In-Depth Guide to Belt Conveyors: Systems, Components, and Applications

Belt conveyors play a critical role in various industries, facilitating the efficient and reliable transportation of materials. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of belt conveyors, covering their components, types, applications, and more. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a thorough understanding of belt conveyors and how they can optimize your operations.
We’ll answer key questions such as:
- What are belt conveyors, and what components do they include?
- What types of belt conveyors are available?
- How do you design and select the right belt conveyor?
- What are the specific applications and benefits of using belt conveyors?
This guide aims to provide practical and insightful information to help you make informed decisions about belt conveyors in your industrial setup.
Understanding Belt Conveyors
Belt conveyors are mechanical systems designed to transport materials from one point to another. Unlike other types of conveying systems that use chains, spirals, or hydraulics, belt conveyors use a continuous belt loop stretched between two or more pulleys. An electric motor powers these pulleys, causing the belt to move and transport materials along its length. The belt material varies based on the application and the type of items being moved, ranging from rubber to specialized polymers.
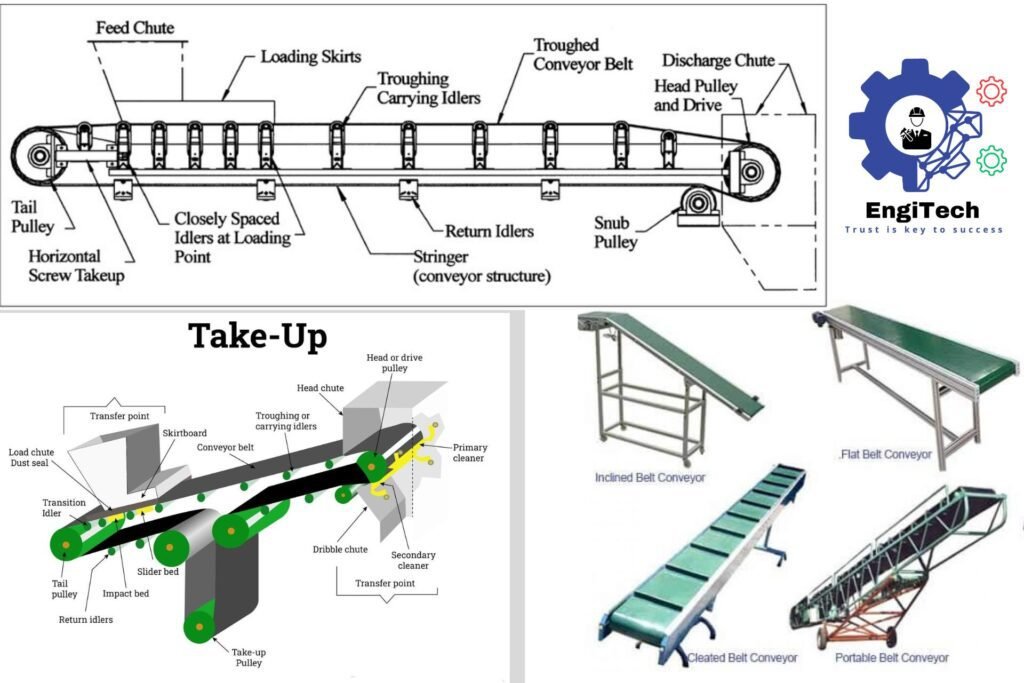
Components of a Belt Conveyor
Belt conveyors consist of several key components, each playing a vital role in the system’s functionality:
- Head Pulley: This pulley, located at the discharge end, drives the conveyor. Coupled with the actuator and electric motor, it provides the necessary pulling force. The head pulley often has the largest diameter and may feature a rough outer surface (lagging) to increase traction.
- Tail Pulley: Situated at the loading end, the tail pulley may have a wing shape to help clean the belt and reduce material buildup. It works with the head pulley to maintain belt tension.
- Idler Rollers: These rollers support the belt along its length, preventing sagging and ensuring smooth operation. They come in various types, including troughing idlers, rubber disk idlers, and trainer idlers, each designed for specific functions like maintaining belt alignment or supporting heavy loads.
- Conveyor Belt: The belt itself is the most critical component, made from materials like rubber, PVC, or other polymers, depending on the application. It must be durable enough to withstand the load and environmental conditions.
- Frame: The frame supports the entire conveyor system. Its design can vary significantly based on the conveyor’s purpose and the load it needs to support.
Types of Belt Conveyors
1. Flat Belt Conveyors
Flat belt conveyors are among the most common and versatile types. They are primarily used for internal transport within facilities. These conveyors consist of a flat belt that runs on a series of pulleys, making them ideal for transporting a wide range of materials.
2. Modular Belt Conveyors
Modular belt conveyors use interlocking rigid pieces, typically made from plastic or metal, instead of a continuous flexible belt. This design allows them to navigate straight lines, curves, inclines, and declines easily. They are particularly useful in food processing and packaging industries due to their ease of cleaning and versatility.
3. Cleated Belt Conveyors
Cleated belt conveyors feature raised sections (cleats) that help prevent materials from sliding back or falling off the conveyor, especially on inclines or declines. The cleats come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to the specific material being transported.
4. Roller Bed Belt Conveyors
Roller bed belt conveyors use rollers beneath the belt to reduce friction and support the belt and the load. These conveyors are suitable for long-distance transport and are often used in sorting and inspection processes. The rollers help minimize energy consumption and allow for smooth material flow.
5. Incline/Decline Belt Conveyors
Incline/decline belt conveyors transport materials up or down an incline. They require tighter tension and a more aggressive surface texture to prevent items from slipping. These conveyors are often used in industries where elevation changes are necessary, such as in loading and unloading applications.
Design and Selection of Belt Conveyors
When designing and selecting a belt conveyor, consider several critical factors:
- Motor and Gearbox Selection: The motor’s power must be adequate to handle the conveyor’s load and length. The gearbox should provide the necessary torque to move the belt and the material.
- Belt Speed: The speed at which the belt moves is crucial for ensuring efficient material transport. It is determined by the drive pulley diameter and its rotational speed.
- Tension and Take-Up: Proper tensioning prevents belt slippage and ensures smooth operation. This can be achieved through various methods, such as screw take-up, gravity take-up, or horizontal take-up.
- Material Considerations: The type of material being transported, the conveyor’s environment, and the length of transport all influence the choice of belt material and design. For example, in food processing, belts must be food-grade and easy to clean.
- Frame Design: The conveyor’s frame must be robust enough to support the weight of the belt and the material. It should also accommodate additional features, such as walkways, guards, or loading chutes.
Applications and Benefits of Belt Conveyors
Belt conveyors are widely used in various industries due to their efficiency and versatility. Some common applications include:
- Mining Industry: Belt conveyors transport bulk materials like coal, ores, and minerals. They are essential in both surface and underground mining operations for moving materials efficiently.
- Food Processing: In food industries, belt conveyors handle delicate items, transporting them through various stages of processing, such as washing, sorting, and packaging.
- Automotive Industry: These conveyors are utilized in assembly lines for transporting parts and finished products. They also handle scrap removal and material recycling processes.
- Retail and Warehousing: Belt conveyors facilitate the efficient movement of goods within warehouses and retail environments. They are used for sorting, packaging, and loading/unloading processes.
- Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceutical industries, belt conveyors transport products through different stages of manufacturing, ensuring hygiene and minimizing contamination risks.
Benefits of Belt Conveyors
- Efficiency: Belt conveyors offer a continuous and efficient method of transporting materials, significantly reducing manual labor and operational costs.
- Versatility: They can handle a wide range of materials, from delicate items to heavy bulk materials.
- Safety: Properly designed and maintained belt conveyors reduce the risk of workplace injuries compared to manual handling.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Belt conveyors provide a cost-effective solution for long-distance transport, especially when compared to alternative methods like trucks.
Common Problems and Maintenance Tips
While belt conveyors are reliable, regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity:
- Mistracking: Mistracking occurs when the belt veers off its intended path, potentially causing damage to the conveyor and surrounding equipment. Regular inspection and adjustment of the idler rollers can prevent this issue.
- Slippage: Slippage happens when the belt loses traction with the pulleys, often due to inadequate tension or worn lagging. Ensuring proper tension and regularly checking the condition of the pulleys can mitigate this problem.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the belt and other components can wear out. Regular inspections help identify worn parts that need replacement before they cause significant issues.
- Material Spillage: Spillage can occur if the belt is overloaded or if the material isn’t properly contained. Using skirts or additional containment methods can help manage this issue.
Conclusion
Belt conveyors are an essential component in many industries, providing a versatile and efficient solution for material transport. Understanding the different types, components, and design considerations can help you choose the right system for your needs. Regular maintenance and proper operation ensure the longevity and efficiency of your belt conveyor system.
For more detailed articles and resources on belt conveyors and related technologies, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and best practices in the field!


