Gantry Cranes: The Ultimate Guide

Gantry cranes are a vital part of modern industrial and construction environments. These cranes, characterized by their versatile and robust design, are essential for lifting and moving heavy loads with precision and ease. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into everything you need to know about gantry cranes, including their types, uses, advantages, key components, safety considerations, and the future of this indispensable machinery.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes are a type of overhead crane with a single or double girder configuration supported by freestanding legs that move on wheels or along a track. Unlike overhead cranes, which are typically fixed to a structure, gantry cranes are mobile and can be used both indoors and outdoors. They are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, shipping, construction, and more, where heavy lifting is required.
Definition and Basic Concept
A gantry crane consists of a bridge (girder), legs, and a trolley with a hoist. The bridge spans the width of the area to be serviced, while the legs support the bridge and move along a track or rail system. The trolley, which travels along the bridge, houses the hoist mechanism for lifting and lowering loads. Gantry cranes can be manually operated or motorized, depending on the application and capacity requirements.
Types of Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. Here, we explore the most common types of gantry cranes:
1. Full Gantry Crane
Full gantry cranes are large, robust cranes designed to handle heavy loads. They consist of two legs that support the entire structure, with the bridge spanning the width of the working area. Full gantry cranes are commonly used in shipyards, rail yards, and large manufacturing plants.
2. Semi-Gantry Crane
Semi-gantry cranes have one leg running on a rail or track while the other end is supported by a wall-mounted runway. This configuration allows for efficient use of space, making semi-gantry cranes ideal for facilities with limited floor space. They are often used in workshops and warehouses.
3. Portable Gantry Crane
Portable gantry cranes, also known as mobile gantry cranes, are smaller and more versatile. They can be easily moved and positioned, making them suitable for various indoor and outdoor applications. These cranes are commonly used in maintenance shops, small manufacturing units, and construction sites.
4. Adjustable Gantry Crane
Adjustable gantry cranes offer flexibility in terms of height and span adjustments. They can be easily customized to suit different lifting needs and work environments. These cranes are particularly useful in applications where load sizes and weights vary frequently.
5. Rubber-Tired Gantry Crane (RTG)
Rubber-tired gantry cranes are specialized cranes used in container terminals and intermodal yards. They are equipped with rubber tires instead of rails, allowing them to move freely within the yard. RTGs are designed to handle containers and are capable of lifting heavy loads efficiently.
6. Rail-Mounted Gantry Crane (RMG)
Rail-mounted gantry cranes are similar to RTGs but are equipped with steel wheels that run on rails. RMGs are commonly used in ports and rail yards for stacking and moving containers. They are known for their high lifting capacity and precision.
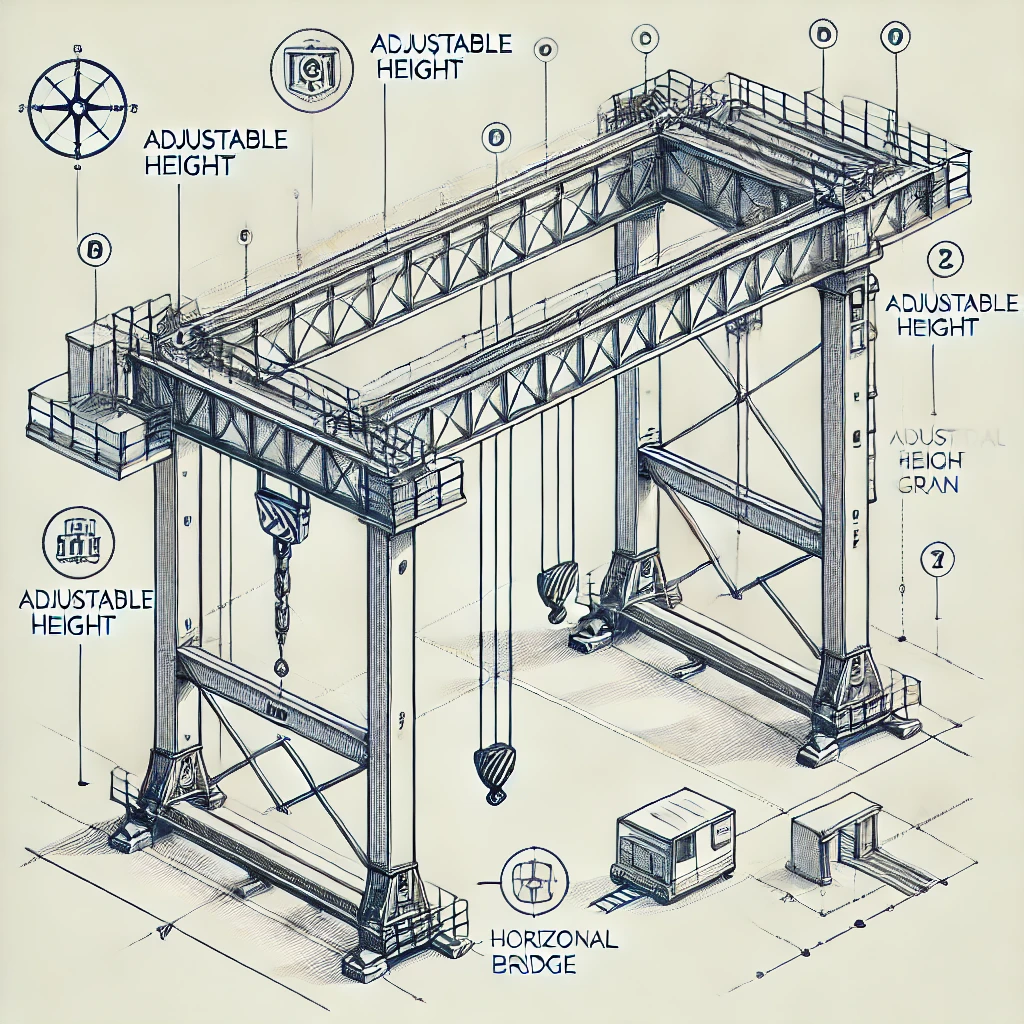

Key Components of Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes consist of several key components, each playing a crucial role in their operation. Understanding these components is essential for anyone involved in the design, operation, or maintenance of gantry cranes.
1. Bridge/Girder
The bridge or girder is the horizontal beam that spans the width of the crane’s working area. It supports the trolley and hoist mechanism and is a critical component of the crane’s structure. Bridges can be single-girder or double-girder, depending on the load capacity and application.
2. Legs
The legs are vertical supports that hold up the bridge and allow the crane to move along the ground or track. In full gantry cranes, the legs are typically equipped with wheels or tracks, enabling movement along a designated path.
3. Trolley
The trolley is a movable component that travels along the bridge. It houses the hoist mechanism and allows for precise positioning of the load. Trolleys can be manually operated or motorized, depending on the crane’s design.
4. Hoist
The hoist is the lifting mechanism of the crane. It consists of a drum or chain, a motor, and a lifting hook or attachment. The hoist raises and lowers the load and can be electric, hydraulic, or manual, depending on the crane’s specifications.
5. End Trucks
End trucks are located at the ends of the bridge and support the bridge’s movement along the rails or track. They contain the wheels and drive mechanisms that allow the crane to travel back and forth.
6. Controls
The controls of a gantry crane include the electrical or hydraulic systems that operate the crane’s movements. These controls can be manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic, depending on the level of automation required.
Applications of Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes are used in a wide range of industries and applications. Their versatility and ability to handle heavy loads make them an invaluable asset in various settings. Here are some common applications of gantry cranes:
1. Shipping and Ports
Gantry cranes are extensively used in shipping ports for loading and unloading cargo from ships. They handle containers, bulk materials, and heavy machinery, making them essential for efficient port operations.
2. Construction
In the construction industry, gantry cranes are used to lift and position heavy materials such as steel beams, concrete panels, and large equipment. They are particularly useful in building bridges, high-rise structures, and industrial facilities.
3. Manufacturing
Gantry cranes play a vital role in manufacturing plants, where they are used to move raw materials, finished products, and machinery. They are commonly found in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and heavy machinery production.
4. Rail Yards
In rail yards, gantry cranes are used to load and unload freight cars. They handle a variety of cargo, including containers, automobiles, and bulk materials. Rail-mounted gantry cranes are particularly efficient in these applications.
5. Maintenance and Repair
Portable and adjustable gantry cranes are frequently used in maintenance and repair shops. They provide the flexibility to lift and move equipment and components, making them ideal for tasks such as engine repairs and machinery maintenance.
Advantages of Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes offer numerous advantages, making them a preferred choice in many industrial and commercial settings. Here are some key benefits of using gantry cranes:
1. Versatility
Gantry cranes are highly versatile and can be used in various applications, both indoors and outdoors. Their ability to handle different types of loads and their adaptability to different environments make them a valuable asset.
2. Mobility
Unlike fixed overhead cranes, gantry cranes are mobile and can be easily moved within a facility or between job sites. This mobility is especially useful in construction and maintenance applications.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Gantry cranes are often more cost-effective than fixed overhead cranes, especially for temporary or short-term projects. They require less infrastructure and can be easily disassembled and relocated.
4. Customizability
Gantry cranes can be customized to meet specific lifting needs and requirements. Adjustable gantry cranes, in particular, offer the flexibility to change height and span, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
5. Space Efficiency
Semi-gantry cranes and portable gantry cranes are designed to optimize space usage. They can operate in areas with limited floor space and can be used in conjunction with other equipment.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Safety is a critical aspect of gantry crane operation. Ensuring the safe use of gantry cranes involves proper training, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety protocols. Here are some key safety considerations and best practices:
1. Operator Training
Operators should receive comprehensive training on the safe operation of gantry cranes. This includes understanding the crane’s controls, load capacity, and safety features. Proper training helps prevent accidents and ensures efficient operation.
2. Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure the safe and reliable operation of gantry cranes. This includes checking the structural integrity of the crane, inspecting the hoist and trolley, and verifying the condition of electrical and hydraulic systems.
3. Load Capacity
It is crucial to adhere to the crane’s load capacity limits. Overloading a gantry crane can lead to structural damage, equipment failure, and serious accidents. Operators should be aware of the crane’s rated capacity and never exceed it.
4. Safe Lifting Practices
Operators should follow safe lifting practices, such as properly securing the load, using appropriate rigging, and avoiding sudden movements. It is also important to ensure that the load is evenly distributed and balanced.
5. Environmental Considerations
Gantry cranes used outdoors should be designed to withstand environmental conditions such as wind, rain, and temperature variations. Operators should be aware of weather-related risks and take appropriate precautions.
The Future of Gantry Cranes
The future of gantry cranes is shaped by technological advancements, increasing automation, and a focus on sustainability. Here are some trends and developments that are expected to impact the gantry crane industry:
1. Automation and Smart Technologies
Automation is transforming the operation of gantry cranes. Smart technologies, such as IoT (Internet of Things) sensors and data analytics, enable real-time monitoring and control of crane operations. This enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves safety.
2. Energy Efficiency
As industries prioritize sustainability, there is a growing focus on energy-efficient gantry crane designs. This includes the use of energy-saving motors, regenerative braking systems, and eco-friendly materials.
3. Advanced Materials
The use of advanced materials, such as high-strength steel and lightweight composites, is enhancing the performance and durability of gantry cranes. These materials contribute to reduced weight and increased load capacity.
4. Customization and Flexibility
The demand for customized gantry cranes is on the rise. Manufacturers are offering modular designs and flexible configurations to meet the specific needs of different industries. This trend is expected to continue as businesses seek tailored solutions.
5. Safety Innovations
Advancements in safety technology are improving the safety features of gantry cranes. This includes the development of advanced collision avoidance systems, remote monitoring, and automated emergency response systems.
Conclusion
Gantry cranes are an essential component of modern industrial and construction environments. Their versatility, mobility, and ability to handle heavy loads make them indispensable in various applications. As technology continues to evolve, gantry cranes are becoming more advanced, efficient, and safe. Whether used in shipping, construction, manufacturing, or maintenance, gantry cranes play a critical role in enhancing productivity and efficiency.
For businesses considering the acquisition of gantry cranes, it is important to carefully assess their specific needs and choose the right type of crane that meets their requirements. Proper training, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety protocols are key to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of gantry cranes.
The future of gantry cranes is bright, with ongoing innovations and advancements shaping the industry. As automation, energy efficiency, and customization continue to drive developments, gantry cranes will remain a vital asset in the industrial landscape.
FAQs about gantry cranes:
1. What is a gantry crane, and how does it work?
- A gantry crane is a type of overhead crane with a bridge supported by freestanding legs that move on wheels or tracks. It consists of a horizontal beam (bridge) and a trolley with a hoist for lifting and moving heavy loads. The crane can be used both indoors and outdoors, and it operates by moving the trolley along the bridge to position the hoist directly above the load, which can then be lifted and transported.
2. What are the different types of gantry cranes?
- The main types of gantry cranes include Full Gantry Cranes, Semi-Gantry Cranes, Portable Gantry Cranes, Adjustable Gantry Cranes, Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes (RTG), and Rail-Mounted Gantry Cranes (RMG). Each type has specific features and is suited for different applications and environments.
3. What are the key components of a gantry crane?
- The key components of a gantry crane include the bridge (girder), legs, trolley, hoist, end trucks, and controls. The bridge supports the trolley and hoist, while the legs support the bridge and move along the ground or tracks. The trolley houses the hoist mechanism, and the controls manage the crane’s movements.
4. How do you choose the right gantry crane for your application?
- Choosing the right gantry crane depends on several factors, including the load capacity, span, height, lifting speed, and the specific requirements of the application. Consider the type of load, the working environment, the frequency of use, and any space constraints. Consulting with a crane manufacturer or supplier can help determine the best crane for your needs.
5. What are the safety considerations for operating gantry cranes?
- Safety considerations include proper operator training, regular inspections and maintenance, adherence to load capacity limits, and safe lifting practices. It’s also important to ensure the crane is designed to withstand environmental conditions and to follow industry standards and regulations.
6. What are the advantages of using gantry cranes?
- Gantry cranes offer several advantages, including versatility, mobility, cost-effectiveness, customizability, and space efficiency. They can be used in various industries and applications, both indoors and outdoors, and can handle a wide range of loads.
7. What maintenance is required for gantry cranes?
- Regular maintenance for gantry cranes includes inspecting and lubricating moving parts, checking electrical and hydraulic systems, verifying the condition of the hoist and trolley, and inspecting the crane’s structural components. Proper maintenance helps ensure safe and reliable operation and extends the lifespan of the crane.
8. Can gantry cranes be used outdoors?
- Yes, gantry cranes can be used outdoors. Many types, such as Rubber-Tired Gantry Cranes (RTG) and Rail-Mounted Gantry Cranes (RMG), are specifically designed for outdoor use in environments like ports, rail yards, and container terminals. Outdoor gantry cranes are built to withstand environmental conditions such as wind, rain, and temperature variations.
9. How is a gantry crane different from an overhead crane?
- The primary difference is that gantry cranes have freestanding legs that move on wheels or tracks, making them mobile. In contrast, overhead cranes are typically fixed and supported by building structures. Gantry cranes can be used both indoors and outdoors, while overhead cranes are usually installed indoors.
10. What are the typical applications of gantry cranes?
- Gantry cranes are used in various applications, including shipping and ports for loading and unloading cargo, construction sites for lifting materials, manufacturing plants for moving machinery, rail yards for handling freight, and maintenance shops for repairs.
These FAQs provide a general overview and address some of the most common questions about gantry cranes. If you have more specific inquiries or need further details, feel free to ask!
At EngiTech.in, we are dedicated to providing the latest and most comprehensive insights into industrial engineering equipment, including gantry cranes, blowers, industrial dryers, and more. Our platform is a valuable resource for professionals, company owners, and enthusiasts seeking in-depth knowledge, expert analysis, and innovative solutions. Whether you’re looking to enhance operational efficiency, stay updated on industry trends, or make informed purchasing decisions, EngiTech.in is your go-to destination for all things related to industrial machinery. Explore our expertly crafted articles, detailed guides, and product reviews, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of industrial engineering. Join our community and empower your business with cutting-edge information and resources.