Experts Guide to CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machines

Did you know that the global CNC machine market is projected to reach $100.9 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.5%? Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines have transformed manufacturing forever, creating precision parts that would be impossible to produce manually. Whether you’re a manufacturing professional looking to upgrade your facility, an entrepreneur considering investment in CNC technology, or simply curious about how modern products are made, understanding CNC machines is increasingly essential in today’s automated world.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about CNC machines—from basic principles to advanced applications, selection criteria, maintenance best practices, and future trends. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to make informed decisions about CNC technology for your specific needs and understand how these remarkable machines are shaping our manufacturing future.
Table of Contents
What Are CNC Machines? Understanding the Basics
The Core Concept: How CNC Machines Work
CNC machines are automated manufacturing systems that execute pre-programmed sequences of commands to control machining tools. Unlike conventional manual machine tools that require constant operator attention, CNC machines follow digital instructions to perform complex manufacturing operations with minimal human intervention.
The “numerical control” in CNC refers to the precise positioning instructions that guide cutting tools along multiple axes. These instructions come from computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software, which translates 3D models into a specialized language called G-code that the CNC machine can understand and execute.
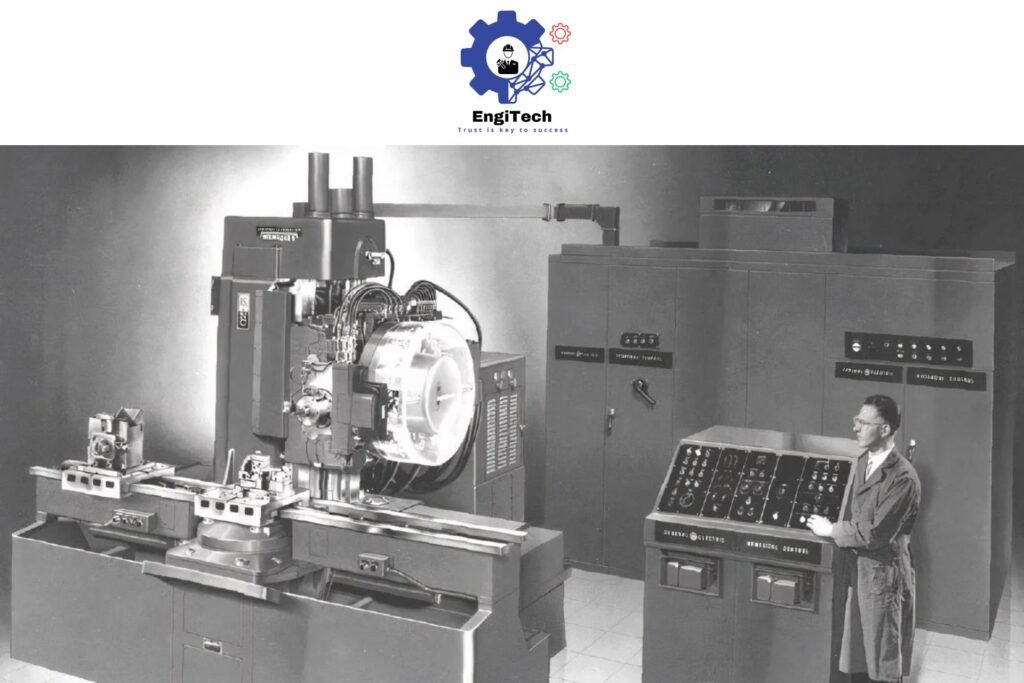
The Evolution of CNC Technology
CNC technology has come a long way since its inception in the 1940s and 1950s:
- 1940s-1950s: The concept of numerical control was developed at MIT, initially using punched tape to program machine movements
- 1960s-1970s: The introduction of computer controls began replacing earlier hardwired systems
- 1980s-1990s: Integration of CAD/CAM software revolutionized programming capabilities
- 2000s-Present: Advanced multi-axis machines, integrated sensors, IoT connectivity, and AI-enhanced operations have become standard
Today’s CNC machines represent the culmination of decades of technological advancement, offering unprecedented precision, speed, and versatility.

Key Components of a CNC Machine
Every CNC machine, regardless of type, shares these fundamental components:
- Controller: The “brain” of the system—a computer that processes programming instructions and converts them to mechanical actions
- Drive system: Motors (typically servo or stepper motors) that precisely position machine components
- Mechanical structure: The physical framework providing stability during operations
- Cutting tools: Specialized implements that perform the actual material removal
- Feedback systems: Sensors that monitor position, speed, and other parameters to ensure accuracy
- User interface: The means by which operators program and monitor the machine
Understanding these components helps explain how CNC machines achieve their remarkable precision—often working to tolerances measured in thousandths of an inch (or hundredths of a millimeter).
Types of CNC Machines: A Comprehensive Overview
CNC Mills: Versatile Material Removal
CNC milling machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. They’re extremely versatile and can create complex shapes with high precision. Modern CNC mills typically offer:
- 3-axis configurations: Moving in X, Y, and Z dimensions for basic cutting operations
- 4-axis and 5-axis capabilities: Adding rotational movements for creating more complex geometries
- Vertical or horizontal spindle orientation: Each offering specific advantages for different applications
Mills excel at creating parts with flat surfaces, contours, slots, holes, and three-dimensional shapes, making them among the most common CNC machines in manufacturing facilities.
CNC Lathes: Masters of Rotational Symmetry
While mills keep the workpiece stationary and move cutting tools, CNC lathes do the opposite—they rotate the workpiece against stationary cutting tools. This design makes lathes ideal for creating parts with rotational symmetry:
- Cylindrical components
- Threads and grooves
- Tapered shapes
- Contoured profiles
Modern CNC lathes often include “live tooling” capabilities that allow milling operations to be performed on the same machine, significantly expanding their versatility.
CNC Routers: Large-Format Precision
CNC routers function similarly to mills but are optimized for working with larger materials, particularly:
- Wood and wood composites
- Plastics and acrylics
- Soft metals like aluminum
- Foam and composite materials
With their expansive work areas, CNC routers excel in industries like furniture manufacturing, sign making, and architectural millwork.
Plasma, Laser, and Waterjet Cutters
These specialized CNC machines use different energy sources to cut materials:
- Plasma cutters: Use electrically charged gas to cut conductive materials, primarily metals
- Laser cutters: Employ focused light beams for precise cutting and engraving of various materials
- Waterjet cutters: Utilize high-pressure water streams (often with abrasive additives) to cut virtually any material
Each cutting technology offers specific advantages in terms of precision, material compatibility, cut quality, and operating costs.
EDM Machines: Precision Through Electrical Discharge
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) uses electrical sparks to erode material with extreme precision. Two primary types exist:
- Wire EDM: Uses a thin wire electrode to cut through conductive materials with remarkable accuracy
- Sinker EDM: Employs a shaped electrode to create precise cavities and complex shapes
EDM technology excels at working with hardened materials and creating shapes that would be difficult or impossible with conventional cutting methods.
3D Printers and Additive Manufacturing
While traditional CNC machines remove material (subtractive manufacturing), CNC-controlled 3D printers add material layer by layer (additive manufacturing). Modern manufacturing often combines both approaches to leverage their respective strengths.

CNC Programming: From Design to Finished Part
CAD/CAM Software Workflow
Creating parts with CNC machines typically follows this workflow:
- Design phase: Creating a digital model using CAD software
- Manufacturing preparation: Using CAM software to define toolpaths and machining parameters
- Post-processing: Converting toolpaths into machine-specific G-code
- Execution: Loading the program into the CNC controller and running the operation
This digital workflow enables manufacturers to visualize and simulate operations before cutting begins, reducing errors and optimizing production efficiency.
G-Code: The Language of CNC
G-code (sometimes called RS-274) is the standard programming language for CNC machines. While most operators now use CAM software rather than writing G-code manually, understanding its basic principles remains valuable:
- G-commands: Control motion and machine states (G01 for linear movement, G02/G03 for circular movement, etc.)
- M-commands: Handle miscellaneous functions like coolant control and tool changes
- Coordinate specifications: Define where and how the machine should move
Modern CNC systems often add proprietary extensions to standard G-code, enhancing capabilities for specific applications.
Advanced Programming Techniques
As CNC technology has evolved, so have programming approaches:
- Parametric programming: Using variables and equations to create flexible, adaptable programs
- Macro programming: Creating reusable routines for common operations
- Conversational programming: User-friendly interfaces that simplify programming for less technical operators
- Feature-based machining: Automatically generating toolpaths based on part features rather than raw geometry
These advanced techniques help manufacturers maximize productivity while maintaining precision and quality.
Selecting the Right CNC Machine: Key Considerations
Matching Machine Capabilities to Your Requirements
When evaluating CNC machines, consider:
- Material compatibility: Ensure the machine can effectively work with your target materials
- Size capacity: Confirm the work envelope accommodates your typical part dimensions
- Precision requirements: Verify the machine can maintain tolerances needed for your applications
- Production volume: Match machine speed and automation features to your throughput needs
- Complexity of parts: Choose axis configuration based on the geometrical complexity of typical parts
Carefully matching machine capabilities to your specific requirements prevents both underbuying (limiting capabilities) and overbuying (wasting resources on unnecessary features).
Evaluating Quality and Performance Metrics
Key performance indicators for CNC machines include:
- Positioning accuracy: How precisely the machine can move to a specified location
- Repeatability: Consistency when returning to the same position multiple times
- Resolution: The smallest increment of movement the machine can reliably execute
- Rigidity: Resistance to deflection during cutting operations
- Maximum speeds and feeds: Limitations on cutting parameters that affect production rates
These metrics directly impact part quality, production efficiency, and overall equipment effectiveness.
Cost Considerations Beyond Purchase Price
The true cost of CNC equipment extends far beyond the initial purchase:
- Installation and setup expenses
- Training requirements for operators and programmers
- Tooling and fixturing investments
- Maintenance costs over the machine’s lifetime
- Energy consumption during operation
- Software licensing for programming and operation
Calculating the total cost of ownership provides a more accurate basis for comparing options than focusing solely on purchase price.
CNC Machine Setup and Operation: Best Practices
Workholding Solutions: Securing Materials Effectively
Proper workholding is critical for CNC machining success:
- Vises: Traditional mechanical clamps for holding prismatic parts
- Chucks: Typically used in lathes to grip cylindrical workpieces
- Vacuum tables: Common in routing applications for sheet materials
- Custom fixtures: Purpose-built devices for specific parts or families of parts
- Magnetic workholding: Used for ferrous materials on surface grinders and milling applications
The ideal workholding solution balances security (preventing movement during cutting) with accessibility (allowing tool paths to reach necessary features).
Tool Selection and Management
Cutting tools directly impact machining quality, efficiency, and cost:
- Material considerations: Match tool materials (high-speed steel, carbide, ceramic, etc.) to workpiece materials
- Geometry optimization: Select appropriate cutting angles and features for specific operations
- Tool life management: Implement systems to track usage and replace tools before failure
- Tool presetting: Measure tools offline to minimize machine downtime during tool changes
- Tool libraries: Maintain digital databases of tool specifications for programming accuracy
Effective tool management maximizes productivity while maintaining part quality and minimizing unexpected downtime.
Optimizing Machining Parameters
Fine-tuning cutting parameters significantly impacts results:
- Cutting speeds: The velocity of the tool relative to the workpiece
- Feed rates: How quickly the tool advances through the material
- Depth of cut: How much material is removed in each pass
- Coolant application: Type and delivery method of cooling and lubrication
- Entry and exit strategies: How tools engage and disengage from the material
Modern CAM software often suggests starting parameters, but optimization for specific applications typically requires experience and experimentation.
Maintaining CNC Machines: Ensuring Longevity and Precision
Preventive Maintenance Schedules
Regular maintenance prevents costly breakdowns and maintains precision:
- Daily checks: Visual inspections, coolant levels, and basic cleaning
- Weekly tasks: Lubricant levels, filter conditions, and more thorough cleaning
- Monthly procedures: Alignment checks, belt tensions, and wear inspections
- Quarterly operations: Calibration verification and preventive part replacements
- Annual maintenance: Comprehensive inspection and overhaul of critical systems
Documenting all maintenance activities creates valuable historical data for predicting future needs and optimizing maintenance intervals.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even well-maintained machines occasionally develop problems:
- Positioning errors: Often related to backlash, loose components, or controller issues
- Finish quality problems: Frequently caused by tool wear, vibration, or parameter selection
- Unexpected shutdowns: Typically triggered by safety systems detecting abnormal conditions
- Communication errors: Usually stemming from software conflicts or network problems
- Mechanical binding: Generally resulting from debris, damage, or lubrication failures
Systematic troubleshooting approaches help identify root causes quickly, minimizing downtime and preventing recurrence.
Calibration and Accuracy Verification
Maintaining precision requires periodic verification and adjustment:
- Laser calibration: Using interferometer technology to measure and correct positioning errors
- Ball bar testing: Evaluating circular interpolation accuracy to detect mechanical issues
- Artifact inspection: Creating test parts with known dimensions to verify overall accuracy
- Thermal compensation: Adjusting for dimensional changes caused by temperature variations
- Electronic leveling: Ensuring machine geometrical alignment remains within specifications
Regular calibration prevents the gradual degradation of accuracy that can occur over time due to wear, impacts, and environmental factors.
Advanced CNC Applications and Innovations
Multi-Axis Machining: Beyond Traditional Limitations
Advanced CNC machines with 4, 5, or even more axes enable:
- Complex geometries: Creating organic shapes and undercuts impossible with 3-axis machines
- Single-setup manufacturing: Completing parts in one operation rather than multiple setups
- Improved surface finish: Maintaining optimal tool orientation relative to surfaces
- Enhanced accuracy: Eliminating alignment errors from multiple setups
- Reduced cycle times: Minimizing non-cutting time through optimized tool paths
While multi-axis machining requires more sophisticated programming and setup, the results often justify the additional complexity.
Automation and Robotics Integration
Modern CNC cells frequently incorporate automation for greater efficiency:
- Pallet changers: Allowing setup of new workpieces while the machine continues operating
- Robotic loading/unloading: Automating material handling between operations
- Tool changing systems: Automatically selecting and installing appropriate cutting tools
- In-process measurement: Verifying dimensions during machining to ensure quality
- Adaptive control systems: Adjusting parameters based on real-time feedback
These automation technologies enable “lights-out manufacturing”—fully unattended operation during nights and weekends.
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
CNC machines are central to Industry 4.0 implementations:
- IoT connectivity: Machine monitoring and data collection for analysis
- Digital twins: Virtual representations that mirror physical machines in real-time
- Predictive maintenance: Using data patterns to anticipate failures before they occur
- Remote monitoring and operation: Managing equipment from anywhere in the world
- Artificial intelligence integration: Optimizing parameters and detecting anomalies automatically
These smart manufacturing capabilities transform traditional CNC operations into data-driven, continuously improving production systems.
CNC Machining: Industries and Applications
Aerospace: Where Precision Meets Performance
The aerospace industry relies heavily on CNC machining for:
- Structural components: Lightweight yet strong airframe parts
- Engine components: Precision turbine blades and combustion chambers
- Hydraulic system parts: Critical fluid control components
- Tooling and fixtures: Manufacturing equipment for composite structures
- Prototype development: Rapid creation of test components
CNC’s ability to work with exotic alloys while maintaining tight tolerances makes it irreplaceable in aerospace manufacturing.
Automotive Manufacturing: Balancing Volume and Precision
Automotive applications for CNC machining include:
- Engine components: Blocks, heads, crankshafts, and connecting rods
- Transmission parts: Gears, shafts, and valve bodies
- Molds and dies: For mass production of plastic and metal components
- Prototype parts: For testing new designs before full production
- Custom aftermarket components: Performance and specialty parts
CNC machines in automotive settings often emphasize throughput while maintaining necessary quality standards.
Medical Device Manufacturing: When Lives Depend on Precision
Medical applications demand the highest levels of precision and consistency:
- Implantable devices: Joint replacements, dental implants, and bone screws
- Surgical instruments: Precision tools for delicate procedures
- Diagnostic equipment components: Parts for imaging and testing devices
- Custom patient-specific devices: Tailored solutions for unique anatomical requirements
- Laboratory equipment: Precision apparatus for research and testing
The medical industry often pushes CNC capabilities to their limits, requiring exceptional surface finishes and dimensional control.
Consumer Electronics: Miniaturization and Complexity
Electronics manufacturing employs CNC machining for:
- Enclosures and housings: Precisely fitting protective shells for devices
- Heat sinks and thermal management: Components that dissipate heat effectively
- Testing fixtures: Custom equipment for quality assurance
- Prototype development: Rapid iteration of new designs
- Mold tooling: Production equipment for plastic injection molding
The trend toward smaller, more feature-rich electronics continuously challenges CNC capabilities.
The Future of CNC Technology: Emerging Trends
Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining Additive and Subtractive Processes
Next-generation machines increasingly combine capabilities:
- 3D printing with integrated machining: Adding material, then finishing with precision cutting
- Wire arc additive manufacturing with CNC finishing: Creating near-net-shape parts efficiently
- Laser cladding with machining centers: Repairing and modifying existing components
- Sheet lamination with CNC contouring: Building composite structures layer by layer
These hybrid approaches leverage the strengths of both additive and subtractive technologies.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
AI is transforming CNC operations through:
- Autonomous optimization: Self-adjusting cutting parameters for optimal results
- Predictive maintenance: Anticipating failures before they cause downtime
- Quality assurance: Detecting anomalies that might indicate problems
- Design optimization: Suggesting improvements based on manufacturing data
- Energy efficiency: Minimizing power consumption while maintaining performance
As these technologies mature, they’re making CNC machining smarter, more efficient, and more reliable.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in CNC operations:
- Energy-efficient machines: Reducing power consumption through improved designs
- Minimal quantity lubrication: Decreasing coolant use while maintaining performance
- Material optimization: Reducing waste through improved nesting and programming
- Recycling programs: Capturing and reprocessing chips and scrap material
- Longer machine lifecycles: Designing equipment for durability and upgradeability
These sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but often reduce operating costs as well.
FAQs About CNC Machines
What’s the difference between CNC machining and conventional machining?
Conventional machining relies heavily on operator skill and manual control, while CNC machining uses computer-controlled automation to execute precise, repeatable operations. CNC machines follow programmed instructions, maintaining consistent quality regardless of operator experience. This automation enables complex operations that would be difficult or impossible to perform manually and allows one operator to simultaneously manage multiple machines.
How accurate are CNC machines?
Modern CNC machines typically achieve positioning accuracies between ±0.0001″ and ±0.001″ (0.0025mm to 0.025mm), depending on machine type, quality, and maintenance condition. High-precision machines used in aerospace and medical applications can achieve even tighter tolerances. However, actual part accuracy depends on multiple factors beyond machine capabilities, including tool selection, fixturing methods, material properties, and environmental conditions like temperature stability.
What materials can be machined using CNC equipment?
CNC machines can process an extraordinarily wide range of materials:
- Metals: From soft aluminum to hardened tool steels and exotic alloys
- Plastics: Both engineering-grade thermoplastics and commodity materials
- Wood and composites: Natural lumber, plywood, particle board, and fiber-reinforced materials
- Ceramics and glass: Using specialized tools and techniques
- Foams and soft materials: For prototyping, packaging, and specialized applications
The appropriate machine type, tooling, and parameters must be selected based on specific material properties.
How much does a CNC machine cost?
CNC machine prices span an enormous range based on capabilities:
- Entry-level desktop mills and routers: $1,000-$10,000
- Mid-range industrial equipment: $25,000-$200,000
- High-end multi-axis machining centers: $250,000-$1,000,000+
- Specialized or extremely large machines: Can exceed several million dollars
Remember that purchase price represents only part of the total cost of ownership, which also includes installation, training, tooling, maintenance, and operational expenses.
What skills are needed to operate CNC machines?
Modern CNC operation requires a blend of technical skills:
- CAD/CAM software proficiency: For creating and preparing digital models
- CNC programming knowledge: Understanding G-code and machine control interfaces
- Setup expertise: Workholding, tool selection, and machine preparation
- Measurement and quality control: Verifying dimensional accuracy and surface quality
- Problem-solving abilities: Diagnosing and resolving issues that arise during production
While full mastery takes time, basic CNC operation can be learned relatively quickly with proper training and guidance.
Conclusion: Embracing the CNC Revolution
Computer Numerical Control machines have fundamentally transformed manufacturing, enabling levels of precision, complexity, and efficiency previously impossible. From aerospace components requiring perfect accuracy to mass-produced consumer goods needing consistent quality, CNC technology touches virtually every aspect of our modern world.
As we’ve explored in this comprehensive guide, CNC machines continue to evolve—incorporating more axes, smarter controls, greater automation, and tighter integration with other manufacturing technologies. Understanding these capabilities and trends positions manufacturers to make informed decisions about implementing and optimizing CNC technology in their operations.
Whether you’re considering your first CNC purchase, looking to upgrade existing equipment, or simply fascinated by the technology behind modern manufacturing, staying informed about CNC developments will remain valuable as these remarkable machines continue reshaping how we create the physical objects that drive our economy and enhance our lives.
For more detailed information and resources on CNC machines and their applications, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated with the latest advancements and best practices in CNC technology!