A die is pressed against the material, following a preset design.
- Laser/Knife Blades: A laser beam or cutting tool moves along a programmed path to slice the material into shape.
- Waste Removal
After the cut is made, excess material (known as the “matrix”) is automatically stripped or peeled away, leaving behind neat, individual labels. - Inspection & Sorting
Advanced systems may include optical scanners or sensors that check for defects. The completed labels are then either stacked, rolled, or conveyed for further processes like printing or packaging. - Data and Control
Modern machines come equipped with user-friendly interfaces and software that allow real-time adjustments. Operators can change speeds, cut shapes, or material thickness settings with a few taps, optimizing production efficiency.
This automation not only delivers speed and precision but also significantly lowers the margin of error. Data-driven feedback loops let you monitor output and adjust processes accordingly, ensuring you always operate at peak productivity.
6. Features to Look for in a Quality Label Cutting Machine
Not all machines will suit every application. When choosing your label cutting machine, keep these features in mind to ensure you’re investing wisely:
- Cutting Precision and Speed
Look for machines with advanced servo motors or laser modules that can handle intricate designs at high speeds without sacrificing accuracy. - Versatile Material Handling
A versatile machine should be able to handle a variety of materials, including paper, fabric, and plastic films. This is especially vital if your product lines change frequently. - Automated Adjustments
Machines that automatically adjust cutting depth or tension control can reduce downtime and operator error. This feature is particularly useful for businesses that run different label sizes or materials back-to-back. - User-Friendly Controls
An intuitive interface can significantly reduce the learning curve. Touchscreen panels, clear labeling, and robust help menus can make day-to-day operations more efficient. - Safety Features
High-speed lasers or blades present inherent risks. Look for robust safety features like protective enclosures, emergency stop buttons, and safety interlocks. - Integration Capability
Modern production lines often involve multiple processes—printing, cutting, laminating, packaging, etc. A label cutting machine that seamlessly integrates with existing hardware and software will streamline operations. - Maintenance Accessibility
Quick-access panels, replaceable parts, and easy-to-reach lubrication points can drastically cut maintenance times and costs. - Warranty and Support
Reputable manufacturers usually back their machines with comprehensive warranties and customer support. This is invaluable if issues arise or you need training.
By carefully evaluating these features, you can confidently select the best machine for your requirements—one that enhances your workflow instead of hindering it.
7. Best Practices for Maintaining Your Label Cutting Machine
Like any piece of equipment, a label cutting machine requires consistent maintenance to deliver optimal performance. Proper upkeep not only extends the machine’s lifespan but also reduces costly downtime.
- Regular Cleaning
Residual adhesives, tiny paper fibers, and dust can accumulate quickly. Wipe down the feeding mechanism and cutting assembly at least once per shift using manufacturer-approved cleaning solutions. - Lubrication Schedule
Bearings, gears, and other moving parts need lubrication as specified in the machine’s manual. Over-lubrication can be just as damaging as under-lubrication, so always follow recommended guidelines. - Blade/Die Inspection
If you use physical dies or cutting blades, inspect them regularly for wear and tear. Dull or damaged blades will compromise cut accuracy and may damage materials. - Calibration Checks
Laser-based systems or machines with servo motors should be routinely calibrated to maintain precision. Small calibration errors can escalate quickly and jeopardize product quality. - Software Updates
For digitally controlled machines, stay on top of firmware or software updates offered by the manufacturer. These updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes. - Proper Storage
If you keep extra dies, blades, or laser modules, store them in a clean, moisture-free environment. Rust or contamination can cause irreparable damage. - Scheduled Professional Service
Even with vigilant in-house maintenance, it’s wise to schedule professional servicing at least once a year. Experts can catch potential issues before they become major problems.
Adhering to these best practices ensures that your label cutting machine remains a reliable backbone of your production process—producing consistent, high-quality labels around the clock.
8. Common Troubleshooting Tips
Despite robust engineering, even the best machines can face occasional hiccups. Here are some quick troubleshooting measures to help you identify and resolve common issues:
- Material Slippage
- Possible Causes: Excessive tension, worn-out rollers, or incorrect feeding alignment.
- Quick Fix: Adjust tension settings, clean or replace rollers, and ensure material is loaded squarely.
- Inconsistent Cuts
- Possible Causes: Dull blades, misaligned dies, or software calibration errors.
- Quick Fix: Inspect cutting tools for wear, recalibrate your machine, and verify that the design file aligns properly.
- Machine Overheating
- Possible Causes: Continuous high-speed operation without adequate cooling.
- Quick Fix: Pause the machine to cool down, clean ventilation fans, and check for blocked air pathways.
- Label Adhesive Build-Up
- Possible Causes: Sticky adhesives accumulating on blades or machine parts.
- Quick Fix: Clean all components with a solvent recommended by the manufacturer. Consider using non-stick coatings or Teflon-based solutions on cutting surfaces.
- Error Codes on Digital Displays
- Possible Causes: Software glitches, sensor malfunctions, or hardware faults.
- Quick Fix: Consult the machine’s user manual or contact technical support for the specific error code. Perform a system reset if instructed.
By systematically diagnosing issues using these guidelines, you can rapidly get your label cutting machine back on track. If problems persist, don’t hesitate to reach out to the manufacturer or a qualified technician.
9. Integrating Label Cutting Machines With Production Lines
To fully capitalize on the efficiency gains offered by a label cutting machine, seamless integration into your existing production line is crucial. This often involves ensuring that the machine’s output matches the speed and format of subsequent processes—whether that’s label inspection, lamination, or final packaging.
9.1 Workflow Optimization
- Inline vs. Offline Setup:
- Inline: The cutting machine is placed directly after a printing press or another converting system, allowing labels to flow continuously from one stage to the next.
- Offline: The label cutting machine operates as a standalone unit. While it may require extra handling, it offers more flexibility for businesses that juggle diverse materials.
- Synchronization:
Coordinating speed controls between machines prevents material bottlenecks or excessive downtime. Modern machines often support protocols like OPC-UA for industrial automation communication.
9.2 Software and Data Integration
- Design Software Compatibility:
If you use Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW for label design, ensure the cutting machine’s software can interpret vector files accurately. - Real-Time Monitoring:
Integrating the machine with your Manufacturing Execution System (MES) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software provides insights into production rates, material usage, and error logs.
9.3 Safety and Compliance
- Regulatory Requirements:
Industries like food and pharmaceuticals might require specialized label construction for safety or legal compliance. Verify that your system meets these regulations. - Operator Training:
Make sure all staff who interact with the label cutting machine understand not only how to operate it, but also how it connects to adjacent equipment. Misalignment or speed mismatches can cause jams and wasted materials.
With thorough planning and the right technology, integrating a label cutting machine can feel almost seamless. The end result? A faster, more reliable, and more profitable labeling operation.
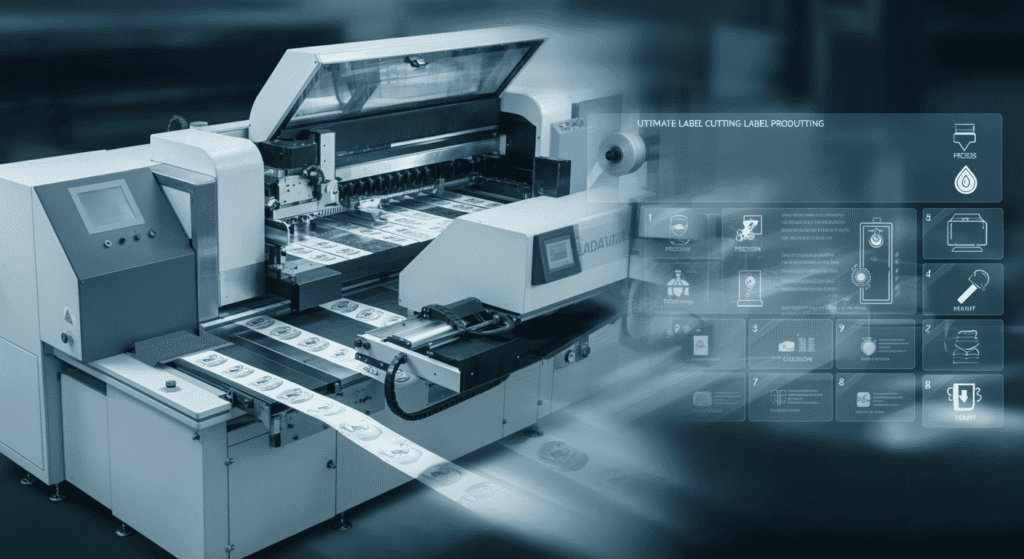

10. The Future of Label Cutting Technology
Label cutting is hardly stagnant. As global consumer trends shift toward more personalized products and sustainable materials, label cutting machine technologies are evolving to keep pace.
- Smart Automation
Machines are likely to become even more autonomous, relying on sensors and AI algorithms to self-adjust cutting depth, track material usage, and detect potential flaws before they escalate. - Eco-Friendly Solutions
Environmentally conscious brands demand lower energy consumption and waste output. Future label cutting machines will likely place a premium on efficiency—both operationally and in material usage. - On-Demand Customization
With the rise of personalized packaging and micro-targeted marketing campaigns, short-run label printing and cutting will continue to grow in importance. Expect more compact, high-speed digital cutters optimized for quick design turnarounds. - Advanced Laser and Hybrid Systems
Hybrid technologies that combine laser cutting with other finishing techniques (like embossing or foiling) could further streamline label production. This one-stop approach can eliminate the need for multiple machines. - Augmented Reality (AR) in Training and Maintenance
Some manufacturers are exploring the use of AR goggles that guide operators through complex maintenance tasks or troubleshooting steps. This can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall productivity.
Staying informed on these trends ensures your business can anticipate changes and invest in a label cutting machine that remains viable for years to come.
FAQs About Label Cutting Machines
Below are some frequently asked questions that can help you clarify common concerns and optimize your purchasing or operating decisions.
Q1: How do I determine the right cutting technology for my labels?
A1: Start by evaluating your materials, production volume, and design complexity. For example, rotary die-cutting suits large, uniform runs; whereas laser or digital plotter machines excel at rapid customization.
Q2: What is the typical lifespan of a label cutting machine?
A2: With regular maintenance and periodic part replacements, many machines can operate effectively for 10+ years. Actual lifespan varies based on usage intensity and care.
Q3: Are there specific certifications or standards I should look for?
A3: Yes. Look for CE (Conformité Européenne) marking in Europe or UL (Underwriters Laboratories) listing in North America to ensure basic safety and quality standards. Industry-specific standards like ISO 9001 can also indicate robust quality control.
Q4: Can a label cutting machine handle multiple label shapes on a single roll?
A4: Absolutely. Advanced machines can read digital files containing various shapes and adjust cuts on the fly, making them ideal for businesses producing varied label designs in a single run.
Q5: Do I need specialized operators or a dedicated team?
A5: While having knowledgeable staff is always beneficial, many modern machines feature user-friendly software and automated adjustments. A single trained operator can often oversee multiple processes once the system is properly configured.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Whether you’re scaling up a small operation or optimizing a large-scale production environment, investing in a label cutting machine can profoundly impact your efficiency, precision, and bottom line. From laser systems that deliver intricate cuts to robust rotary die-cutters designed for massive runs, there’s a solution tailored for nearly any labeling challenge. As consumer trends lean toward customization and eco-conscious practices, staying on the cutting edge of label technology is not just a luxury—it’s a strategic necessity.
Key Takeaways:
- A label cutting machine drastically reduces manual labor, cuts production times, and ensures impeccable consistency.
- Different machine types—rotary die, flatbed, laser, or plotter—offer specialized advantages depending on your materials and volume needs.
- Proper maintenance routines can extend machine life, minimize downtime, and uphold high-quality output.
- Newer innovations like AI-driven controls, hybrid cutting processes, and eco-efficient designs will shape the future of labeling.
By making an informed decision and investing in the right label cutting machine, you set the stage for an agile, competitive, and forward-thinking operation. Ready to take the next step? Contact us today to learn how you can revolutionize your labeling processes, boost productivity, and enhance your brand’s visual impact.
Stay Connected with EngiTech
EngiTech is your trusted source for in-depth knowledge on industrial mechanical engineering machines and technologies. Stay ahead with the latest innovations, expert insights, and practical guides designed to help you make informed decisions for your business and engineering needs. Join our growing community of professionals and industry leaders to stay updated and competitive in the ever-evolving world of industrial technology.


