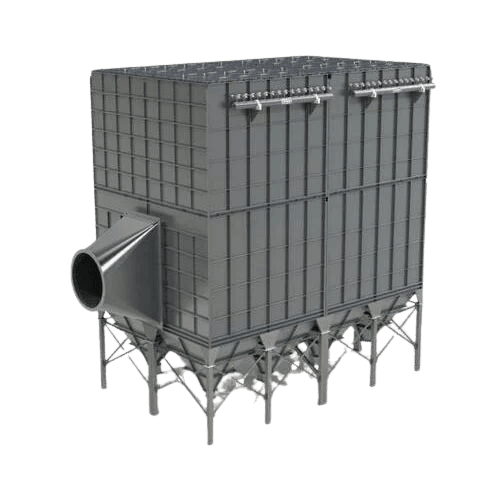
Comprehensive Guide to Bag Filters: Functionality, Types, and Benefits

In industries where dust, particulate matter, and contaminants pose challenges, bag filters play a crucial role in maintaining air quality and protecting equipment. From cement plants to pharmaceuticals and metal processing, bag filters are essential for ensuring cleaner air and a safer work environment. In this guide, we’ll delve deep into what bag filters are, their functionality, different types, and the specific advantages they offer across various industries.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Bag Filters
Bag filters, also known as fabric filters or dust collectors, are air pollution control devices designed to capture and remove particles, dust, and other contaminants from industrial exhaust or gas streams. These filters are highly effective in capturing particulate matter that could otherwise escape into the atmosphere, making them essential in industries where dust control is crucial.
Bag filters consist of fabric filter bags suspended in a housing, and the design ensures that dust-laden air passes through the bags, trapping particulates on the surface while clean air exits. Due to their high filtration efficiency, bag filters are commonly used in industries ranging from manufacturing to energy production.
How Bag Filters Work
The working principle of bag filters is relatively simple yet highly effective. As air laden with dust or particulate matter is drawn into the system, it flows through the filter media (the bag). This bag is made of a fabric material, usually treated to enhance its filtration properties. Particles are trapped on the fabric’s surface, allowing clean air to pass through. Over time, the collected dust forms a “dust cake,” which further improves the filtration process.
Once the dust cake becomes too thick, the bag filter undergoes a cleaning process (either manual or automated), depending on the type of system. This cleaning dislodges the dust, which then falls into a hopper for disposal or recycling. The cycle then repeats, ensuring continuous operation without compromising air quality.
Types of Bag Filters
Understanding the different types of bag filters can help industries choose the most suitable option for their specific applications. The three primary types are Pulse Jet, Reverse Air, and Shaker bag filters.
3.1 Pulse Jet Bag Filters
Pulse Jet Bag Filters are among the most popular types of bag filters. In this design, the bag filter is cleaned by a high-pressure jet of air that dislodges dust particles from the filter surface. This process happens continuously without interrupting filtration, making Pulse Jet Bag Filters ideal for large-scale industrial applications where downtime is costly.
Advantages:
- High efficiency in dust collection
- Continuous operation
- Suitable for fine dust particles
3.2 Reverse Air Bag Filters
Reverse Air Bag Filters operate by reversing the airflow direction, sending air back through the filter bags to dislodge dust particles. This cleaning mechanism is slower and less aggressive than Pulse Jet cleaning, making Reverse Air Bag Filters suitable for more sensitive applications.
Advantages:
- Gentle on filter bags, extending their lifespan
- Suitable for medium to large particulate matter
- Lower energy consumption during cleaning
3.3 Shaker Bag Filters
Shaker Bag Filters clean by physically shaking the bags to dislodge the dust cake. This method requires periodic downtime, as the system must be paused for cleaning. Despite this, Shaker Bag Filters are often used in smaller-scale applications where continuous operation is not critical.
Advantages:
- Simple operation
- Low capital cost
- Effective for larger particles
Key Components of Bag Filters
To better understand how bag filters work and their applications, it’s essential to know their primary components:
- Filter Bags: The heart of the system, made from fabrics like polyester, fiberglass, or other specialized materials.
- Cages: Provide structural support to the filter bags, preventing collapse.
- Dust Hopper: Collects dislodged dust after the cleaning process.
- Cleaning Mechanism: Varies depending on the type (pulse jet, reverse air, shaker).
- Inlet and Outlet Ducts: Ensure proper airflow into and out of the system.
These components work in tandem to maintain effective filtration and dust removal.
Industries That Use Bag Filters
Bag filters find application in various industries, each with its own unique filtration needs. Below are some of the key industries that heavily rely on bag filters:
- Cement Industry: Controls dust emissions from cement kilns and grinding mills.
- Pharmaceuticals: Maintains cleanliness in production environments where particulate control is critical.
- Metal Processing: Captures metallic dust and fumes from smelting and welding processes.
- Power Plants: Filters particulate matter from boiler exhaust gases, protecting the environment.
- Food Processing: Ensures clean air in food production, packaging, and transportation processes.
In each of these industries, bag filters contribute to cleaner air and regulatory compliance by reducing emissions.
Benefits of Bag Filters
Bag filters offer a range of advantages, which is why they are the preferred choice for many industrial dust control applications. Here are some key benefits:
- High Filtration Efficiency: Bag filters can capture particles as small as 1 micron, ensuring optimal air cleanliness.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for a wide variety of dust types and industries.
- Compliance with Environmental Standards: Many industries face strict regulations for emissions, and bag filters help meet those standards.
- Cost-Effective: Long-lasting and low maintenance, making them a cost-efficient solution over time.
- Energy Efficiency: While the cleaning mechanisms may vary, modern bag filters are designed to consume minimal energy.
Choosing the Right Bag Filter for Your Application
When selecting a bag filter, it’s important to consider several factors, including:
- Type of Dust: Fine dust requires different filtration media than coarser dust.
- Temperature: Certain filter materials are better suited to high temperatures.
- Moisture Levels: Moist environments can cause dust to clump, making it harder to filter effectively.
- Space Constraints: Some filter systems, such as Pulse Jet, require more space for operation.
By considering these factors, industries can select the right bag filter to ensure effective dust control.
Bag Filter Maintenance and Best Practices
For optimal performance, regular maintenance is crucial. Below are some best practices to maintain your bag filter system:
- Inspect Filter Bags Regularly: Look for wear and tear, as damaged bags can compromise efficiency.
- Monitor Airflow: A sudden drop in airflow can indicate that the filter bags are clogged.
- Clean Filter Bags Properly: Ensure that the cleaning mechanism is functioning as intended.
- Check Seals and Gaskets: Any leaks in the system can reduce its overall efficiency.
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of the bag filter and ensures continued high performance.
Common Problems and Solutions in Bag Filters
Bag filters are generally reliable, but problems can still arise. Some common issues include:
- Bag Leakage: This can occur if the bags are not properly sealed or are damaged.
- Solution: Regularly check for leaks and replace damaged bags promptly.
- Inadequate Cleaning: If the cleaning mechanism fails, dust can build up and reduce efficiency.
- Solution: Ensure cleaning systems are working and inspect the filter bags for blockages.
- Abrasion of Bags: Over time, dust particles can wear down the filter fabric.
- Solution: Use filter bags made from more robust materials, such as fiberglass, if abrasion is an issue.
Bag Filter Efficiency and Environmental Impact
In recent years, environmental concerns have led to more stringent regulations on industrial emissions. Bag filters play a vital role in helping industries meet these standards by capturing harmful particulates before they can be released into the atmosphere.
Environmental Impact:
- Reduces air pollution by trapping dust and particulate matter.
- Promotes compliance with environmental regulations such as the EPA’s Clean Air Act.
- Contributes to workplace safety by improving air quality for workers.
By implementing bag filters, industries not only comply with regulations but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about bag filters
1. What are bag filters?
Bag filters are air pollution control devices designed to capture dust, particulate matter, and other contaminants from industrial exhaust or gas streams. They consist of fabric filter bags that trap particles as air flows through them, allowing clean air to exit.
2. How do bag filters work?
Bag filters operate by passing dust-laden air through a fabric filter bag. Particles are trapped on the fabric’s surface, while clean air passes through. Over time, the filter collects dust, which is then removed through a cleaning mechanism, such as pulse jet or reverse air, to maintain efficiency.
3. What are the different types of bag filters?
The main types of bag filters include:
- Pulse Jet Bag Filters: Use high-pressure jets of air for cleaning.
- Reverse Air Bag Filters: Reverse the airflow to dislodge dust.
- Shaker Bag Filters: Utilize mechanical shaking to remove dust.
4. What industries commonly use bag filters?
Bag filters are widely used in various industries, including:
- Cement manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Metal processing
- Power generation
- Food processing
5. How do you choose the right bag filter for your application?
Selecting the right bag filter depends on factors such as the type of dust, temperature, moisture levels, and space constraints. It is important to consider these factors to ensure optimal filtration performance.
6. What are the benefits of using bag filters?
Benefits of bag filters include:
- High filtration efficiency
- Versatility in applications
- Compliance with environmental standards
- Cost-effectiveness
- Energy efficiency
7. How often should bag filters be maintained?
Regular maintenance is crucial for bag filters. Inspect filter bags, monitor airflow, and ensure proper cleaning at regular intervals. Maintenance frequency depends on the application and dust load but typically includes checks every few months.
8. What are common problems with bag filters and their solutions?
Common problems include:
- Bag Leakage: Check and replace damaged bags.
- Inadequate Cleaning: Ensure cleaning mechanisms are functioning properly.
- Abrasion of Bags: Use more durable filter materials if needed.
9. How do bag filters impact the environment?
Bag filters help reduce air pollution by trapping dust and particulate matter before it is released into the atmosphere. This contributes to compliance with environmental regulations and improves overall air quality.
10. What is the lifespan of a bag filter?
The lifespan of a bag filter depends on factors such as the type of dust, operating conditions, and maintenance. With proper care, filter bags can last several years, but regular inspections and timely replacements are necessary to ensure continuous performance.
These FAQs address the most common queries related to bag filters, providing valuable information for users seeking to understand their functionality, benefits, and maintenance.
Conclusion: Bag Filters – A Vital Part of Industrial Filtration
Bag filters are essential components in many industries, providing an effective solution for dust control and air quality management. Whether it’s the cement industry, food processing, or metalworking, bag filters offer a versatile and efficient way to capture particulate matter, ensuring cleaner air and a safer environment. Their role in reducing emissions and meeting environmental regulations cannot be overstated.
When selecting a bag filter, it’s important to choose one that fits the specific needs of your industry and application. With proper maintenance and attention to common issues, bag filters can offer long-lasting, cost-effective performance.
To learn more about bag filters and how they can optimize dust control in your industry, visit EngiTech for comprehensive resources and the latest updates on industrial filtration technology.