Applications of Agitated Thin Film Dryers: Unveiling Their Industrial Significance | EngiTech
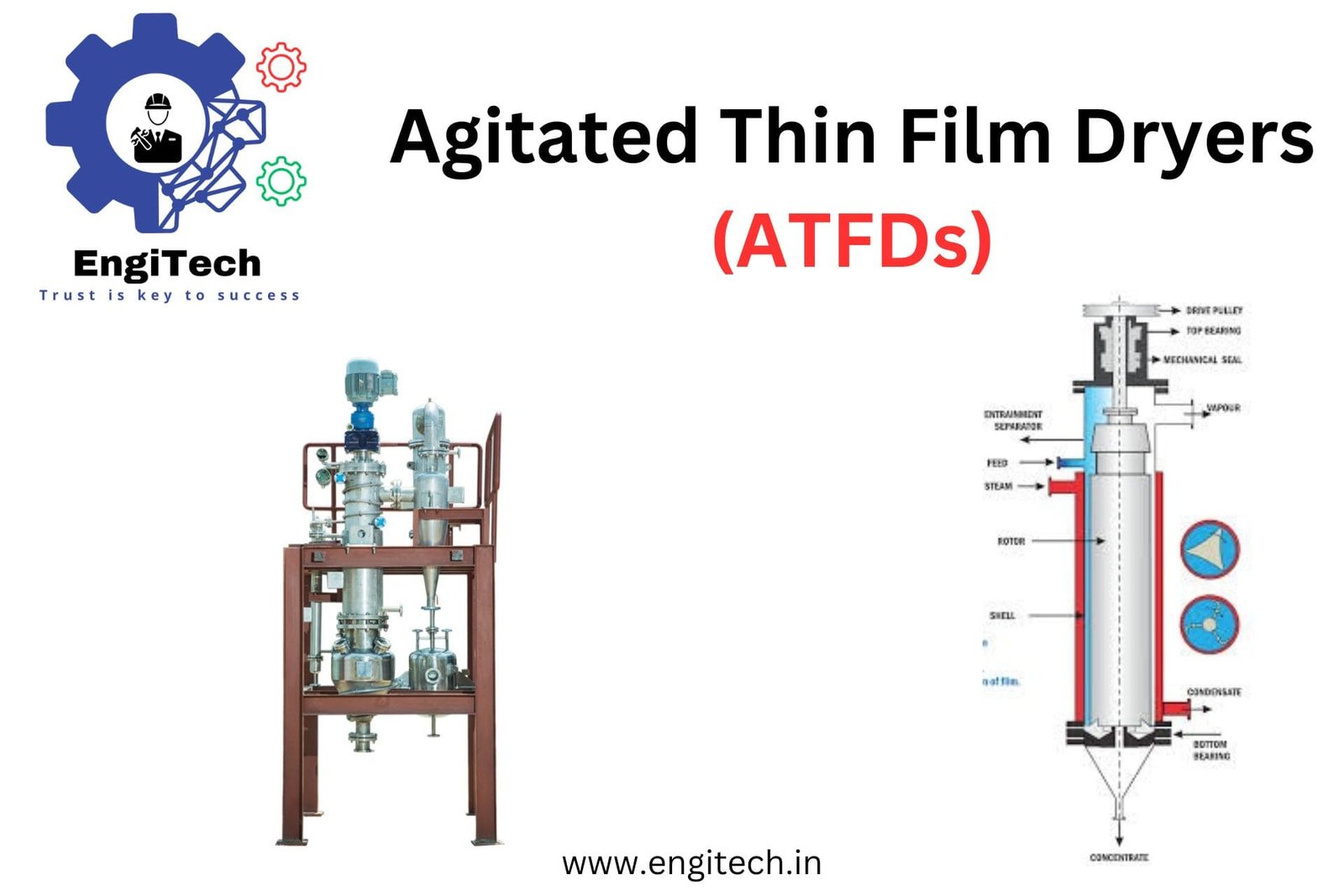
Agitated Thin Film Dryers (ATFDs) are a cornerstone in many industrial processes, particularly where precise drying and concentration of heat-sensitive or viscous products are essential. Their unique design and operating principles allow them to handle complex materials that conventional drying technologies might struggle with.
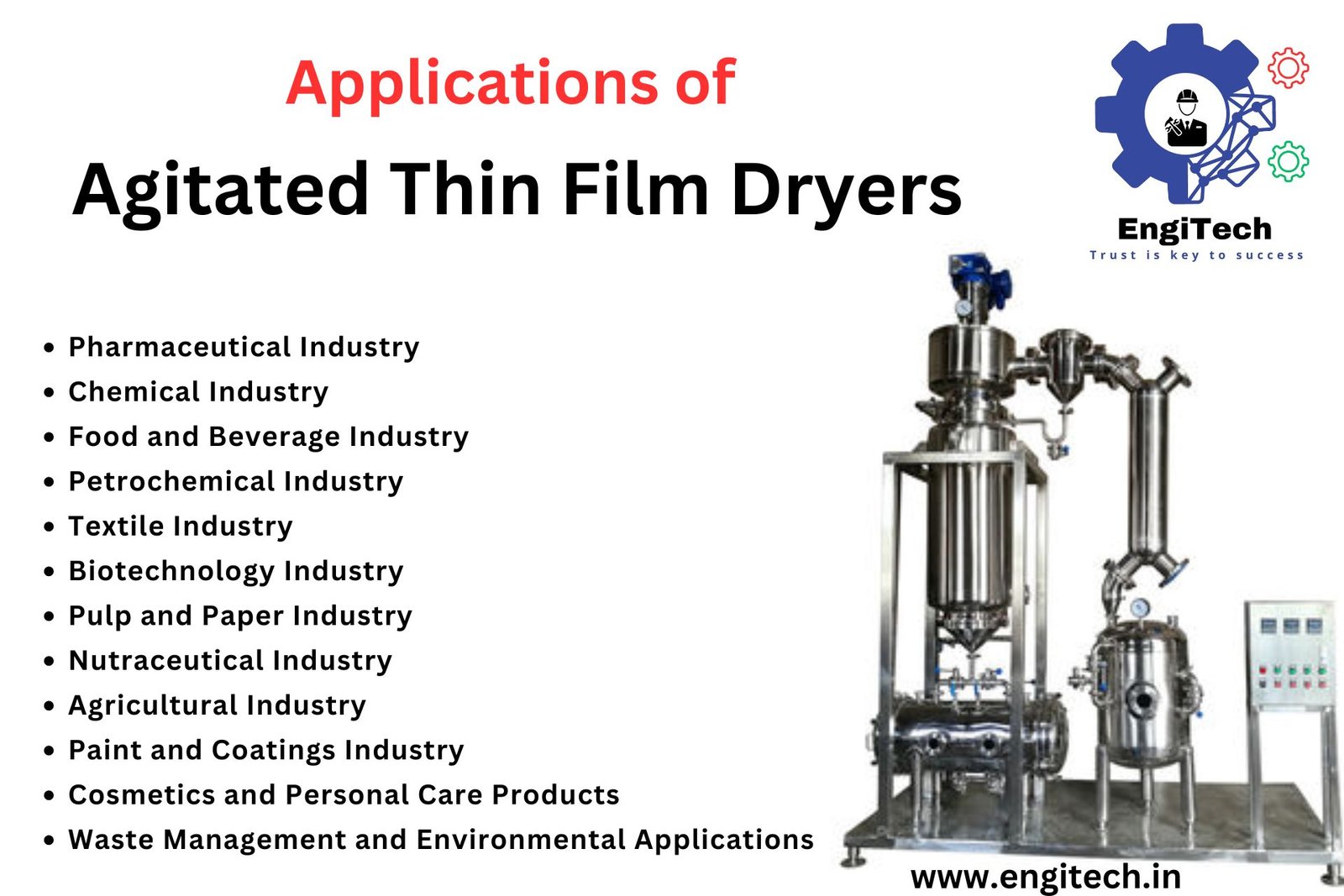
In this blog, we will explore the diverse applications of Agitated Thin Film Dryers across various industries, demonstrating their importance in modern manufacturing and processing.
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Drying of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs): One of the most critical applications of ATFDs is in the pharmaceutical industry, where they are used to dry Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). The gentle and controlled drying environment provided by ATFDs ensures that these sensitive compounds do not degrade during the process. ATFDs offer precise temperature control, which is crucial in maintaining the stability and potency of APIs. This makes ATFDs the preferred choice for drying antibiotics, vitamins, hormones, and other heat-sensitive drugs.
- Solvent Recovery: ATFDs also play a pivotal role in solvent recovery processes within the pharmaceutical sector. Solvents used in drug production are often expensive and hazardous, making their recovery both economically and environmentally important. The thin film and high agitation in ATFDs facilitate efficient evaporation of solvents, allowing them to be condensed and reused, thus reducing waste and operational costs.
2. Chemical Industry
- Concentration of Chemicals: The chemical industry relies heavily on ATFDs for the concentration of various chemical solutions. For example, in the production of polymers, resins, and adhesives, ATFDs are used to remove excess solvents or water, resulting in a more concentrated and pure final product. The ability to handle viscous materials makes ATFDs indispensable in this industry, where conventional dryers may fail.
- Drying of Inorganic and Organic Compounds: ATFDs are also used to dry a wide range of inorganic and organic compounds, including catalysts, pigments, and intermediates in chemical reactions. The precise control over the drying process ensures that the desired chemical properties of the compounds are maintained, which is critical for their performance in subsequent processes.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
- Concentration of Juices and Purees: In the food and beverage industry, ATFDs are widely used to concentrate fruit juices, vegetable purees, and other liquid foods. The low residence time and gentle heating ensure that the flavor, color, and nutritional content of the products are preserved. This is particularly important in the production of high-quality juices and purees where retaining the natural characteristics of the raw materials is essential.
- Drying of Heat-Sensitive Ingredients: ATFDs are ideal for drying heat-sensitive ingredients such as enzymes, proteins, and flavors. These ingredients often lose their functionality or degrade when exposed to high temperatures for extended periods. The efficient heat transfer and short drying time in ATFDs minimize the risk of thermal degradation, ensuring that the dried products retain their desired properties.
- Concentration of Dairy Products: ATFDs are also used in the dairy industry to concentrate products like milk, whey, and cream. The high efficiency of ATFDs allows for the rapid concentration of these products without affecting their quality. This is particularly important in the production of condensed milk and other dairy concentrates where preserving the nutritional value and flavor is crucial.
4. Petrochemical Industry
- Recovery of By-Products: In the petrochemical industry, ATFDs are employed to recover valuable by-products from various processes. For instance, during the production of synthetic fuels and lubricants, ATFDs are used to separate and recover by-products such as waxes and heavy oils. The efficient separation and concentration capabilities of ATFDs make them an essential component in maximizing the yield and profitability of petrochemical processes.
- Drying of High-Viscosity Products: The petrochemical industry often deals with high-viscosity products such as bitumen, asphalt, and resins. ATFDs are uniquely suited to handle these materials due to their robust design and ability to maintain a uniform thin film on the drying surface. This ensures consistent drying and prevents the formation of hard crusts or deposits that can occur with other drying methods.
5. Waste Management and Environmental Applications
- Treatment of Industrial Wastewater: ATFDs are increasingly being used in the treatment of industrial wastewater, particularly in processes where water needs to be removed from sludge or other waste materials. The ability of ATFDs to handle high solids content and viscous materials makes them ideal for concentrating and drying wastewater streams, reducing the volume of waste that needs to be disposed of and facilitating the recovery of valuable resources.
- Recovery of Solids from Liquid Waste: In addition to wastewater treatment, ATFDs are also used to recover solids from liquid waste streams in various industries. This includes the recovery of salts, metals, and other valuable materials from waste liquids, which can then be recycled or reused in the production process. The efficiency of ATFDs in these applications contributes to both cost savings and environmental sustainability.
6. Textile Industry
- Drying of Textile Chemicals: The textile industry uses a wide range of chemicals in processes such as dyeing, printing, and finishing. ATFDs are employed to dry these chemicals, particularly when they are in solution form and need to be concentrated or dried before being applied to fabrics. The precise control offered by ATFDs ensures that the chemicals are dried to the correct consistency, which is crucial for achieving the desired effects on textiles.
- Concentration of Dyes and Pigments: ATFDs are also used to concentrate dyes and pigments used in the textile industry. The ability to handle viscous and sticky materials makes ATFDs ideal for concentrating these substances, ensuring that they are at the correct concentration for use in textile production. This not only improves the quality of the final product but also reduces waste and costs associated with the dyeing process.
7. Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
- Drying of Cosmetic Ingredients: In the cosmetics and personal care industry, ATFDs are used to dry a variety of ingredients, including essential oils, fragrances, and active ingredients used in skincare and haircare products. The gentle drying environment provided by ATFDs ensures that these sensitive ingredients retain their efficacy and do not degrade during the drying process.
- Concentration of Emulsions and Gels: ATFDs are also used to concentrate emulsions and gels used in cosmetic formulations. The ability to achieve high levels of concentration without compromising the stability or texture of the product is a key advantage of using ATFDs in this industry. This allows manufacturers to produce high-quality, concentrated products that are both effective and appealing to consumers.
8. Biotechnology Industry
- Drying of Bioproducts: The biotechnology industry often deals with bioproducts such as enzymes, proteins, and cells that require careful drying to maintain their activity and functionality. ATFDs are ideal for this purpose due to their gentle drying environment and precise temperature control. This ensures that the biological activity of the products is preserved, which is essential for their use in various applications, including pharmaceuticals, food production, and research.
- Concentration of Fermentation Broths: In biotechnological processes, fermentation broths often need to be concentrated before further processing or purification. ATFDs are used to efficiently remove water from these broths, resulting in a more concentrated product. The ability to handle the high viscosity and sensitivity of these broths makes ATFDs a valuable tool in the biotechnology industry.
9. Pulp and Paper Industry
- Concentration of Black Liquor: In the pulp and paper industry, ATFDs are used to concentrate black liquor, a by-product of the pulping process. Black liquor contains lignin, hemicellulose, and other organic compounds, which need to be concentrated before being burned for energy recovery. The high efficiency of ATFDs in concentrating black liquor makes them an essential component in the energy recovery process in pulp and paper mills.
- Drying of Pulp Slurries: ATFDs are also used to dry pulp slurries, reducing their moisture content before they are further processed into paper or other products. The ability to handle the high solids content and viscosity of pulp slurries makes ATFDs ideal for this application, ensuring consistent drying and high-quality final products.
10. Nutraceutical Industry
- Drying of Nutraceutical Ingredients: The nutraceutical industry, which includes the production of dietary supplements, functional foods, and other health-related products, relies on ATFDs for drying various ingredients. These include vitamins, minerals, herbal extracts, and other bioactive compounds. The gentle drying process provided by ATFDs ensures that the nutritional and bioactive properties of these ingredients are preserved, which is critical for their effectiveness.
- Concentration of Herbal Extracts: ATFDs are also used to concentrate herbal extracts, which are often used in nutraceutical products. The ability to achieve high levels of concentration without degrading the active compounds in the extracts is a key advantage of using ATFDs in this industry. This ensures that the final products are potent and effective, meeting the high standards expected by consumers.
11. Agricultural Industry
- Drying of Fertilizers and Pesticides: The agricultural industry uses ATFDs to dry and concentrate fertilizers, pesticides, and other agrochemicals. The ability to handle viscous and heat-sensitive materials makes ATFDs ideal for producing high-quality, concentrated products that are easy to handle and apply. This not only improves the efficiency of agricultural practices but also reduces the environmental impact of these chemicals.
- Concentration of Plant Extracts: ATFDs are also used to concentrate plant extracts used in the production of natural fertilizers, pesticides, and other agricultural products. The efficient concentration capabilities of ATFDs ensure that these extracts are potent and effective, providing a natural alternative to synthetic chemicals in agriculture.
12. Paint and Coatings Industry
- Concentration of Paints and Coatings: In the paint and coatings industry, ATFDs are used to concentrate paints, varnishes, and other coatings. The ability to handle viscous materials and achieve high levels of concentration without affecting the quality of the product is a key advantage of using ATFDs in this industry. This ensures that the final products are consistent in quality and performance.
- Drying of Resins and Binders: ATFDs are also used to dry resins and binders used in the production of paints and coatings. The precise control over the drying process ensures that these materials are dried to the correct consistency, which is crucial for achieving the desired properties in the final product.
Conclusion
Agitated Thin Film Dryers have proven to be invaluable across a wide range of industries, offering unparalleled efficiency and precision in drying and concentrating complex materials. From pharmaceuticals to food processing, and petrochemicals to biotechnology, ATFDs provide solutions to some of the most challenging drying applications. Their ability to handle heat-sensitive, viscous, and difficult-to-dry materials makes them indispensable in modern industrial processes.
As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the applications of ATFDs are likely to expand even further. Their versatility, efficiency, and precision will continue to make them a preferred choice for drying and concentration processes, contributing to the development of high-quality products and sustainable industrial practices.
By understanding the diverse applications of Agitated Thin Film Dryers, businesses can better appreciate their value and consider their implementation in relevant processes. Whether it’s enhancing product quality, improving operational efficiency, or achieving sustainability goals, ATFDs offer a robust and reliable solution that can meet the needs of various industries.
With their growing importance in modern industry, investing in Agitated Thin Film Dryers is not just a choice; it’s a strategic decision that can drive innovation, efficiency, and success in today’s competitive market.
From EngiTech Team
We are committed to empowering mechanical engineering professionals and enthusiasts with the knowledge they need to excel in their fields. Our expert team of industry experts delivers high-quality, reliable content that covers everything from the intricate design of components to the management of large-scale manufacturing systems. Whether you’re looking to deepen your understanding, stay updated with the latest industry trends, or find practical solutions to complex engineering challenges, EngiTech is your trusted resource for comprehensive, actionable insights.