The Future of Automation and Robotics: A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Robots
Automation and robotics have revolutionized the industrial landscape, transforming manufacturing processes and enhancing productivity. Industrial robotics have become integral to modern production lines, offering precision, efficiency, and flexibility. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of industrial robots, exploring their types, applications, benefits, and the future of automation in industries. Whether you’re an engineering professional or a company owner looking to enhance your knowledge of industrial robots, this guide will provide valuable insights into this rapidly evolving field.
What Are Industrial Robots?
Industrial robots are programmable robot systems designed to perform a variety of tasks in manufacturing and production environments. These tasks can range from simple repetitive actions to complex processes that require precision and adaptability. Industrial robots are equipped with various tools and end-effectors, allowing them to handle tasks such as welding, painting, assembly, packaging, labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing.
Types of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots come in different shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications and tasks. Here are some of the most common types of industrial robots:
- Articulated Robots: Design: Articulated robots, specifically the articulated arm type, have rotary joints (ranging from two to ten or more) that allow for a wide range of motion. These joints resemble a human arm, providing flexibility and dexterity.
Applications: Commonly used in welding, material handling, and assembly operations that benefit from selective compliance assembly robot arm capabilities. The history and development of industrial robotics began in the mid-20th century, with the introduction of the first articulated robot arms for manufacturing. Over time, innovations such as the SCARA robot (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm) were developed to enhance precision in material handling and assembly tasks. These advancements enabled greater flexibility and efficiency, especially through improvements like parallel rotary joints for increased compliance and speed.
SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm):Design: SCARA robots have a rigid structure with two parallel rotary joints that provide compliance in a horizontal plane. - SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm):Design: SCARA robots have a rigid structure with two parallel rotary joints that provide compliance in a horizontal plane.
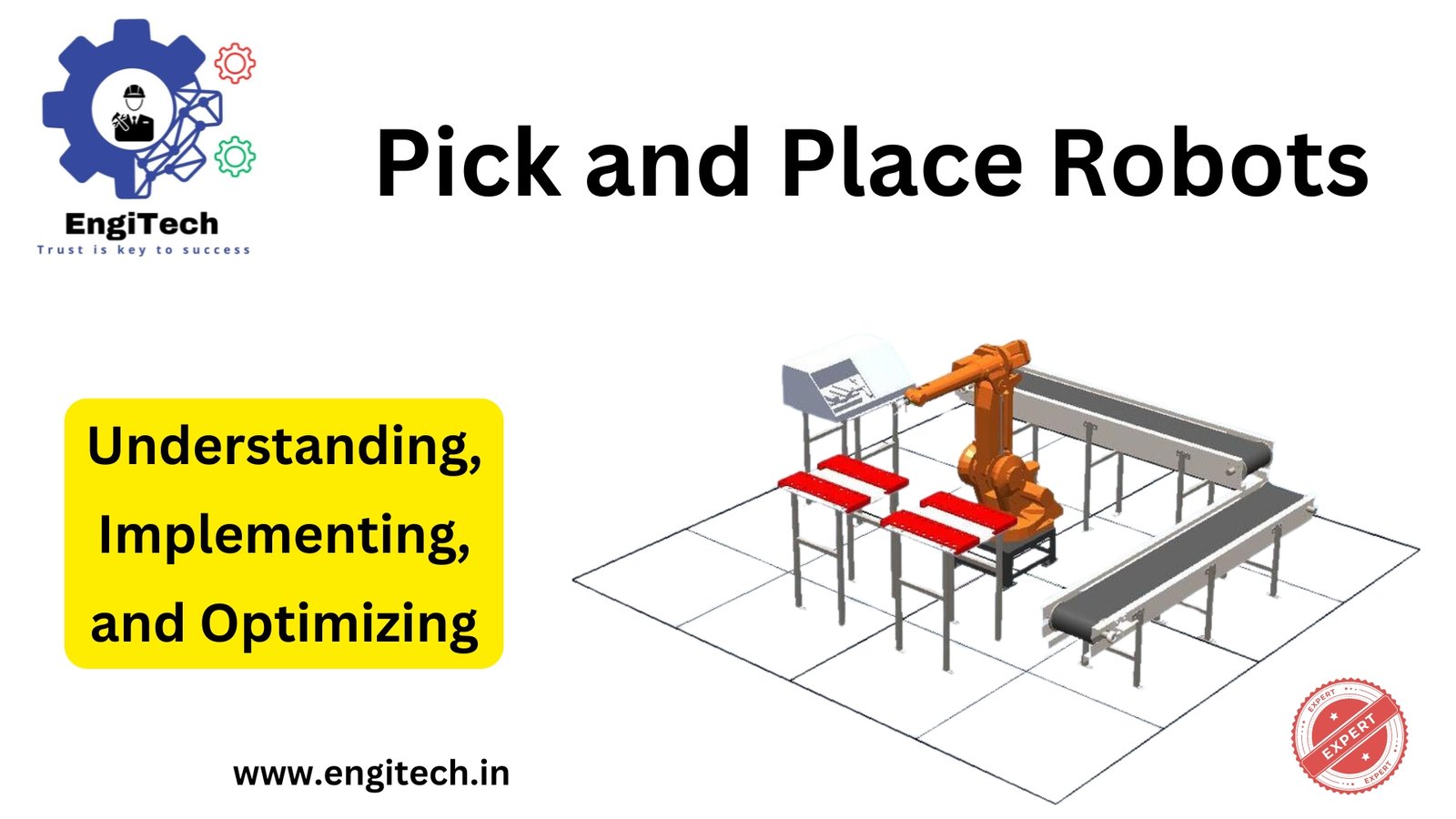
Applications: Ideal for pick-and-place tasks, assembly, and packaging. Delta Robots: Design: Delta robots have a spider-like structure with parallel arms connected to a common base, allowing high-speed and precise movements. There are different classifications and standards for industrial robots, including delta robots. Industrial robots are generally categorized based on their mechanical structure—such as articulated, SCARA, cartesian, and delta robots—as well as by their applications and the environments in which they operate. International standards like ISO 8373 also define and classify industrial robots according to their design and intended use. - Delta Robots:
Design: Delta robots have a spider-like structure with parallel arms connected to a common base, allowing high-speed and precise movements.
Applications: Frequently used in high-speed pick-and-place tasks, packaging, and material sorting. Cartesian Robots: Design: Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (X, Y, and Z), which are crucial for achieving the required number of axes, and have a straightforward design. Compact industrial robots differ from traditional models mainly in their reduced size, lighter weight, and adaptability in tight workspaces, while still maintaining the necessary number of axes for complex movements. This allows them to perform effectively in smaller automated environments where larger, traditional robots may not fit. - Cartesian Robots:
Design: Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (X, Y, and Z), which are crucial for achieving the required number of axes, and have a straightforward design.
Applications: Suitable for tasks like CNC machine automation, 3D printing, and simple pick-and-place operations due to their ease of use. Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Design: Cobots are designed for ease of use to work alongside human operators, featuring safety sensors and mechanisms to prevent accidents. When choosing the right industrial robot for your specific business needs, consider factors such as the type of tasks you need automated, the workspace available, the required payload and reach, and the desired level of collaboration with human workers. Evaluating features like collaborative robots and overall ease of use will ensure the robot integrates smoothly into your production process and maximizes efficiency. - Collaborative Robots (Cobots):
Design: Cobots are designed for ease of use to work alongside human operators, featuring safety sensors and mechanisms to prevent accidents.
Applications: Used in environments where human-robot collaboration is required, such as in assembly lines and quality control. Leading robotic companies like ABB, KUKA, and FANUC each offer a wide range of industrial robots tailored to these applications. ABB is known for its advanced collaborative robots and user-friendly software, KUKA specializes in flexible automation solutions with precise motion control, while FANUC stands out for its reliability and high-speed robots used extensively in manufacturing environments.
Cylindrical Robots:Design: Cylindrical robots have a rotary joint at the base and a prismatic joint to extend their arm vertically. - Cylindrical Robots:
Design: Cylindrical robots have a rotary joint at the base and a prismatic joint to extend their arm vertically.
Applications: Common in machine loading, assembly operations, and material handling.
Applications of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are employed across various industries, each leveraging their capabilities to improve efficiency, precision, and safety. Here are some key applications:
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has been a pioneer in adopting a comprehensive range of industrial robots. They are used for tasks such as:
- Welding: Robots perform precise and consistent welds on car bodies.
- Painting: Robots ensure even and high-quality paint finishes.
- Assembly: Robots assemble various car components with accuracy.
2. Electronics Industry
In electronics manufacturing, robots handle delicate and intricate tasks such as:
- Circuit Board Assembly: Robots place and solder components on circuit boards.
- Testing and Inspection: Robots conduct thorough testing and inspection robots of electronic products.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
Industrial robots in the food and beverage sector help in:
- Packaging: Robots handle the packaging of products with speed and precision.
- Palletizing: Robots stack and arrange products on pallets for shipping.
- Processing: Robots assist in food processing tasks such as slicing and sorting.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry utilizes robots for:
- Dispensing and Filling: Robots precisely dispense and fill medications into containers.
- Inspection: Robots inspect pharmaceutical products for defects and contamination.
- Packaging: Robots package medications efficiently and safely.
5. Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, robots are crucial for:
- Composite Material Handling: Robots handle delicate composite materials used in aircraft.
- Assembly: Robots assemble intricate components of aircraft with precision.
- Painting and Coating: Robots apply coatings evenly on aircraft surfaces.
6. Metal and Machinery Industry
Robots in the metal and machinery industry perform tasks such as:
- Cutting and Machining: Robots handle cutting, drilling, and machining operations.
- Welding: Robots provide consistent and precise welding for metal parts.
- Material Handling: Robots move heavy metal parts and components safely.
Benefits of Industrial Robots
The adoption of traditional industrial robots offers numerous benefits that contribute to the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing processes:
- Increased Productivity: Robots operate continuously without breaks, significantly increasing production rates.
- Enhanced Precision and Quality: Robots perform tasks with high accuracy, reducing errors and ensuring consistent product quality.
- Improved Safety: Robots handle hazardous tasks while adhering to strict safety standards, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries to human workers.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment in robots can be high, the long-term cost savings from increased efficiency and reduced waste are substantial.
- Flexibility: Robots can be reprogrammed and retooled for different tasks, providing flexibility in manufacturing processes.
- Scalability: Robots enable manufacturers to scale up production quickly to meet increasing demand.
Key Components of Industrial Robots
The key components of industrial robots are integral to their functionality and effectiveness in performing various tasks. At the heart of these machines are robot arms, which provide the necessary range of motion and dexterity for operations. Equipped with advanced sensors, these robots can detect their environment, ensuring accurate positioning and task execution. According to the International Federation of Robotics, the drive system of an industrial robot is crucial, as it powers the movements of the arms and other components, enabling smooth and precise operations. Together, these elements create a robust framework that allows industrial robots to excel in manufacturing processes.
Industrial robots have several primary components that work in unison to facilitate their operations. The robot arms are designed to replicate human-like movements, allowing for intricate tasks such as assembly, welding, and packaging, similar to systems developed by ABB Robotics. Sensors play a vital role in providing feedback to the robot, enabling it to adjust its actions in real-time based on environmental conditions or task requirements. Additionally, the drive system, which can include electric motors or hydraulic actuators, powers the movement of the robot’s components, ensuring efficient and accurate performance in various industrial applications.
The Controller
The controller is a critical component of any industrial robot, acting as the brain that governs its operations. It processes inputs from various sensors and executes commands to control the robot’s movements. In industrial robotics, the controller is programmed with specific tasks and routines, enabling the robot to perform operations such as assembly, welding, and material handling with precision and efficiency. The integration of sophisticated algorithms and real-time data processing capabilities allows the controller to adapt to changing conditions and optimize the robot’s performance.
In addition to basic control functions, modern robot controllers often feature advanced capabilities such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. This allows them to analyze data from previous tasks, improving their efficiency over time. The robot system’s controller communicates with other machinery in the production line, ensuring seamless integration and coordination in automated processes. This level of connectivity is crucial for optimizing workflows and enhancing overall productivity in industrial environments.
Moreover, the controller’s user interface plays a significant role in simplifying the programming and monitoring of the robot simulation software. Operators can easily input commands, adjust settings, and track performance metrics through intuitive dashboards. This ease of use empowers manufacturers to maximize the potential of their robotic systems, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime in production operations.
The Robotic Arm
The robotic arm is a fundamental component of industrial robots, designed to mimic the movements and dexterity of a human arm. These robotic arms can be classified based on their configuration, including articulated arms, SCARA arms, and Cartesian arms. Articulated arms, often equipped with multiple rotary joints, offer a wide range of motion and flexibility, making them ideal for complex tasks such as welding and assembly. The number of axes in a robotic arm determines its degrees of freedom, allowing it to reach various positions and orientations within its workspace.
Each joint in a robotic arm is typically equipped with rotary joints, allowing for smooth and precise movements. The design and engineering of these joints are crucial, as they dictate the arm’s reach, payload capacity, and overall performance. A well-designed articulated arm can perform intricate tasks quickly and accurately, making it a valuable asset in industrial settings.
Moreover, advancements in robotics have led to the development of specialized robotic arms tailored for specific applications. For example, some robotic arms are designed for high-speed pick-and-place operations, while others are optimized for assembly tasks requiring high precision. This specialization enhances the versatility and efficiency of robotic systems, enabling manufacturers to adapt to evolving production needs and market demands.
The End Effector
The end effector is the part of the robot that interacts directly with the environment, performing tasks such as gripping, welding, or painting. It is a crucial component of industrial robots, as it determines the robot’s capabilities and suitability for specific applications. Various types of end effectors exist, including grippers, suction cups, and welding torches, each designed for different tasks and materials.
Grippers are among the most common end effectors, allowing robots to grasp and manipulate objects securely. These devices can be mechanical or pneumatic, with designs that accommodate various shapes and sizes of items. Suction cups, on the other hand, are ideal for handling smooth and flat surfaces, making them popular in packaging and assembly lines. The choice of end effector greatly influences the robot’s efficiency and effectiveness in completing its designated tasks.
Furthermore, the development of smart end effectors is an emerging trend in industrial robotics. These devices incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms, enabling them to adapt to different objects and conditions autonomously. This technological advancement enhances the flexibility of robotic systems, allowing them to tackle a wider range of applications in dynamic manufacturing environments.
The Sensors
Sensors are pivotal components in industrial robots, providing critical data that enables them to interact effectively with their environment. These devices can detect various parameters, such as distance, pressure, temperature, and light, allowing robots to perform tasks with greater accuracy and safety. Advanced sensors, such as vision systems, are increasingly used in robotics to enhance perception and decision-making capabilities.
Vision systems, for example, enable robots to “see” their surroundings, identifying objects, obstacles, and even quality defects in products. By integrating cameras and image processing algorithms, robots can adjust their actions in real-time based on visual input. This capability is particularly valuable in applications like quality control, where precise measurements are essential for maintaining product standards.
In addition to vision systems, other types of sensors, such as proximity sensors and force sensors, play vital roles in ensuring safe and efficient robot operation. Proximity sensors help robots navigate their environment without colliding with objects, while force sensors provide feedback on the grip strength of end effectors, preventing damage to delicate items. Together, these sensors enhance the overall functionality and performance of industrial robots, making them more capable of adapting to various tasks and conditions.
The Drive
The drive system of an industrial robot is essential for powering its movements and enabling it to perform tasks with precision and speed. This system typically consists of motors, gearboxes, and actuators that work together to control the robot’s joints and end effectors. The choice of drive technology can significantly impact the robot’s performance, including its speed, accuracy, and payload capacity.
In industrial robotics, electric motors are commonly used due to their efficiency and ease of control. These motors can be coupled with different types of gear systems to optimize torque and speed for specific applications. For example, high-speed applications may require motors with a direct drive system, while applications that involve heavy lifting may utilize geared motors to provide the necessary force.
Moreover, advancements in drive technologies, such as servomotors and stepper motors, are enhancing the capabilities of industrial robots. Servomotors, for instance, offer precise control over position and high speed, making them ideal for applications that require high accuracy. As technology continues to evolve, the drive systems of industrial robots are becoming more sophisticated, allowing for greater flexibility and performance in a wide range of manufacturing processes.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Industrial Robots
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing industrial robots comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and installing industrial robots can be significant, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Maintenance and Downtime: Regular maintenance is essential to keep robots functioning optimally, and any downtime can impact production schedules.
- Skilled Workforce: Operating and maintaining robots requires a skilled workforce with specialized training in robotics and automation.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating robots with existing production systems and workflows can be complex and require careful planning.
- Cybersecurity: As robots become more connected, ensuring cybersecurity to protect against potential cyber threats is crucial.
What are the roles of industrial robots?
Industrial robots play crucial roles in manufacturing and production processes, including assembly, welding, painting, packaging, and quality control. They enhance efficiency by performing repetitive tasks with precision and speed, reducing human error. Additionally, industrial robots improve workplace safety by taking on hazardous jobs that might pose risks to human workers.
The Future of Industrial Robots
The future of industrial robots looks promising, with advancements in technology continuing to enhance their capabilities and applications, as highlighted in the IFR study World Robotics. Here are some key trends shaping the future of industrial robots:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is enabling robots to become smarter and more autonomous. AI-powered robots can analyze data, learn from their experiences, and make real-time decisions to optimize production processes.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to work safely alongside humans, prioritizing worker safety. Future cobots will likely have enhanced sensory capabilities and improved interaction with human operators, further blurring the lines between human and robotic workforces.
3. Advanced Sensors and Vision Systems
The development of advanced sensors and vision systems is improving the perception and accuracy of robots. These technologies enable robots to perform intricate tasks that require high levels of precision and adaptability.
4. Increased Connectivity and IoT Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is facilitating greater connectivity between robots and other industrial equipment. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration into smart factory environments.
5. Flexible and Modular Robotics
Future industrial robots, including autonomous mobile robots, will be more flexible and modular, allowing for easy reconfiguration and adaptation to different tasks and production requirements. This flexibility will enable manufacturers to respond more quickly to changing market demands.
6. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Robotics
As industries focus on sustainability, the development of eco-friendly robots that consume less energy and reduce waste will become a priority. These robots will contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices and reduce the environmental impact of industrial operations.
Conclusion
Industrial robots have become an indispensable part of modern manufacturing, particularly those developed by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, offering unparalleled benefits in terms of productivity, precision, and safety. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities and applications of industrial robots will only expand, driving further innovation and efficiency in industries worldwide. By understanding the different types of industrial robots, their applications, and the future trends shaping their development, companies can make informed decisions to harness the full potential of automation and robotics in their operations.
For more detailed information on industrial robots and other advancements in automation, visit EngiTech . Stay updated with our latest blogs to enhance your knowledge and improve your industrial processes.