Induced Draft Fans (ID Fans) : working principles, applications, and benefits
Induced draft fans (ID fans) play a crucial role in various industrial processes, particularly in power plants, chemical manufacturing, and HVAC systems. These fans manage and control airflow, ensuring efficient and safe operation of combustion systems and other industrial applications. This comprehensive guide explores the working principles, applications, benefits, and advancements of induced draft fans.
What is an Induced Draft Fan?
An induced draft fan (ID fan) creates a negative pressure or draft to draw flue gases from industrial processes through a chimney or exhaust stack. ID fans regulate the flow of gases, ensuring proper ventilation and preventing the buildup of harmful substances in the system.
How Induced Draft Fans Work
- Airflow Creation: ID fans create a negative pressure that pulls flue gases from the combustion chamber or other industrial processes.
- Gas Movement: The fan moves the gases through ducts and filters, ensuring that harmful particulates are removed before the gases are expelled into the atmosphere.
- Control and Regulation: Control the speed and operation of ID fans to maintain the desired airflow and pressure, ensuring efficient and safe system operation.
- Exhaust: Release the cleaned flue gases through a chimney or exhaust stack, minimizing environmental impact.
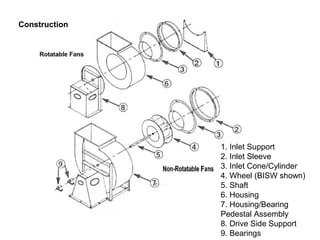

Applications of Induced Draft Fans
1. Power Plants:
- Assist in the combustion process by drawing flue gases from boilers.
- Maintain optimal combustion conditions, improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
2. Chemical Manufacturing:
- Remove hazardous gases from chemical reactors and other processes.
- Ensure safe working conditions and prevent the buildup of toxic substances.
3. HVAC Systems:
- Provide ventilation and exhaust in large buildings and industrial facilities.
- Maintain indoor air quality and control temperature and humidity levels.
4. Cement Plants:
- Remove exhaust gases from kilns and coolers.
- Improve the efficiency of the cement manufacturing process.
5. Metal Smelting:
- Extract and filter flue gases from smelting furnaces.
- Reduce emissions and recover valuable materials from the exhaust.
Benefits of Using Induced Draft Fans
Improved Efficiency: ID fans enhance the efficiency of combustion processes by ensuring proper airflow and optimal combustion conditions.
Emission Control: By drawing flue gases through filters and scrubbers, ID fans help reduce harmful emissions, contributing to environmental protection.
Enhanced Safety: The negative pressure created by ID fans prevents the buildup of toxic gases, ensuring safe working conditions in industrial facilities.
Versatility: ID fans can be used in various industries, including power generation, chemical manufacturing, HVAC, cement production, and metal smelting.
Reliability: Designed for continuous operation, ID fans provide reliable performance and minimal downtime, essential for critical industrial processes.
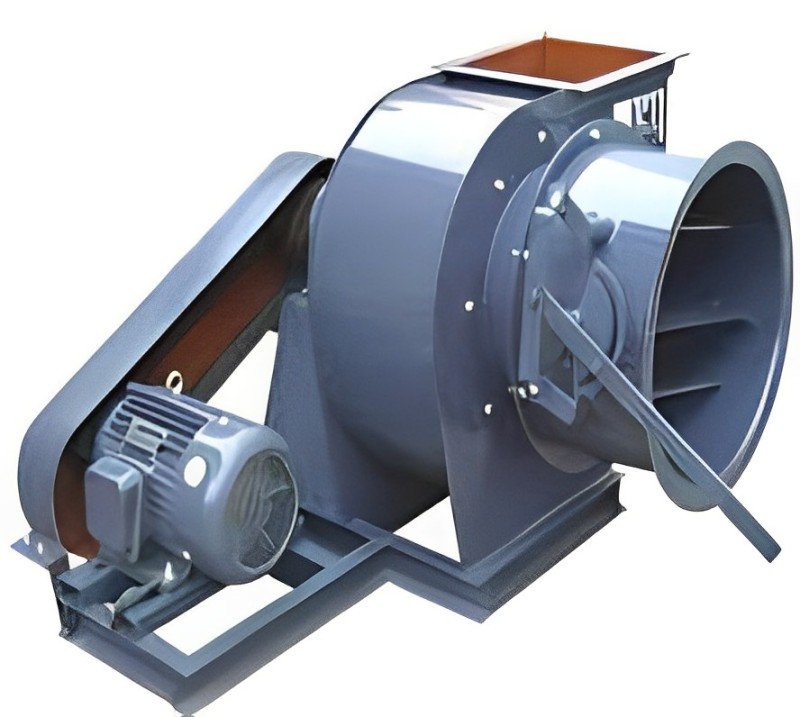

Key Considerations for Selecting an Induced Draft Fan
System Requirements: Understand the specific requirements of your industrial process, including airflow, pressure, and temperature, to select the appropriate ID fan.
Fan Capacity: Choose a fan with the capacity to handle the volume of gases generated by your process. Ensure the fan can maintain the desired pressure and airflow.
Material Construction: Select a fan constructed from materials that can withstand the corrosive and high-temperature environment of your process.
Energy Efficiency: Evaluate the energy efficiency of the fan. Look for features such as variable speed drives and optimized blade designs to reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
Maintenance and Durability: Consider the ease of maintenance and the durability of the fan. Choose designs that allow easy access for cleaning and servicing, and ensure the fan can withstand continuous operation.
Technological Advancements in Induced Draft Fans
Variable Speed Drives: Modern ID fans often come equipped with variable speed drives, allowing precise control over fan speed and airflow. This feature enhances energy efficiency and allows for better process control.
Advanced Blade Designs: Innovations in blade design have improved the performance and efficiency of ID fans. Optimized blade shapes reduce turbulence and increase airflow, leading to lower energy consumption and better overall performance.
Noise Reduction Technologies: New technologies have been developed to reduce the noise generated by ID fans. These advancements include aerodynamic blade designs and sound-dampening materials, improving the working environment in industrial facilities.
Smart Control Systems: Integration with smart control systems allows for real-time monitoring and adjustment of fan operation. These systems provide data on airflow, pressure, and energy consumption, enabling more efficient and reliable operation.
Materials and Coatings: Advances in materials and coatings have enhanced the durability and corrosion resistance of ID fans. High-performance alloys and protective coatings extend the lifespan of the fans and reduce maintenance requirements.
Conclusion
Induced draft fans are essential components in various industrial processes, providing efficient and reliable airflow management. By understanding their working principles, applications, benefits, and key considerations, you can optimize their use in your operations. Continuous advancements in ID fan technology promise even greater efficiency, reliability, and environmental benefits, making them indispensable in modern industrial systems.
For more in-depth articles and resources on industrial fan technologies and innovations, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and applications in the industry!