Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Use Cases and Sensors in Factory
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming the way industries do business, creating much-needed efficiency and productivity gains. Reports show that more than 75% of manufacturing business around the world are currently adopting or considering an adoption of IIoT solutions for competitive edge. But what does IIoT mean, and how does it change the game for industry? This blog will guide you through the available use cases of the IIoT and howsensors in factories are connected for the things-to-cloud strategy.
You’ll see how IIoT can help you to streamline your manufacturing processes, maximize uptime and save money, and enable you to make better operational decisions. Let’s take them one at a time.
Table of Contents
What is IIoT?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the integration of connected devices, sensors, and intelligent systems in an industrial environment through secure networks that helps in collecting, sharing and analyzing data in real time. Whereas the Internet of Things (IoT) in general is oriented toward the consumer sector, IIoT is specifically aimed at industries such as manufacturing, logistics, energy and healthcare.
How Does IIoT Work?
Collection of Data
Smart factory sensors placed in machines and equipment gather real-time data on critical measurements such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and machine performance.
Data Transmission
This information is then transmitted to one or more centralized platforms (deployed in local servers or the cloud) using WiFi, Bluetooth, or other IoT-capable communication protocols.
Data Analysis
Sophisticated algorithms and AI systems process the data to produce actionable insights, notify managers of potential issues, or even automate certain processes.
Actionable Outputs
IIoT devices subsequently act on these insights to make decisions regarding operations, which could involve beginning a maintenance process, modifying production schedules, or minimizing energy usage.
Through IIoT, businesses can optimize their operations faster, smarter and leaner.
Why is IIoT Important?
From increasing worker safety to predicting equipment failures, before they occur, IIoT solutions are transforming industries with functionality that was previously unimaginable, only ten years ago. It’s an essential step in solving problems such as aging equipment, unforeseen downtime and excessive operational costs.
Pro Tip: Combine robust data analytics with high-quality sensors developed specifically for your factory’s specific process to get the most out of IIoT.
Here Are The Key Advantages of IIoT in Manufacturing
Predictive Maintenance
In a factory, unplanned downtimes can cost manufacturers tens of thousands of dollars per hour. Why IIoT predictive maintenance systems can detect anomalies in machine performance and predict breakdowns before they happen. For instance:
A factory sensor monitoring motor vibration could alert if it sensed an abnormal vibration, giving managers an opportunity to act before something broke.
Enhanced Quality Control
Production quality can be real-time tracked by IIoT systems and defects can be detected in the earliest period.
Sensors with AI can sense anomalies in size, weight or content during production so that only high-quality products reach customers.
Higher Operational Efficiency
With factory sensors and smart networks, workers can spot bottlenecks in production and attack inefficiencies. This can ultimately yield a substantial output gain at a reduced operating cost.
Energy Optimization
Today’s sensors monitor the amount of energy used on factory equipment and systems. The insights help factories:
Reduce energy waste.
Run operations during non-peak hours when electricity is less expensive.
Worker Safety
IIoT enhances health and safety at work by recording data about environmental conditions such as air quality, heat/vibration exposure, and radiation. Warnings can help prevent hazards before they cause harm to workers.
Key takeaways: IIoT addresses key manufacturing pain points, with actionable insights that drive efficiency, safety and long-term profits.
Top IIoT Applications in Factories
The potential of IIoT is huge, and here are three examples that industrial managers are already using to their advantage:
Predictive Maintenance
How It Works:
Vibration Monitoring Sensors on equipment recognize slight shifts in vibration frequency.
Metrics are compared to baselines in a real time analysis of the data.
Real-World Example:
A car company utilized predictive maintenance to shrink an average of 12 hours a month of downtime down to just 2 hours, resulting in additional millions of dollars saved year over year.
Quality Control
How It Works:
Optical Scanners examine each product for quality while taking high-resolution pictures during final assembly.
If a problem is identified the system can automatically reject and discard the faulty product.
Industries Impacted:
- Electronics manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical production
Energy Optimization
How It Works:
Smart Energy Meters AEMs, analyzing energy consumption machine-wise.
Systems adapt power consumption on the fly, eliminating wasted usage.
Benefit:
Energy-optimized factories were found to achieve up to 20% lower energy costs per year.
Helping Sensors Bring IIoT to Life
Sensors are the lifeblood of any IIoT solution. Without them, IIoT systems wouldn’t be able to collect much of the critical data required for optimization.
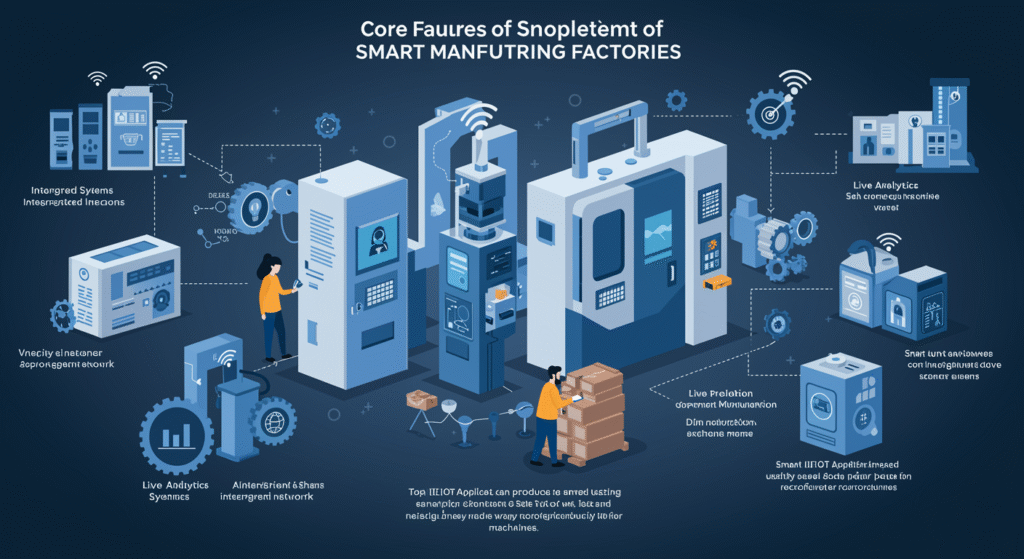
Types of Factory Sensors
- Vibration Sensors: For monitoring performance of the machine and fault finding.
- Temperature Sensors: Prevent machines from overheating and keep production conditions in the ideal state.
- Pressure Sensors: Used in industries such as oil refining, they help avoid accidents due to pressure irregularities.
- Proximity Sensors: Monitor tool, part, or product position during assembly.
- Energy Meters: Measure and evaluate power usage for potential cost savings.
Sensor Placement in a Factory
The proper positioning of sensors is highly critical for the optimal data acquisitions. For example:
- Vibration sensors shall be mounted on motors, pumps and rotating equipment.
- Temperature sensors need to be located next to heat generating equipment such as heaters.
With factory sensors these manufacturers can strategically create a strong ecosystem for industrial of things that meets their needs.
Did You Know? Today’s sensors are largely equipped with built-in self-calibration, which means IIoT installations are simpler and more reliable.
IIoT Implementation Challenges and Remedies
There are obstacles to any solution. Below are usual obstacles they encounter on the path of IIoT adoption, and how to overcome them.
Data Overload
Factories generate huge amounts of data every day and traditional systems will struggle with that.
SOLUTION: Use cloud storage and AI-based analytical tools.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Legacy equipment may not support IIoT-enabled technologies.
Solution: Retrofit machines with IoT adaptor devices or invest in hybrid solutions.
Cyber security Risks
Hacked systems can also leak sensitive data.
Solution: Use strong encryption and work with secure IOT providers.
High Initial Costs
The common thread, of course, is that IIoT deployment means significant up-front investment in sensors, systems and education.
Solution: Use small pilot to test RO before general implementation.
Dealing with these challenges proactively will help ensure manufacturers realize IIoT’s full potential without undue delay.
Future Trends in IIoT
The world of IIoT is ever changing. Here are the trends that will be shaping its future:
5G Connectivity
With even more reach and reliability than today’s wireless networks, 5G will enable larger IIoT deployments.
AI-Powered Insights
AI and machine learning will automate the analysis of data, helping to quickly uncover inefficiencies and improve processes.
Edge Computing
More factories are also starting to include edge computing, which involves analyzing data locally rather than sending it to a cloud server, in order to minimize latency.
Green Manufacturing
Look for an explosive increase in energy-efficient IIoT solutions that decrease carbon footprints.
These technologies must be invested in now so that businesses can remain competitive in future years.
FAQ
What is IIoT?
- The idea of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is simply to connect a variety of industrial systems and devices and collect and share data to make the system more efficient (and effective).
How do factory sensors work?
- Sensors installed at factories collate data in real time on multiple measures such as temperature, pressure and vibration, which is uploaded onto IIoT platforms for analysis.
Why is predictive maintenance important?
- Predictive maintenance prevents downtime by detecting issues with equipment before they can fail.
What industries use IIoT?
- Manufacturing, energy, healthcare, agriculture, and logistics are the major industries.
What are the issues that are hard to address when deploying IIoT?
- Major concerns are high costs, integration hurdles, information overload and cyber threats.
Conclusion
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing industries by offering smarter, more efficient and cost-effective products and services. Its applications range from predictive maintenance to energy optimization and it is simply invaluable. With the increasing availability of advanced factory sensors and by addressing the challenges associated with their implementation, it becomes possible for factories to be resilient and ready for the future.
Begin your IIoT journey today and lead yourself ahead in a competitive environment. For similar guides, browse through or drop your queries in the comment section and be a part of the discussion.
Further Reading & Credible Sources
- IIoT Case Studies – Businesses Leading the Way to The Digital Era
- Designing Smart Factories with IIoT
- The Role of Sensors in IIoT