6-Axis Robots: Revolutionizing Automation with Precision and Versatility
In the realm of automation and robotics, 6-axis robots have emerged as game-changers, offering unparalleled precision, flexibility, and efficiency. Whether you’re in manufacturing, automotive, electronics, or any industry where complex movements are required, 6-axis robots provide the solutions you need to streamline operations and increase productivity.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what 6-axis robots are, how they work, their applications, benefits, and why they are crucial for industries aiming to stay competitive in today’s fast-evolving technological landscape
Table of Contents
What is a 6-Axis Robot?
A 6-axis robot is an industrial robot that can move in six different directions or axes: up and down, left and right, forward and backward, plus rotational movement. These axes allow for a high degree of flexibility, enabling the robot to perform complex tasks that require precise movements, such as assembly, welding, painting, and material handling.
The six axes of motion correspond to the robot’s joints, which mimic the movements of a human arm. This flexibility allows the robot to work in a confined space or perform tasks that require maneuvering around obstacles.
Key Features of 6-Axis Robots:
- Six Degrees of Freedom (DOF): The robot can move and rotate in six directions, providing unmatched versatility.
- Programmable Movements: Capable of complex and repeatable tasks, 6-axis robots are highly customizable.
- Precision: Accuracy levels are often within fractions of a millimeter, making these robots ideal for precision-driven industries.
How 6-Axis Robots Work
To understand how a 6-axis robot operates, it’s important to break down its six degrees of freedom. The robot has six joints that allow it to move and rotate in specific ways:
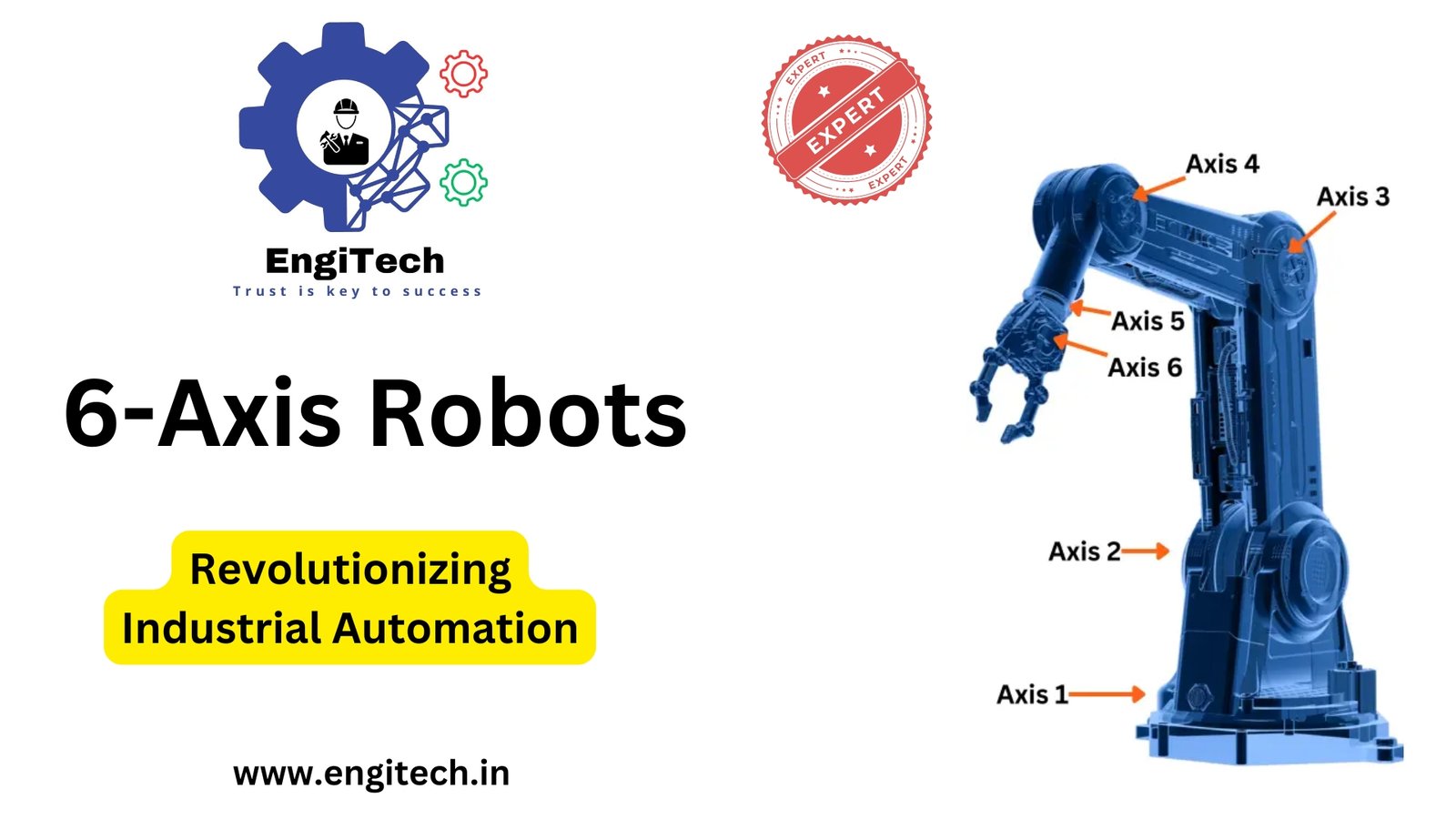
- Base Rotation (Axis 1): The first joint allows the robot to rotate at its base, enabling it to turn left and right.
- Arm Extension (Axis 2): This axis moves the arm forward and backward, determining how far the robot can reach.
- Arm Elevation (Axis 3): This joint allows for vertical movement, controlling the height of the robot’s arm.
- Wrist Roll (Axis 4): The robot’s wrist can rotate around its own axis, which is essential for aligning tools.
- Wrist Pitch (Axis 5): This axis moves the wrist up and down, enabling the robot to tilt objects or tools.
- Wrist Yaw (Axis 6): This joint allows the wrist to rotate side-to-side, offering the final level of control.
These six axes work together in a synchronized manner, allowing the robot to perform tasks that would be impossible for robots with fewer axes. 6-axis robots are typically programmed using specialized software, which allows operators to input tasks, trajectories, and parameters that the robot follows with precision.
Key Components of a 6-Axis Robot
Understanding the anatomy of a 6-axis robot is crucial for knowing how it operates:
- Controller: The brain of the robot, controlling its movement and decision-making based on pre-programmed instructions.
- Arm: The main body of the robot, which supports the end-effector and provides the movement required for tasks.
- End-Effector: The tool attached to the robot’s arm, such as a gripper, welder, or drill, depending on the application.
- Sensors: Provide feedback to the controller, allowing the robot to make adjustments in real-time.
- Drive System: Powers the joints and allows the arm to move smoothly through its six axes.
Each component plays a vital role in the robot’s overall functionality, allowing it to complete complex tasks efficiently and with precision.
Applications of 6-Axis Robots
One of the major strengths of 6-axis robots is their versatility, allowing them to be used in a wide range of industries. Below are some common applications:
1. Manufacturing:
6-axis robots are widely used in assembly lines for tasks like part assembly, quality inspection, and packaging. They can handle delicate components with precision and speed, improving overall efficiency.
2. Automotive Industry:
In automotive manufacturing, 6-axis robots are used for welding, painting, and assembling car parts. Their precision ensures consistency in production, while their speed helps manufacturers meet high demands.
3. Electronics:
In electronics manufacturing, these robots are used for tasks like soldering, circuit assembly, and testing. Their ability to perform intricate tasks without error makes them ideal for this industry.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry:
6-axis robots are employed for tasks such as drug dispensing, lab automation, and packaging. Their ability to operate in sterile environments makes them valuable in pharmaceutical applications.
5. Food and Beverage:
In food processing, 6-axis robots are used for packaging, sorting, and palletizing. They can work in fast-paced environments where speed and precision are critical.
6. Aerospace:
In the aerospace industry, these robots handle tasks such as drilling, riveting, and assembling aircraft parts. Their high precision ensures the safety and reliability of aircraft components.
Benefits of 6-Axis Robots
The widespread adoption of 6-axis robots is largely due to the numerous benefits they offer, including:
1. High Flexibility:
With six degrees of freedom, 6-axis robots can perform a wide range of tasks, from simple pick-and-place operations to complex assembly processes.
2. Precision and Accuracy:
These robots are known for their ability to perform tasks with extreme precision, often with tolerances as low as 0.01 mm. This level of accuracy is essential in industries like electronics and aerospace.
3. Increased Productivity:
By automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, 6-axis robots can operate 24/7, leading to significant increases in productivity.
4. Cost Efficiency:
While the initial investment in a 6-axis robot can be high, the long-term cost savings from reduced labor and increased efficiency can quickly offset the expense.
5. Safety:
6-axis robots can work in hazardous environments or handle dangerous materials, reducing the risk of injury to human workers.
6. Compact Design:
Despite their capabilities, many 6-axis robots are designed to be compact, making them suitable for environments with limited space.
Comparing 6-Axis Robots with Other Industrial Robots
1. 4-Axis vs. 6-Axis Robots:
A 4-axis robot can perform simpler tasks such as pick-and-place operations but lacks the versatility of a 6-axis robot. The additional two axes in a 6-axis robot allow for more complex movements, making it suitable for tasks like welding and painting.
2. SCARA Robots vs. 6-Axis Robots:
Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms (SCARA) are ideal for high-speed assembly tasks but are limited in flexibility compared to 6-axis robots. SCARA robots are often preferred for tasks that require horizontal movements, while 6-axis robots excel in tasks requiring 3D movements.
3. Cartesian Robots vs. 6-Axis Robots:
Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) and are often used for tasks that require precise linear motion. However, they lack the flexibility of 6-axis robots, which can move and rotate in multiple directions.
Choosing the Right 6-Axis Robot for Your Industry
Selecting the right 6-axis robot for your application involves considering several factors:
- Payload Capacity: How much weight the robot needs to handle.
- Reach: The distance the robot needs to cover.
- Speed: The required speed for task completion.
- Precision: The level of accuracy needed for the task.
- Environment: Whether the robot will operate in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or sterile environments.
Consulting with experts and conducting a thorough needs assessment can help ensure that you select the right robot for your specific application.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing 6-Axis Robots
While 6-axis robots offer significant advantages in automation, implementing them comes with certain challenges that need careful consideration. Let’s explore some of the key challenges industries face when integrating these robots into their operations.
1. High Initial Investment
The upfront cost of purchasing and installing a 6-axis robot can be substantial. While the long-term ROI (Return on Investment) is typically favorable, the initial expenses—such as the cost of the robot, installation, and software programming—can be prohibitive for smaller companies.
2. Technical Complexity
Programming and operating a 6-axis robot requires specialized knowledge and training. These robots often need skilled technicians to configure them properly for specific tasks. Companies may need to invest in training or hire technical experts to ensure the robot functions efficiently.
3. Space Requirements
Despite their flexibility, 6-axis robots require a considerable amount of space for optimal operation. Businesses must ensure that their workspace can accommodate the robot’s range of movement without obstructing other operations or posing safety risks to human workers.
4. Maintenance Costs
Like any complex machinery, 6-axis robots require regular maintenance to operate effectively over time. Routine inspections, part replacements, and software updates can add to the long-term operational costs.
5. Safety Concerns
While 6-axis robots are often designed to work safely alongside humans (especially collaborative robots or “cobots”), there are still safety concerns. Companies need to ensure proper safety protocols, including protective barriers, sensors, and emergency stop functions, to avoid accidents.
6. Integration with Existing Systems
In industries where robots must be integrated with other machines or systems (e.g., conveyor belts, sensors, or other robots), the process can be complex and time-consuming. Compatibility issues with existing infrastructure may arise, requiring modifications or additional investment in new technologies.
7. Adaptation to Changing Tasks
Although 6-axis robots are incredibly versatile, they may need reprogramming or adjustments to tackle new or evolving tasks. This adaptability, while a benefit, can be a challenge for industries that have rapidly changing production demands.
8. Downtime During Implementation
The process of integrating 6-axis robots into an existing production line can lead to downtime, which may disrupt normal operations. Companies must plan for this transition period to minimize impact on productivity.
The Future of 6-Axis Robots in Industry
As industries continue to evolve toward greater automation and efficiency, 6-axis robots are set to play an increasingly pivotal role. Several trends and innovations are shaping the future of these versatile machines, making them even more valuable across various sectors.
1. Advances in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing robotics. In the near future, 6-axis robots will become more autonomous, learning from their environments and improving their own performance over time. These robots will be capable of adjusting to new tasks without needing extensive reprogramming, further reducing the need for human intervention.
2. Cobots and Human-Robot Collaboration
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans safely and effectively. As cobots become more advanced, 6-axis robots will increasingly be used in environments where they assist human workers rather than replace them. This will lead to safer, more productive workspaces where humans and robots can perform tasks together.
3. Integration with IoT (Internet of Things)
As IoT technologies become more prevalent in industrial settings, 6-axis robots will be able to communicate seamlessly with other machines and systems. This real-time data exchange will enable more efficient workflows and smarter decision-making processes. IoT integration will also allow robots to perform predictive maintenance, detecting potential issues before they cause downtime.
4. Enhanced Precision and Miniaturization
Future advancements in robot design will allow 6-axis robots to become even more precise and compact. This miniaturization will make them accessible to industries that previously couldn’t accommodate larger robots, such as electronics manufacturing, where small-scale operations require extreme accuracy.
5. Expansion into New Industries
While 6-axis robots are currently popular in manufacturing and automotive sectors, their use is expanding into other fields. Healthcare, agriculture, and logistics are industries likely to benefit from the adaptability and precision of 6-axis robots in the near future. For example, in healthcare, robots may assist in surgeries, while in agriculture, they could be used for precision planting and harvesting.
6. Lower Costs and Increased Accessibility
As technology improves and the market becomes more competitive, the cost of 6-axis robots is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to small and medium-sized businesses. More affordable robots will lead to broader adoption across industries, driving innovation and productivity.
7. Robots as a Service (RaaS)
A rising trend is Robots as a Service (RaaS), where companies can lease robots instead of purchasing them outright. This model reduces the financial barrier for businesses looking to integrate automation but unable to make large capital investments. With RaaS, 6-axis robots can be rented for specific projects or periods, providing flexibility and cost savings.
Conclusion: Why Your Industry Needs 6-Axis Robots
In today’s fast-paced and competitive industrial environment, staying ahead means embracing cutting-edge technologies that enhance productivity, precision, and flexibility. 6-axis robots offer these advantages and more, making them an essential tool for businesses aiming to improve their operations and remain competitive.
Key Takeaways:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: 6-axis robots can perform repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy, reducing errors and increasing output.
- Unmatched Flexibility: The six degrees of freedom allow these robots to handle complex movements and tasks that other types of robots cannot perform.
- Cost-Effectiveness Over Time: While the initial investment may be high, the long-term benefits—such as reduced labor costs and increased uptime—make 6-axis robots a smart financial decision.
- Future-Ready Technology: As industries evolve, the adaptability of 6-axis robots will ensure they remain relevant and beneficial, especially as they integrate with AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies.
For industries that rely on precision, flexibility, and efficiency, 6-axis robots are a game-changer. Whether you’re in manufacturing, automotive, electronics, or pharmaceuticals, these robots will help streamline your operations and set you up for long-term success.
Ready to explore how 6-axis robots can transform your business operations? Visit EngiTech for comprehensive resources and stay updated on the latest innovations in industrial automation. Discover expert insights, case studies, and in-depth guides tailored to help you choose the right robotic solutions for your industry.


