Imagine running a fast-paced production line where every second counts. You have a thousand units to label or package, your team is rushing around to meet deadlines, and a single jam can throw off your entire schedule. Sound familiar? If you’ve ever faced the anxiety of manual bottlenecks in labeling, sealing, or product assembly, then discovering an applicator machine might be the game-changer you need.
In this comprehensive guide, we’re about to unravel all the complexities surrounding applicator machines. You’ll learn what they are, how they work, the different types on the market, and how to choose the right one for your specific needs. We’ll also dive into best practices for maintenance, troubleshooting, and safety—essential knowledge if you want to keep your operations running smoothly.
By the end of this article, you’ll not only understand how an applicator machine can revolutionize your packaging or labeling line, but you’ll also have the confidence to select, install, and optimize one for maximum efficiency. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What Is an Applicator Machine?
At its core, an applicator machine is a piece of equipment designed to automatically apply a substance—such as labels, adhesives, or coatings—onto a product or surface. These machines are common in industries where products must be labeled, wrapped, glued, or otherwise modified with precision and speed. The primary goal is to reduce manual labor, minimize errors, and improve throughput. In an increasingly competitive market, the ability to quickly and accurately apply a label or packaging material can make or break your bottom line.
The Rise of Automation in Modern Production
Automation isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a driving force reshaping the way we manufacture, package, and distribute goods. As labor costs increase and consumer demands shift toward personalized or small-batch products, businesses must adapt. Applicator machines fulfill a critical role in this evolving ecosystem by handling repetitive, detail-oriented tasks with little margin for error.
Why Businesses Turn to Applicator Machines
- Consistency: An automated system can apply the same label or adhesive with precise placement, eliminating the slight deviations that often occur with manual application.
- Speed: Applicator machines can operate around the clock, offering higher throughput rates than human workers.
- Scalability: Need to ramp up production for a seasonal spike? Automated systems are easier to scale as your business grows.
- Quality Control: Modern applicator machines can be integrated with sensors, vision systems, or scanning devices that verify the correct placement and orientation of a label or material.
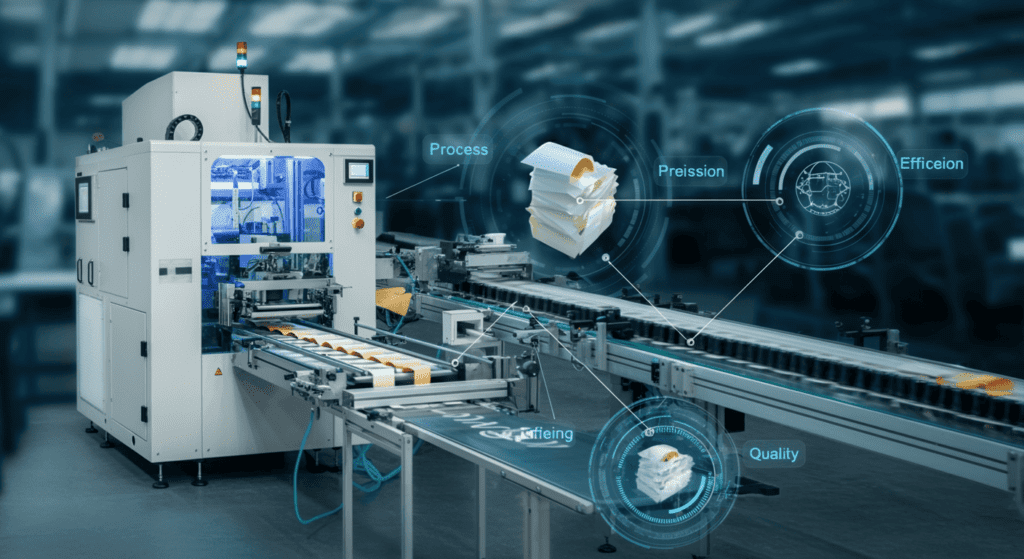
Types of Applicator Machines
Applicator machines come in a variety of forms, each specialized for different tasks or industries. Understanding these categories will help you pinpoint which machine best suits your needs.
- Label Applicators
- Overview: Designed specifically for applying labels of all shapes and sizes to products or packaging surfaces.
- Use Cases: Food packaging, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and any scenario requiring branded labeling or barcodes.
- Adhesive Applicators
- Overview: Dispense and apply adhesives—hot melt, cold glue, or pressure-sensitive adhesives—onto surfaces.
- Use Cases: Carton sealing, bookbinding, woodworking, and any process requiring a strong, consistent bond.
- Coating Applicators
- Overview: Apply thin films or coatings (e.g., paints, varnishes, protective coatings) on various surfaces.
- Use Cases: Automotive industries for painting and finishing, furniture manufacturing for protective coats, electronics assembly for conformal coatings.
- Thermal Transfer Applicators
- Overview: Combine the functionality of printing and applying labels in one integrated system, using heat to transfer ink onto a label.
- Use Cases: Industries that need on-demand printing of variable data like expiration dates, batch codes, or barcodes.
- Tape and Seal Applicators
- Overview: Specialized in applying sealing tapes or shrink wraps.
- Use Cases: E-commerce fulfillment centers, logistics operations, and packaging lines that require consistent and secure sealing.
- Custom-Built Applicators
- Overview: Tailored to unique product shapes, specialized materials, or unusual production environments.
- Use Cases: Complex shapes, delicate surfaces, or highly regulated industries needing specialized handling.
Each category has its own sub-variations, but this overview highlights the breadth of applicator machines available. To make an informed decision, you should match the machine’s core capabilities with your specific production requirements.
Key Components of an Applicator Machine
Although designs can differ drastically, most applicator machines share a common set of components that ensure smooth, reliable operation.
Feeder or Unwinder
- Purpose: Holds and guides the material (labels, tape, or adhesive film) into the application zone.
- Design Consideration: Must align perfectly with the rest of the machine to avoid material wastage or misalignment.
Applicator Head
- Purpose: The “business end” of the machine, where the label or adhesive meets the product.
- Design Consideration: Some applicator heads are pneumatic, while others are electric. The choice depends on speed requirements and the material properties you’re working with.
Conveyor or Product Transport System
- Purpose: Moves products into alignment with the applicator head.
- Design Consideration: Must be adjustable for different product sizes and shapes. Speed synchronization with the applicator head is crucial.
Sensors and Control Systems
- Purpose: Detect product position, verify label presence, and manage real-time adjustments.
- Design Consideration: Advanced systems use optical, ultrasonic, or laser sensors. They often integrate with PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) or industrial PCs for more complex control.
Discharge or Rewinder
- Purpose: Collects spent liner or backing materials, ensuring a clutter-free work area.
- Design Consideration: Must handle consistent tension to prevent tearing or jamming.
In sophisticated systems, you might also find additional elements like a vision inspection system, reject stations, and advanced HMI (Human-Machine Interface) panels for real-time operational monitoring.
How Does an Applicator Machine Work?
Let’s break down the essential workflow to see how an applicator machine achieves precision and speed simultaneously.
- Material Loading
- Process: An operator or automated feeder loads the roll of labels or adhesives into the machine.
- Goal: Ensure proper alignment and tension for smooth feeding.
- Product Infeed
- Process: The product travels along a conveyor or is placed manually at the correct station.
- Goal: Position the product at the exact point where it meets the applicator head.
- Sensing and Detection
- Process: Photoelectric or other sensors detect the presence and orientation of the product.
- Goal: Trigger the applicator head at the perfect moment to apply the material.
- Application
- Process: The applicator head dispenses the label, adhesive, or coating onto the product.
- Goal: Achieve precise placement with minimal margin of error.
- Verification
- Process: Some systems use cameras or sensors to confirm the successful application.
- Goal: Immediately reject or rework products if the application fails or is off-position.
- Discharge
- Process: The product continues down the production line, or an automated arm picks it up for further processing.
- Goal: Remove finished products without disrupting flow or speed.
- Waste Management
- Process: The spent liner or backing goes onto a rewinder or waste collection system.
- Goal: Keep the workspace clear and safe.
This loop continues indefinitely until you change rolls or adjust settings for a new product run. The beauty of an applicator machine is how seamlessly all these steps flow once the system is configured correctly.
Common Uses and Industries for Applicator Machines
Applicator machines appear in a vast range of sectors. Understanding these helps illustrate just how versatile these systems can be.
Food & Beverage
- Scenario: Accurate labeling of nutritional facts, expiration dates, or promotional stickers.
- Why It Matters: Regulatory compliance is critical, and brand consistency is essential to consumer trust.
Pharmaceutical & Healthcare
- Scenario: Precise and tamper-evident labeling for medication bottles or medical devices.
- Why It Matters: Errors can have serious consequences, so reliability and accuracy are paramount.
E-Commerce & Logistics
- Scenario: High-speed application of shipping labels and sealing tapes to parcels.
- Why It Matters: Speed and efficiency can make or break an e-commerce operation’s profit margins.
Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Scenario: Decorative labels on oddly shaped containers, often with a brand’s aesthetic in mind.
- Why It Matters: Aesthetics and brand identity are crucial in a competitive market.
Automotive & Industrial Manufacturing
- Scenario: Labels that hold safety information, part numbers, or barcodes for inventory tracking.
- Why It Matters: Ensures that automotive parts can be traced and identified quickly, meeting stringent regulatory requirements.
From small boutique operations to global conglomerates, an applicator machine can drastically improve workflow efficiency and quality control in nearly any industry handling repetitive labeling or adhesive-related tasks.
How to Choose the Right Applicator Machine
Selecting an applicator machine goes beyond just looking at price tags and brand names. It requires a thorough assessment of your operational needs, product characteristics, and future growth plans. Below are the key factors to consider.
Production Volume and Speed
- High-Volume Operations: Look for robust, high-speed machines capable of handling thousands of units per hour.
- Small-Scale or Niche Lines: You might opt for a smaller, more flexible applicator that’s cost-effective and easy to switch between product lines.
Type of Material or Label
- Label Adhesive: Pressure-sensitive labels vs. heat-activated adhesives may require different dispensing technologies.
- Substrate Material: Porous vs. non-porous surfaces may influence adhesion properties and drying times.
Product Shape and Size
- Consistency: Are your products identical in shape and size, or do you deal with multiple SKUs?
- Complex Geometries: Some applicator heads can handle curved, cylindrical, or tapered surfaces better than others.
Integration with Existing Systems
- PLC Compatibility: Ensure the machine can communicate with other devices on your production floor.
- Vision or Barcode Systems: If you rely on quality control or inventory tracking, check if the machine supports real-time scanning or coding.
Budget and ROI
- Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings: While some machines are more expensive upfront, they may reduce labor and error rates, delivering a faster payback.
- Service and Maintenance Contracts: Don’t overlook ongoing support, spare parts availability, and training when evaluating total costs.
Your ultimate goal is to find an applicator machine that balances these elements effectively. Conduct thorough research, request product demonstrations, and consult with experts to ensure a wise investment that meets your short- and long-term objectives.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Bringing an applicator machine online isn’t as simple as unboxing and hitting the “Start” button. Proper setup and routine care can make the difference between a smooth-running system and constant headaches.
Pre-Installation Checklist
- Location & Layout: Choose a space with adequate lighting, ventilation, and easy access for operators and technicians.
- Power & Air Requirements: Check voltage compatibility and whether you need a dedicated compressed air line.
- Safety Compliance: Ensure the area meets local and industry-specific safety regulations, including emergency stop switches and lockout/tagout procedures.
Calibration & Initial Setup
- Align Feeder & Applicator Head: Perform test runs to confirm the label or adhesive aligns correctly.
- Set Conveyor Speed: Match the speed of the product transport system with the dispensing rate of the applicator head.
- Sensor Calibration: Fine-tune sensors for accurate detection of product position, label presence, and orientation.
Routine Maintenance
- Cleaning: Wipe down sensors, conveyors, and the applicator head at the end of each shift or production run to remove dust and debris.
- Lubrication: Keep moving parts well-lubricated according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Replace Worn Parts: Periodically inspect rollers, belts, and nozzles for wear or damage.
- Software Updates: Regularly update control software or firmware to fix bugs and optimize performance.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Label Misalignment: Check tension settings on the unwind and rewind system. Adjust sensor sensitivity.
- Inconsistent Adhesion: Inspect adhesives for expiration or contamination. Ensure the substrate is clean and dust-free.
- Frequent Jams: Look for obstructions, debris buildup, or worn rollers.
- Error Codes: Consult the machine’s manual or contact the manufacturer for specialized errors.
Adhering to these best practices can extend the lifespan of your applicator machine, reduce downtime, and maintain high productivity levels.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with the best maintenance routines, problems can still arise. Below are some commonly encountered issues and potential solutions.
Label Skew or Wrinkles
- Cause: Incorrect tension, misaligned rollers, or a label roll that’s not wound properly.
- Solution: Adjust tension controls, realign rollers, or replace poorly wound label rolls.
Adhesive Bleed
- Cause: Excessive adhesive application or a mismatch between the adhesive and substrate.
- Solution: Reduce the adhesive flow rate, switch to a more appropriate adhesive, or adjust conveyor speed to allow the adhesive to settle correctly.
Frequent Breakage of Backing Material
- Cause: Excessive tension or sharp edges on the machine’s path.
- Solution: Decrease tension settings, smooth out any rough edges, and inspect the feeder path for snags.
Inconsistent Label Placement
- Cause: Faulty sensors, incorrect timing, or product orientation issues.
- Solution: Recalibrate sensors, adjust the conveyor speed or the applicator’s dispensing speed, and ensure products are uniformly oriented.
Machine Shutdown or Error Codes
- Cause: Overheating, power surges, or software malfunctions.
- Solution: Inspect the cooling system, verify power supply stability, and consult logs or manufacturer documentation to troubleshoot software issues.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Safety isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a critical component of any automated process. Regulations vary depending on your locale and industry, but some universal practices apply.
Machine Guarding and Emergency Stops
- Importance: Prevent accidental contact with moving parts and enable quick shutdown in emergencies.
- Implementation: Physical guards, light curtains, and strategically placed emergency stop buttons.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
- Importance: Ensures the machine cannot be powered on while maintenance or cleaning is taking place.
- Implementation: Follow standardized lockout/tagout protocols, and train all relevant personnel.
Compliance with Industry Standards
- Pharmaceutical or Food & Beverage: May need to meet FDA or ISO standards for hygiene and traceability.
- Electrical Standards: Machines must comply with local electrical codes (e.g., NFPA 70 in the U.S.).
Operator Training
- Importance: Human error often causes accidents or downtime, so thorough operator training is essential.
- Implementation: Provide comprehensive training on operation, safety features, and basic troubleshooting.
Case Study: Real-World Success Stories
Nothing cements the value of an applicator machine like real-world examples. Below are two hypothetical but representative scenarios.
Food Manufacturer Boosts Productivity by 40%
Challenge: A mid-sized bakery producing artisanal breads found itself lagging behind on labeling tasks. Seasonal spikes in demand frequently led to overtime costs.
Solution: The bakery invested in a high-speed label applicator machine that integrated seamlessly with its existing conveyor system.
Results:
- Productivity Jump: 40% increase in throughput within two months.
- Labor Cost Reduction: Freed up staff for more value-added tasks like product quality checks.
- Improved Quality Control: Labels were consistently applied in the correct position, enhancing brand professionalism.
Cosmetic Firm Achieves Flawless Brand Consistency
Challenge: A specialty cosmetics company wanted to roll out a new product line with complex, die-cut labels that must match the bottle’s contour perfectly. Manual attempts led to frequent misalignment.
Solution: They selected a custom-built applicator machine with adjustable applicator heads, designed to handle intricate shapes.
Results:
- Brand Consistency: Near-zero margin of misalignment errors, significantly boosting shelf appeal.
- Reduced Waste: By automating the process, the company cut label wastage by over 25%.
- Scalable Solution: As new products emerged, minor machine recalibrations easily accommodated varied bottle shapes and label designs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below are some of the most commonly asked questions about applicator machines, designed to help you find quick answers and optimize your production line.
1. How Do I Know Which Applicator Machine Is Right for My Business?
Start by analyzing your production volume, product dimensions, and the materials you need to apply. From there, consult with vendors, request demonstrations, and consider potential future expansion. Balancing immediate needs with long-term goals ensures you choose the best machine for sustained success.
2. What Kind of Maintenance Schedule Should I Follow?
Maintenance frequency varies by machine type and usage. However, a standard routine might include daily cleaning, weekly inspections for wear, and monthly calibrations. Always follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines for best results.
3. Are Applicator Machines Difficult to Operate?
Modern applicator machines often come with user-friendly interfaces. While some training is necessary, operators can typically become proficient within a few days. Comprehensive training materials and vendor support further simplify the learning curve.
4. Can One Machine Handle Multiple Product Lines?
Yes, but only if the machine is designed with adjustable guides, sensors, and applicator heads. Some advanced models allow quick changeovers, making them ideal for facilities that handle multiple SKUs or seasonal product variations.
5. What Is the Typical ROI on an Applicator Machine?
ROI timelines can vary based on your production volume and labor costs. Many businesses see a return on investment within one to three years, thanks to higher throughput, lower labor expenses, and reduced waste.
- External References Links:
- OSHA: Machine Guarding Standards – Essential for safety compliance and risk mitigation.
- FDA: Labeling & Nutrition Guidance – Critical for food and beverage industries.
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems – Understanding these standards can enhance your machine’s integration into broader quality systems.
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of an applicator machine can elevate your production process from a labor-intensive bottleneck to a streamlined, efficient, and cost-effective operation. We’ve covered everything from the core components and different types of applicator machines to practical tips on maintenance, safety, and troubleshooting. With the right machine selection and proper integration, you can dramatically reduce manual errors, cut labor costs, and ensure a uniform application—whether you’re labeling bakery products, sealing e-commerce parcels, or applying adhesives in industrial settings.
Ready to take the next step? Explore your options, consult industry experts, and don’t hesitate to request a live demonstration. An investment in a high-quality applicator machine pays dividends in improved throughput, consistent product quality, and an overall boost to your bottom line. As automation technologies continue to advance, staying ahead of the curve could be your key differentiator in a competitive marketplace.
We’d love to hear about your experience with applicator machines. Share your biggest packaging or labeling challenges in the comments, or reach out to our team for personalized guidance. If you found this guide helpful, spread the word by sharing it on social media or forwarding it to a colleague who might benefit. Your journey to a more efficient and profitable production line starts now—so why wait?
Stay Connected with EngiTech
EngiTech is your trusted source for in-depth knowledge on industrial mechanical engineering machines and technologies. Stay ahead with the latest innovations, expert insights, and practical guides designed to help you make informed decisions for your business and engineering needs. Join our growing community of professionals and industry leaders to stay updated and competitive in the ever-evolving world of industrial technology.