The Ultimate Guide to Drum Dryers: Types, Benefits, and Uses
Drum dryers, also known as rotary dryers, play a crucial role in industrial drying processes. These devices use a rotating drum to dry various materials efficiently. Industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and mining rely on drum dryers for their drying needs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the working principles, types, applications, advantages, and challenges associated with drum dryers.
What is a Drum Dryer?
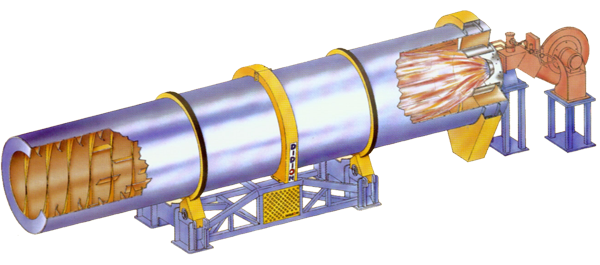
A drum dryer consists of a large, rotating cylindrical drum through which hot air or gas passes. The drum, slightly inclined, uses gravity to assist in moving the material being dried. As the drum rotates, the material cascades through the hot air stream, evaporating moisture and reducing the material’s overall moisture content.
How Drum Dryers Work
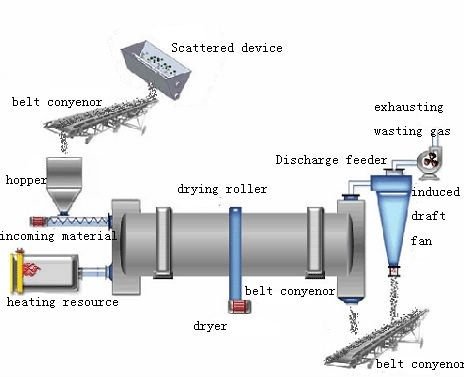
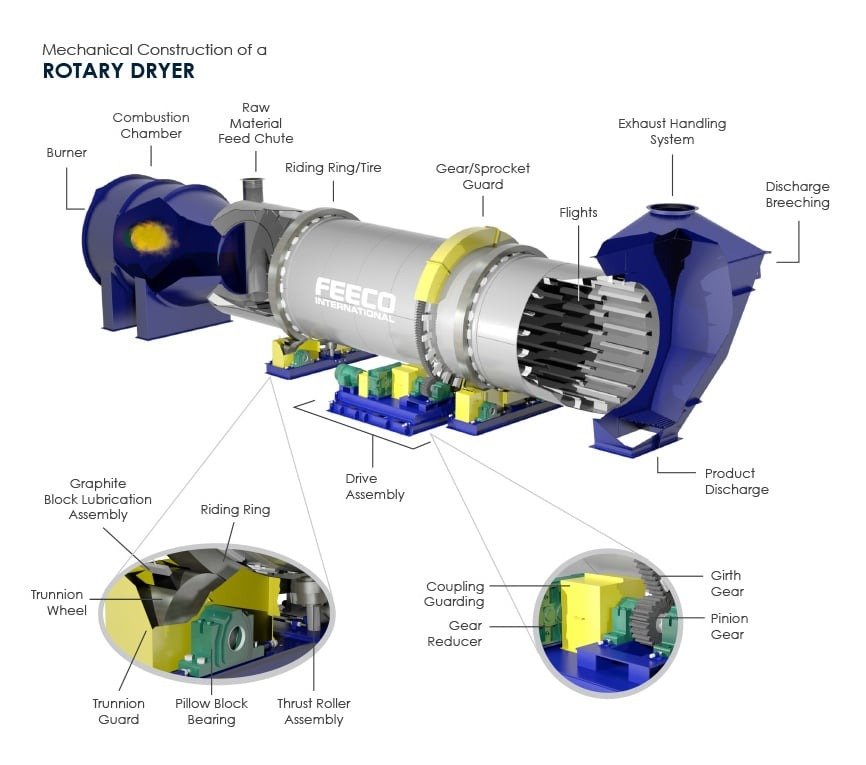
- Feed Material Introduction: Introduce the wet material into the drum dryer via a feed hopper or conveyor system.
- Heat Transfer: Introduce hot air or gas into the drum through a burner or heat exchanger. The heat source can be natural gas, propane, oil, or steam.
- Drum Rotation: Rotate the drum at a controlled speed, causing the material to tumble and cascade through the hot air stream.
- Moisture Evaporation: As the material moves through the drum, the heat evaporates the moisture. The airflow and rotation ensure even drying.
- Exhaust System: Expel the moisture-laden air through an exhaust system equipped with filters to capture any fine particles.
- Discharge: The dried material exits the drum and is collected for further processing or packaging.
Types of Drum Dryers
- Direct Heated Drum Dryers:
- In these dryers, the hot air or gas directly contacts the material. This type is efficient for high-moisture materials but requires proper control to avoid overheating.
- Indirect Heated Drum Dryers:
- These dryers use an external heat source to heat the drum, which then transfers heat to the material. This method is ideal for heat-sensitive materials.
- Single-Pass Drum Dryers:
- The material passes through the drum once. This type is simpler and suitable for materials that dry quickly.
- Triple-Pass Drum Dryers:
- The material passes through three concentric drums, enhancing drying efficiency and energy savings. This type is used for materials requiring extended drying times.
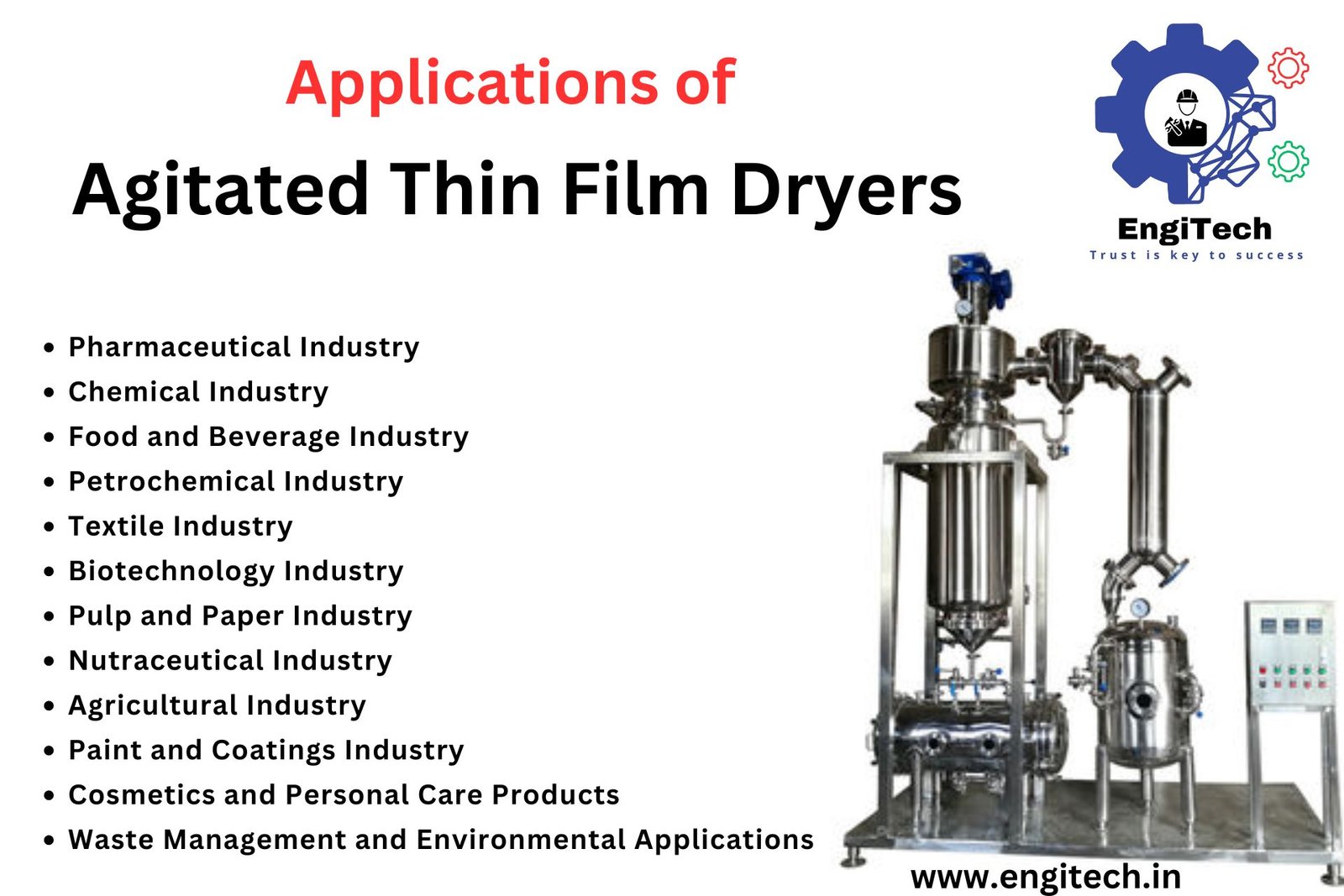
Applications of Drum Dryers
- Food Processing:
- Use drum dryers to dry cereals, grains, fruits, and vegetables, extending shelf life and improving texture.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- Dry active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients to achieve the desired moisture content and stability.
- Chemicals:
- Dry various chemicals, including powders, crystals, and granules, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
- Mining:
- Dry minerals and ores to facilitate processing and improve handling properties.
- Construction:
- Dry materials like sand, cement, and asphalt for use in construction projects.
Advantages of Drum Dryer
- Efficiency:
- Drum dryer offer high drying efficiency due to direct contact between the material and the hot air or gas.
- Versatility:
- Handle a wide range of materials, including solids, pastes, and slurries.
- Scalability:
- Drum dryer come in various sizes, making them suitable for small-scale and large-scale operations.
- Energy Savings:
- Modern drum dryer optimize energy usage, reducing operational costs.
- Uniform Drying:
- The rotating drum ensures even exposure to heat, resulting in uniform drying.
Challenges in Drum Drying
- Initial Cost:
- Drum dryer can have a high initial capital cost, especially for large-scale industrial applications.
- Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance is required to ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime.
- Control Complexity:
- Precise control of temperature, airflow, and drum speed is necessary to avoid over-drying or under-drying.
- Heat Sensitivity:
- Care must be taken when drying heat-sensitive materials to prevent degradation.
Future Trends in Drum Drying
- Automation and Control:
- Advances in automation and control systems improve the precision and efficiency of drum drying processes.
- Energy Efficiency:
- New designs and technologies aim to reduce energy consumption and enhance sustainability.
- Material Innovation:
- Developing new drum materials and coatings extends the lifespan and performance of drum dryers.
- Integration with Other Technologies:
- Drum dryers are increasingly integrated with other processing technologies, such as grinding and pelletizing, to create more streamlined production systems.
Conclusion
Drum dryers provide a versatile and efficient solution for drying various materials. Understanding their working principles, types, applications, and benefits helps industries optimize their drying processes and improve product quality. As technology advances, drum dryer will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and sustainability.
For more in-depth articles and resources on industrial drying technologies and innovations, visit EngiTech.in. Stay updated on the latest advancements and applications in the industry!