Fluid Bed Dryers: Efficient Drying Solutions Explained
Understanding Fluid Bed Dryers
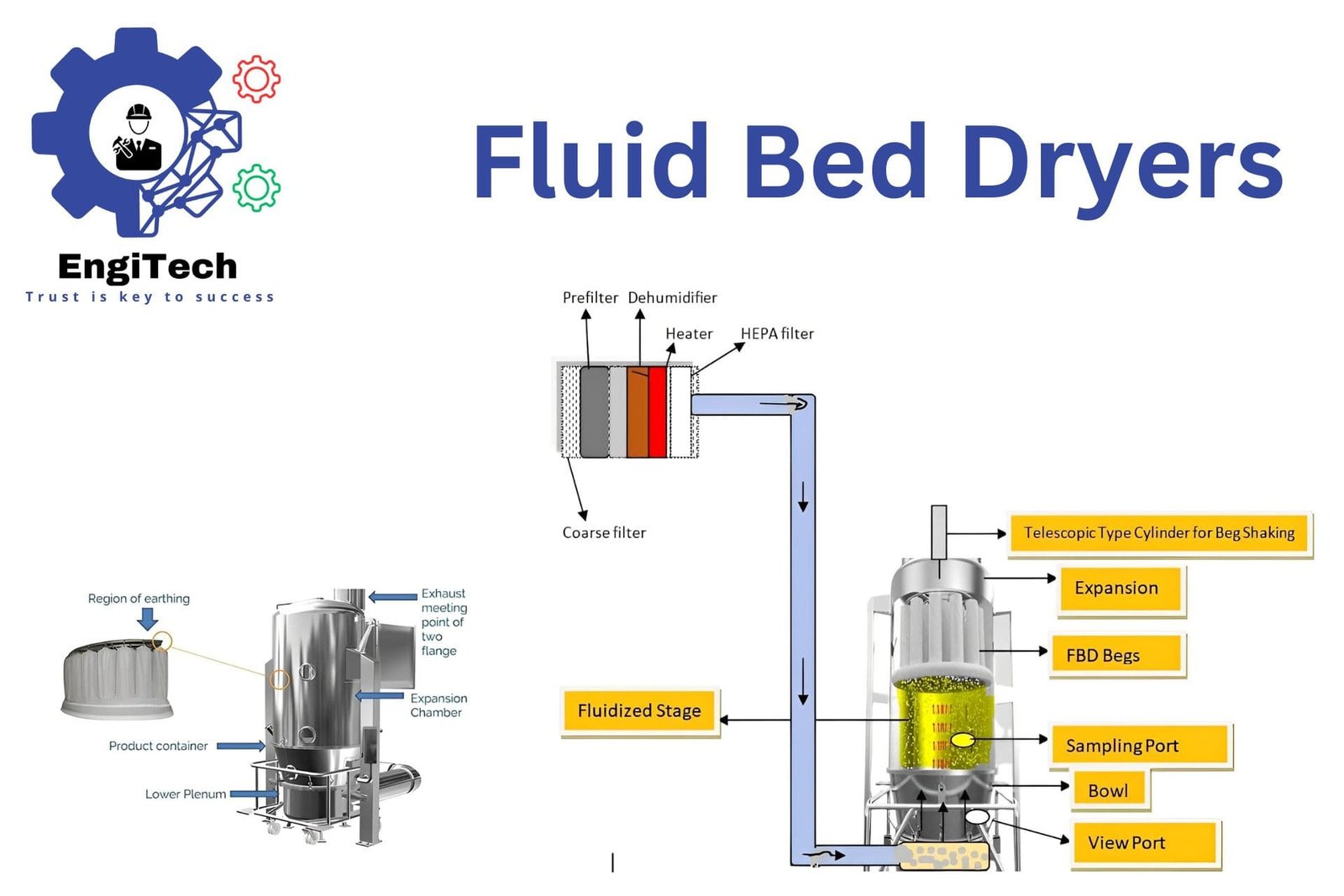
Fluid bed dryers (FBDs) revolutionize the drying process for particulate materials across various industries. By using a stream of hot air to fluidize the material, FBDs ensure efficient and uniform drying. This method is crucial for improving the quality and consistency of products in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
How Fluid Bed Dryers Work
- Fluidization: Place the material in the drying chamber. Introduce hot air from below at high velocity. The air lifts and suspends the particles, causing them to behave like a fluid.
- Heat Transfer: In this fluidized state, particles gain maximum contact with the hot air. This setup allows for rapid and uniform heat transfer, efficiently drying the material.
- Moisture Evaporation: As hot air flows through, it evaporates the moisture from the particles. The air stream carries away the evaporated moisture, leaving dry particles behind.
- Exhaust: The system then filters out any fine particles from the moist air before releasing it, ensuring a clean exhaust.

Types of Fluid Bed Dryers
Batch Fluid Bed Dryers:
- Ideal for small-scale production.
- Process specific amounts of material in each cycle.
Continuous Fluid Bed Dryers:
- Suitable for large-scale operations.
- Provide consistent quality and efficiency by processing materials in a continuous flow.

Vibratory Fluid Bed Dryers:
Effective for drying sticky or cohesive materials.
Use vibrations to assist fluidization.
Rotary Fluid Bed Dryers:
- Combine fluidization with rotary motion.
- Enhance mixing and drying efficiency for thorough processing.
Key Applications
Pharmaceuticals:
- Dry granules, pellets, and powders.
- Essential for producing stable and effective tablets and capsules.
Food Processing:
- Dry grains, cereals, fruits, and vegetables.
- Preserve nutritional value and extend shelf life.
Chemicals:
- Dry powders, crystals, and granules.
- Suitable for heat-sensitive materials, ensuring consistent quality.
Minerals:
- Dry minerals and ores.
- Improve handling and processing efficiency.
Biotechnology:
- Dry biological materials like enzymes and proteins.
- Maintain the stability and activity of sensitive materials.
Advantages of Using Fluid Bed Dryers
- Uniform Drying: Ensure consistent product quality by promoting maximum contact between hot air and particles.
- High Efficiency: Achieve rapid drying times with effective heat transfer and moisture evaporation.
- Versatility: Handle a wide range of materials, including heat-sensitive and diverse particulate properties.
- Scalability: Available in various sizes, suitable for both small-scale and large-scale production.
- Gentle Drying: Preserve the integrity and quality of delicate materials through a gentle drying process.
- Ease of Maintenance: Simplify cleaning and maintenance, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
Selecting the Right Fluid Bed Dryer
- Material Properties: Understand particle size, moisture content, and heat sensitivity to choose the right FBD type and optimize the drying process.
- Production Scale: Match the dryer to your production needs, considering batch or continuous processing.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for energy-efficient features like heat recovery systems and variable airflow control to reduce operating costs.
- Control Systems: Opt for advanced control systems that provide real-time monitoring and adjustment of process parameters for consistent product quality.
- Ease of Cleaning: Choose designs that facilitate quick and thorough cleaning to minimize downtime and ensure hygienic operation.

Technological Advances in Fluid Bed Dryers
- Advanced Control Systems: Modern FBDs come with sophisticated control systems for real-time process monitoring and adjustments, ensuring optimal drying conditions.
- Energy Efficiency Innovations: New designs incorporate features like heat recovery systems and variable airflow control to enhance energy efficiency.
- Multi-Stage Drying: Multi-stage FBDs allow precise control over different drying stages within a single unit, improving efficiency and product quality.
- Continuous Manufacturing Integration: Integrating FBDs with continuous manufacturing processes boosts efficiency and scalability, ideal for large-scale production.
- Customization: Advances in technology enable the customization of FBDs to meet specific application requirements, optimizing drying processes for various materials.
Conclusion
Fluid bed dryers play a transformative role in industrial drying, offering uniform and efficient drying of particulate materials. Understanding their working principle, types, applications, and benefits helps optimize the drying process. The latest advancements continue to expand the capabilities of FBDs, making them indispensable in modern industrial processes.
For more in-depth articles and resources on industrial drying technologies and innovations, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and applications in the industry!


