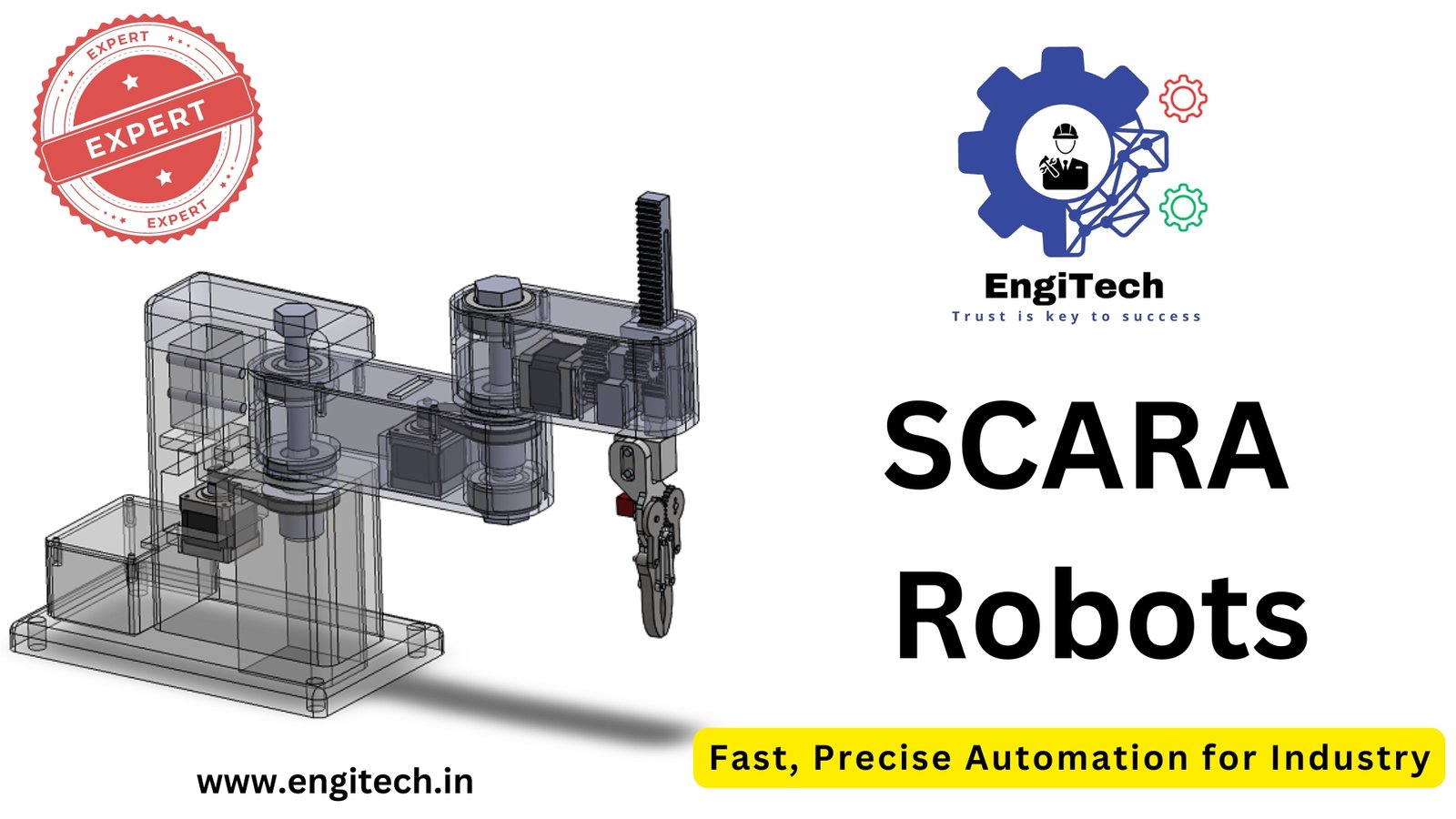
SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm): A Comprehensive Guide
In the rapidly advancing world of industrial automation, robotics technology plays a crucial role in streamlining production processes and improving efficiency. One of the most innovative robotic systems making waves in the industrial sector is the SCARA robot, short for Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm.
This blog post will take an in-depth look at what SCARA robots are, their benefits, applications, and how they compare to other types of robotic arms. If you’re interested in understanding SCARA robots and how they can revolutionize your production line, you’ve come to the right place.
Table of Contents
What is a SCARA Robot?
SCARA robots, or Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arms, are specialized industrial robots designed for high-speed, precise operations such as assembly, pick-and-place tasks, and packaging. The term “Selective Compliance” refers to the robot’s flexibility in certain planes—usually the horizontal plane—while maintaining rigidity in others. This combination allows SCARA robots to excel in tasks requiring both speed and precision.
Key Features of SCARA Robots
- Selective Compliance: SCARA robots are compliant (flexible) in the X-Y plane, making them ideal for lateral movements. However, they maintain rigidity in the Z-axis (vertical plane), allowing precise up-and-down movements.
- High Speed: These robots are renowned for their high-speed operation, often significantly faster than other robot types such as Cartesian or six-axis robots.
- Compact Design: SCARA robots have a compact footprint, making them suitable for installations in tight spaces or compact production environments.
- Cost-Effective: SCARA robots typically have a simpler design and fewer moving parts than six-axis robots, making them more cost-effective for certain applications.
How SCARA Robots Work
SCARA robots consist of a base and a jointed arm, similar to a human arm. The arm moves in a rotary motion, giving it flexibility and speed for lateral movements, while the vertical motion is controlled by an actuator. This design allows the SCARA robot to complete tasks like assembling components, sorting parts, or inserting components into pre-defined locations with a high degree of precision.
Components of a SCARA Robot
- Base: The stationary part of the robot that supports the entire system.
- Rotary Arm: This is the moving part that allows for compliance and high-speed lateral motion.
- Vertical Actuator: A vertical arm that ensures precision in the Z-axis for tasks requiring up-and-down movements.
- End Effector: The tool or attachment at the end of the arm that interacts with the workpiece, such as a gripper or welding tool.
Key Advantages of SCARA Robots
SCARA robots have gained significant popularity in various industries due to their unique advantages. Here’s why they are a preferred choice:
1. Speed and Efficiency
SCARA robots are designed to perform tasks at high speed without sacrificing accuracy. Their ability to quickly pick, move, and place objects makes them ideal for high-volume production lines. Compared to Cartesian robots or six-axis arms, SCARA robots can complete tasks in less time, leading to increased throughput and productivity.
2. Precision
Thanks to their selective compliance and rigid vertical movement, SCARA robots can perform delicate tasks with exceptional precision. Whether it’s assembling electronic components or handling fragile items, SCARA robots ensure consistent accuracy.
3. Cost-Effective Automation
For companies seeking to automate processes without investing heavily in six-axis robots, SCARA robots offer an affordable alternative. They are typically easier to program, maintain, and operate, reducing the overall cost of automation.
4. Compact Footprint
The compact design of SCARA robots makes them ideal for industries where space is a constraint. Their small size allows them to be integrated into crowded production environments without requiring significant space.
5. Flexibility
While SCARA robots excel in tasks that require lateral movement, they also offer flexibility for various applications. They can be used for assembly, palletizing, pick-and-place, and even more delicate operations like soldering or dispensing adhesives.
SCARA Robots vs. Other Types of Robots
When choosing the right robot for your automation needs, understanding the differences between SCARA robots and other types of robots is essential. Here’s how SCARA robots compare to some of the most common robot types:
1. SCARA Robots vs. Cartesian Robots
- Flexibility: SCARA robots offer more flexibility in lateral movements compared to Cartesian robots, which operate along fixed X, Y, and Z axes.
- Speed: SCARA robots are generally faster than Cartesian robots due to their rotary motion.
- Precision: While Cartesian robots are known for their high precision, SCARA robots can match their precision in most tasks requiring lateral movements.
2. SCARA Robots vs. Six-Axis Robots
- Complexity: Six-axis robots can perform a wider range of movements due to their additional degrees of freedom. However, SCARA robots are simpler to program and operate, making them more cost-effective for tasks like assembly or pick-and-place.
- Cost: Six-axis robots are typically more expensive due to their complexity and versatility, whereas SCARA robots offer a more affordable solution for specialized tasks.
- Speed: SCARA robots are generally faster in performing simple pick-and-place tasks compared to six-axis robots.
3. SCARA Robots vs. Delta Robots
- Application: Delta robots are known for high-speed pick-and-place applications, similar to SCARA robots. However, Delta robots are usually used for lightweight tasks, while SCARA robots can handle heavier payloads.
- Precision: SCARA robots offer better precision for tasks requiring vertical movement compared to Delta robots, which excel in horizontal movements.
Common Applications of SCARA Robots
SCARA robots are used in a wide range of industries due to their speed, precision, and flexibility. Here are some of the most common applications:
1. Electronics Assembly
SCARA robots are ideal for assembling small, delicate components like circuit boards and electronic parts. Their precision and speed make them perfect for high-volume production lines in the electronics industry.
2. Pick-and-Place
In packaging and sorting applications, SCARA robots are often employed to pick items from one location and place them in another. Their high-speed operation ensures quick and efficient handling of items, making them a popular choice in industries like food and beverage, consumer goods, and pharmaceuticals.
3. Automotive Industry
SCARA robots are used in automotive manufacturing to perform tasks such as assembling small parts, inserting components, and quality control. Their ability to work quickly and accurately helps improve production efficiency in a highly competitive industry.
4. Medical Device Manufacturing
In the medical industry, SCARA robots are employed in the manufacturing of medical devices where precision and hygiene are critical. They are used for assembling and packaging medical devices in sterile environments.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry
SCARA robots are used in the pharmaceutical industry for tasks like sorting and packaging medications, as well as handling delicate tasks like filling vials or syringes. Their ability to work with precision and maintain hygienic standards makes them ideal for pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Programming and Integration of SCARA Robots
SCARA robots are relatively easy to program and integrate into production systems, thanks to their simple kinematic structure. Most SCARA robots come with user-friendly programming interfaces that allow operators to create customized workflows and control the robot’s movements.
1. Robot Programming Languages
Most SCARA robots use proprietary programming languages or industry-standard robot programming languages like RAPID or KRL. These languages are designed to be intuitive, allowing operators to program the robot for specific tasks with ease.
2. Integration with Production Systems
SCARA robots can be integrated with other automation equipment such as conveyors, cameras, and sensors. They can also be connected to industrial control systems (PLCs) for coordinated control and monitoring.
The Future of SCARA Robots in Automation
As automation continues to evolve, SCARA robots are expected to play an even more significant role in various industries. Advances in robotics technology are likely to improve the capabilities of SCARA robots, making them faster, more precise, and even more affordable. With the ongoing push toward Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, SCARA robots will continue to be an essential tool for companies seeking to enhance their production efficiency.
FAQs about SCARA robots (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm)
1. What is a SCARA Robot?
A SCARA robot, or Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm, is a type of industrial robot known for its high-speed, lateral movement and precision in pick-and-place, assembly, and packaging tasks. It offers compliance in the X-Y plane and rigidity in the Z-axis.
2. How does a SCARA robot work?
SCARA robots operate with a rotary joint that allows selective flexibility in horizontal movements while maintaining rigid vertical movements. This design enables them to perform fast, precise tasks like part insertion, assembly, and pick-and-place operations.
3. What are the primary applications of SCARA robots?
SCARA robots are widely used in electronics assembly, automotive manufacturing, medical device production, pharmaceutical packaging, and high-speed pick-and-place tasks in various industries such as food and beverage.
4. What are the advantages of SCARA robots?
SCARA robots offer high-speed performance, exceptional precision, compact design, and cost-effectiveness. They are perfect for repetitive tasks like assembly, where speed and accuracy are critical.
5. How is a SCARA robot different from a six-axis robot?
SCARA robots are simpler, faster, and less expensive compared to six-axis robots, which offer more flexibility due to their ability to move in multiple planes. However, SCARA robots are more efficient for tasks requiring high speed and precision in the horizontal plane.
6. What industries use SCARA robots?
Industries that commonly use SCARA robots include electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, food and beverage, and consumer goods. Their versatility allows them to handle a wide range of tasks in these sectors.
7. What is the payload capacity of a SCARA robot?
The payload capacity of a SCARA robot can vary, but it typically ranges from 1 kg to 20 kg, depending on the model. Higher payload SCARA robots are used in heavier applications like automotive and large-scale assembly.
8. How fast can a SCARA robot operate?
SCARA robots are known for their high-speed operation, often achieving cycle times as low as 0.3 to 0.5 seconds per operation, making them ideal for fast-paced production environments.
9. What is the precision level of a SCARA robot?
SCARA robots can achieve high precision, typically within a ±0.01 to 0.02 mm tolerance range, depending on the application and the model. This level of accuracy is crucial for delicate assembly and electronic component handling.
10. How much does a SCARA robot cost?
The cost of a SCARA robot varies based on factors like payload capacity, speed, and manufacturer, but generally, a standard SCARA robot can range from $15,000 to $30,000. Additional costs for software, programming, and installation may apply.
11. What is the lifespan of a SCARA robot?
SCARA robots are designed to be durable and long-lasting. With proper maintenance, they typically have a lifespan of 10 to 15 years, depending on usage intensity and working conditions.
12. Can SCARA robots be used in cleanroom environments?
Yes, many SCARA robots are designed for use in cleanroom environments, particularly in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries, where hygiene and contamination control are critical.
13. What kind of software is used to control SCARA robots?
SCARA robots are typically programmed and controlled using robotic automation software, often proprietary to the robot manufacturer. Common programming languages include PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and ROS (Robot Operating System), making it easy to customize operations.
14. How easy is it to program a SCARA robot?
Programming a SCARA robot is relatively straightforward compared to more complex robots like six-axis robots. Most SCARA robots come with user-friendly software that allows operators to define motion paths, sequences, and task-specific instructions using simple commands.
15. What factors should be considered when choosing a SCARA robot?
Key factors to consider include the payload capacity, speed, precision requirements, application needs, and available space. Additionally, assessing the cost, software compatibility, and ease of maintenance is important for making the right decision.
Conclusion
SCARA robots offer a perfect blend of speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness, making them a top choice for industries that require high-speed, accurate assembly and handling processes. Their ability to perform tasks quickly and accurately has earned them a prominent position in fields like electronics, automotive manufacturing, and medical device production.
If you’re considering automating your production line or want to learn more about how SCARA robots can enhance your operations, visit EngiTech for comprehensive resources on the latest innovations and applications in industrial robotics. Discover how SCARA robots can be the solution you need to boost efficiency and productivity in your business.